Javascript_Pre-study_Wk1
console.log()
- used to print out integers or strings
- similar to << cout << OR printf()
- 화면에 출력되는데 사용됨. 스트링은 ("")혹은 ('') 으로 표기. 인티저는 () 로 가능.
- 인티저는 ("")() 둘다 사용가능 하지만 스트링은 ""나 ''가 꼭 필요함. 누락시 syntaxError 발생.
Variables
-
can be declared with let. ex) let myString = "dummy"
-
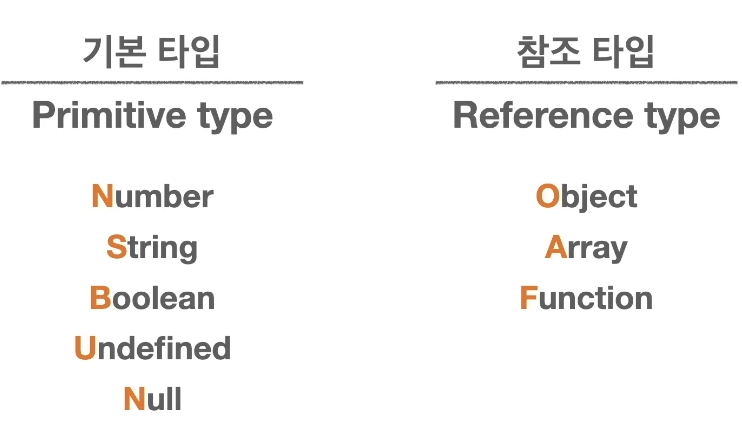
Types of variables
-
within console.log(), arithmetic operations can be done using integer variables
ex) let numero = 3, let dos = 2, --> console.log(numero * dos) will print out 6. NOTE % modulo operator 도 사용 가능함.
Array
needs to have [ ] . ex) let studentsName = ['code kim', 'wecode lee']

Object
needs to have { } --> 데이터 묶음.

-->name 은 key 고 'Code Kim' 은 value.
ex) 
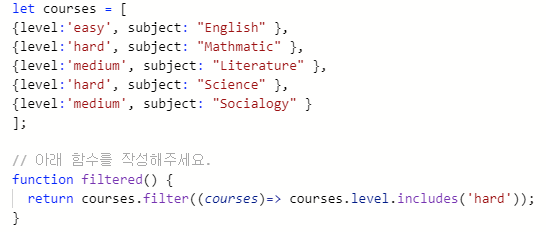
an Array made out of objects. courses.level responds to values in level(key)
courses.subject responds to values in subject(value)
-->
null & undefined
- null is a blank value given. undefined is when a variable is declared but no value is assigned.
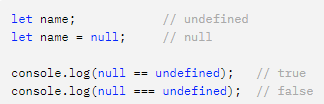
엄격일치연산(===) 와 일반 일치연산(==)의 차이
엄격일치연산은 value 뿐만 아니라 type 도 같아야 한다.
ex) console.log(null == undefined) --> true
console.log(nul === undefined) --> false
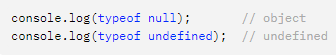
console.log(typeof null) --> object
console.log(typeof undefined) --> undefined
1
문자열의 길이 구하기
string_name.length 를 하면 string 의 길이가 나온다. string_name 은 string variable 이다.
Array (배열)
How to define an array in Javascript
- let myArray = ['일',"이",3,4]
혹은 let multi_dim_array = [['일학년','팔반'],['일학년','삼반']]
Creating a new array with new method
ex) let arr = new Array(4) --> creates an array with four empty slots.
ex)
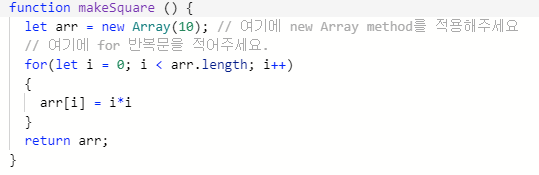
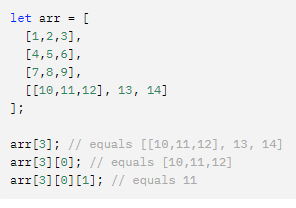
다차원 배열 접근
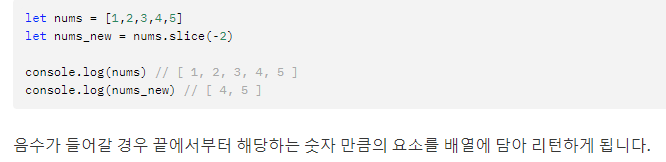
slice() method.
- slice method 은 splice 와 다르게 원본 배열을 변형시키지 않음 --> slice method를 적용한 새로운 변수를 선언해 주어야 함.


ex) 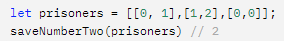
에서 변수에 숫자 2를 담고 싶을때,

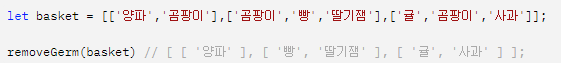
splice() method.
- 배열내의 element 삭제, 대체, 추가 할때 사용


ex)
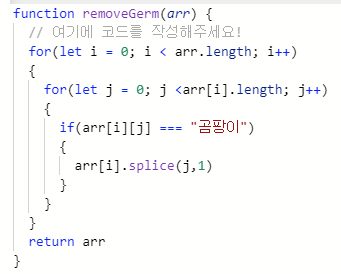
filter method
-조건에 맞는 element 를 모아서 새로운 배열을 반환(조건에 맞지않으면 빈배열 반환)
- filter(callbackFunction, thisArg) 인자를 가짐
- callbackFunction 안에서 3개의 인자 (element, index,array) 중 element 만 필수적
ex) value >10 인 인자들로 이루어진 배열을 생성

arrow function (=>)
- function syntax 를 간결하게 작성할 수 있게 해준다.


filter method 와 arrow function 의 예시
concat method
-주어진 배열에 기존배열을 합쳐서 새로운 배열을 반환
- 원본 배열은 변경되지 않으며 concat 이우 기존 배열을 수정해도 영향받지 않음
- 중복과 상관없이 그냥 배열 합쳐줌
ex)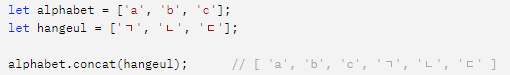
ex2)

ex3)
returns 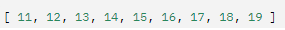
using indexOf()


How to add elements into an Array
--> with push() method ex) myArray.push("wecode") the element "wecode" gets added to the end of myArray.
How to remove elements from an Array

ex) Array.pop()

ex) Array.shift() 는 첫번째 요소를 제거하며 variable 에 assign 하면 제거된 value 를 return 함
for loop
for(let i = 0; i < 5 ; i++) (초기상태; 조건; counter 변화)
{
반복하고자 하는 일
}
두단계씩 가능
for(let i =0; i <5 ; i +=2)
WK2 keywords
배열이 필요한 이유와 선언하는 방법,
배열을 사용하여 다수의 값을 하나의 변수에 저장할 수 있다.
선언 방법:
1) let arr = new Array(“value1”, “value2”, integer)
2) let arr = []; 이후 arr[0] = “value”, arr[1] = integer 등으로 value 주가 가능.
3) 바로 let arr = [“value”, “value”, integer] 도 가능
배열의 값을 추가, 수정, 삭제하는 방법
추가: arr.push()
수정 및 삭제: 

반복문이 필요한 이유와 사용하는 방법:
필요한 이유: 반복적인 일을 조건에 의거하여 보다 간편하고 빠르게 수행하기 위해.
배열과 반복문을 자주 사용하는 이유
반복문에는 카운팅 변수가 있기 때문에 배열의 모든 엘리먼트를 빠르고 쉽게 엑세스 할수 있게 해준다.
배열의 메서드 5가지와 사용방법
Concat()
Filter()
Includes()
indexOf()
pop()
push
WK3: OBJECT(객체)
-
객체란 무엇이며 필요한 이유
-
객체의 값을 추가,수정, 삭제하는 방법
-
객체와 배열이 섞인 복잡한 객체 만들어서 접근하는 방법
-
배열의 타입이 객체인 이유

에서 4개의 property 가 존재, 그중 name, location, age, cats 가 key 이고
'Code Kim', country: 'South Korea', city: 'Seoul', 30, ['냥순','냥돌'] 이 value.
이다. ** location 이라는 key 의 value 는 또다른 object 이다. cats 라는 key 의 value 는 array 이다.
- console.log(myself) 로 출력을 하면 array 와는 다르게 index 가 존재 하지 않으므로 순서가 정해져 있지가 않다. key: value 의 값만 저장된다.
- javascript 의 key 는 string 이다.
How to access data in object
1) Dot Notation (점표기법)
myself.name // 'Code Kim'
myself.age // 30
2) Bracket Notaion (괄호표기법)
myself['name'] // 'Code Kim'
myslef['age'] // 30
- Dot notation 과 Bracket notation 의 차이점
source: https://codeburst.io/javascript-quickie-dot-notation-vs-bracket-notation-333641c0f781

- key 들은 모두 string 이므로 variable 에 저장하여 bracket notation 으로만!!! 접근이 가능하다. ** dot notation 은 변수를 사용할 수 없음.
ex) let myKey = 'cats'
console.log(myself['cats'])
console.log(myself[myKey]) 는 동일하다.
- How to replace a value in an Object (객체 수정)
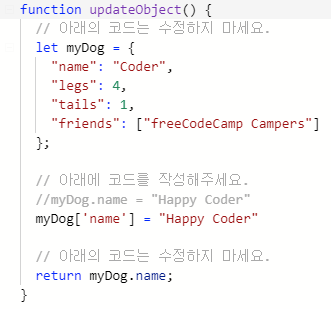
위 코드에서 myDog['name'] = "Happpy Coder" 이 "coder" value 를 replace 한다.
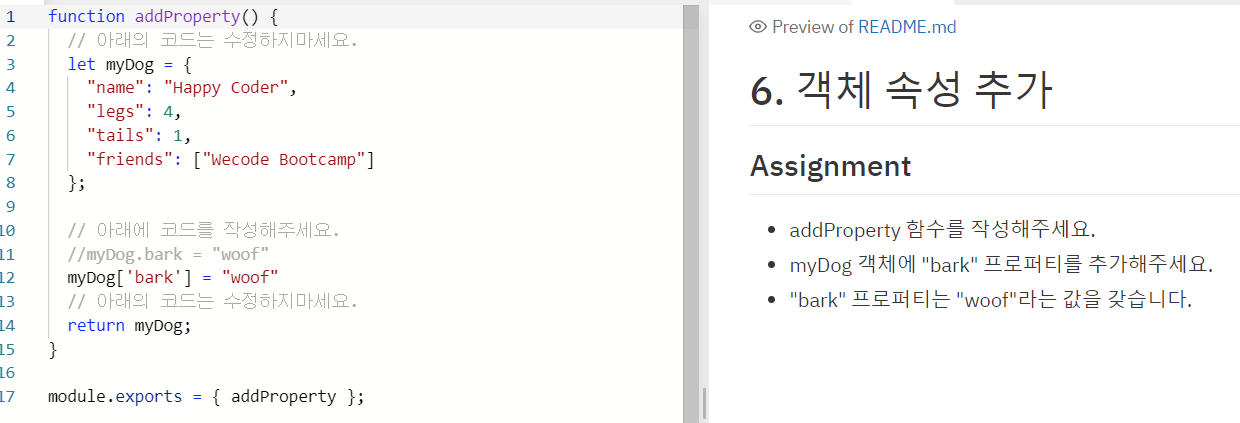
- How to add a property to an Object (객체 속성 추가)
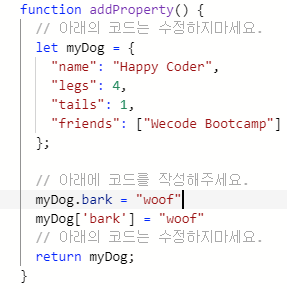
위 코드에서 myDog object 가 상단에 이미 define 되었지만 아래
myDog.bark = "woof" 또는 myDog['bark'] = "woof" 를 통해 새로운 property 를 추가 할 수 있다.
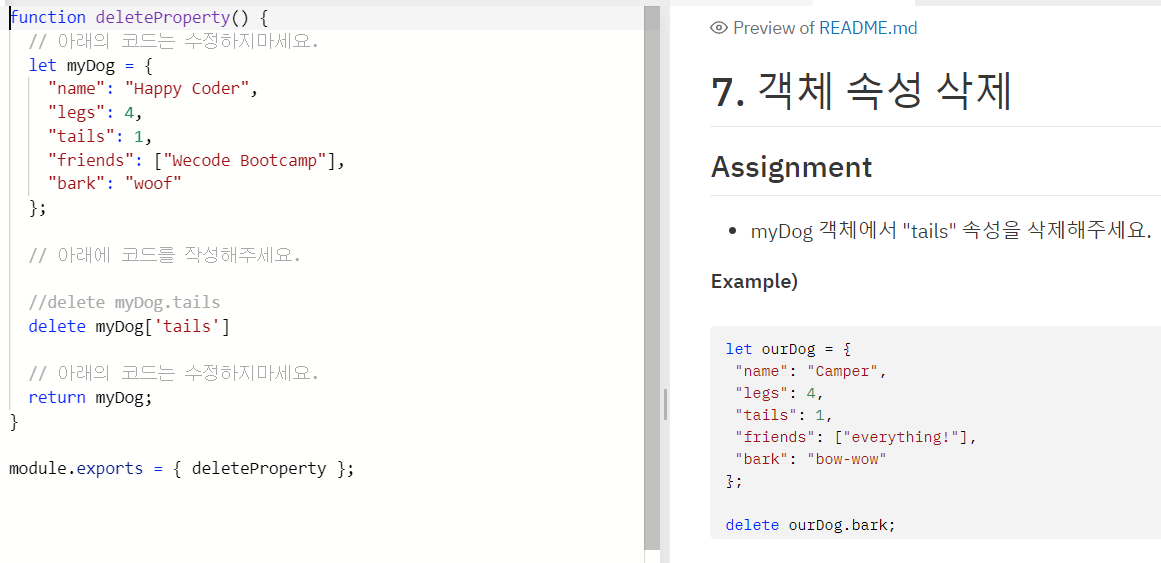
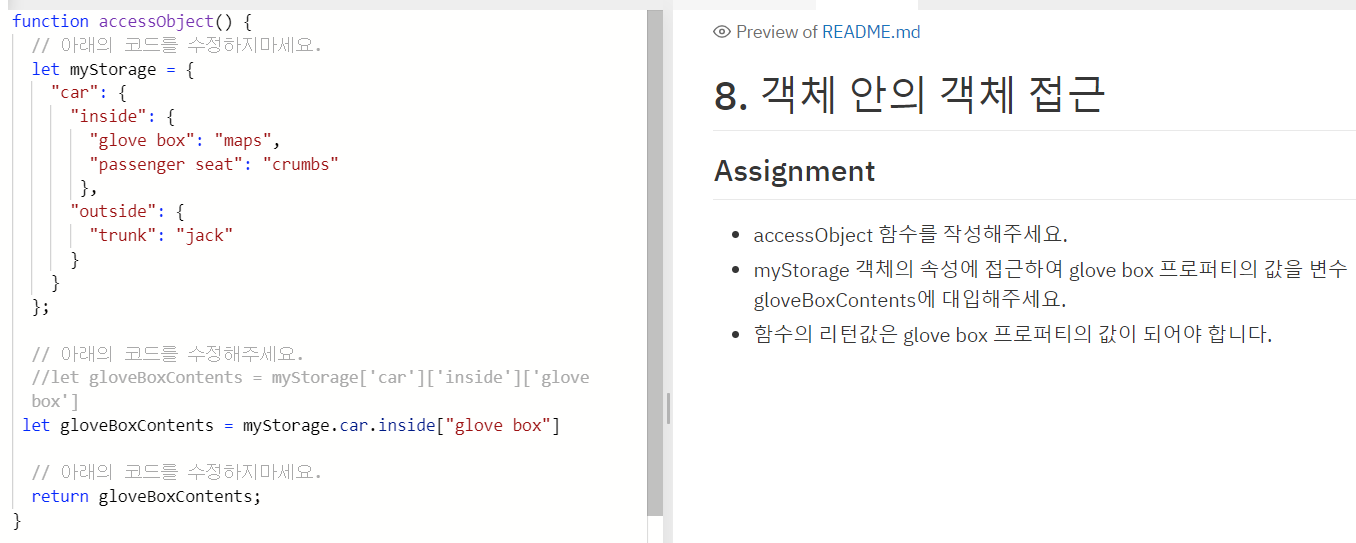
- How to access an object within an object (객체 안의 객체 접근)

위 코드에서 myStorage 라는 Object 안에 "car" Object 안에 "inside" 안에 "glove box" 라는 key 의 value 인 "maps" 에 접근하고 싶다면,
let gloveBoxContents = myStorage.car.inside["glove box"] 또는
let gloveBoxContetns = myStorage['car']['inside']['glove box'] 로 접근 할 수 있다.
주의할 점은 dot notation 안에는 space 가 들어갈 수 없으므로 glove box 로의 접근이 불가능 하다. (glove_box 였다면 가능)
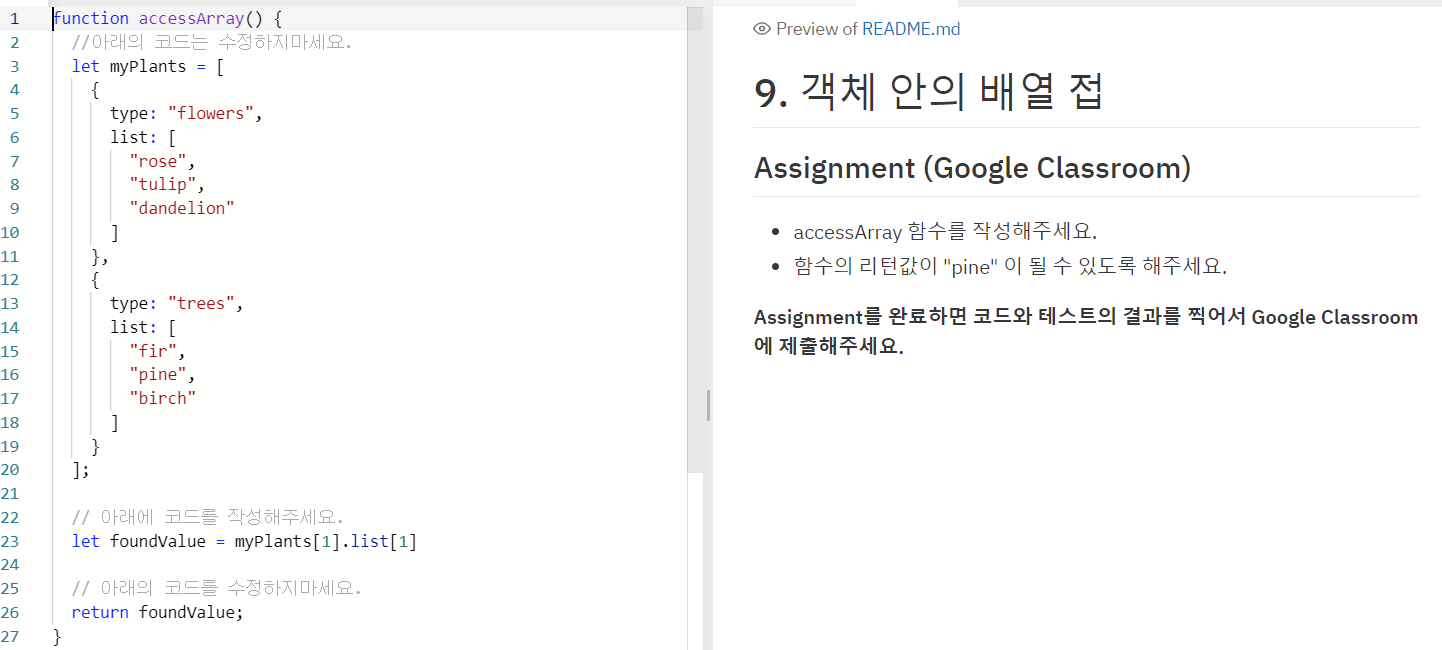
- How to access an array withiin an object (객체 안의 배열 접근)

두번째 list 의 "pine" 값에 access 하고싶은 경우.
myPlants 라는 object 에서 type 과 list 라는 동일한 이름의 key 가 두번 중복되어 있다.
하지만 [] 괄호로 시작하여 {} 로 define 하는 object 와는 달리 index 가 존재 한다는걸 알 수 있고, list property 또한 array 의 형태이기 때문에 index 가 존재 한다.
--> let foundValue = myPlants[1].list[1] // 'pine' 값이 foundValue 에 저장됨.
객체 수정
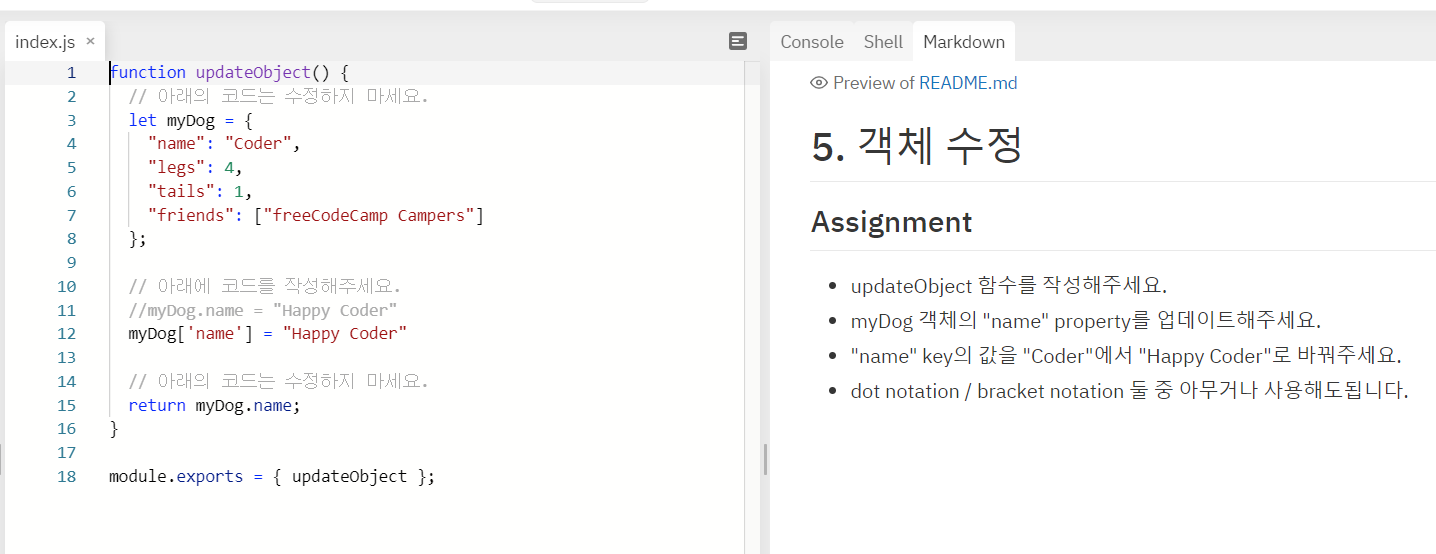
객체 속성 추가
객체 속성 삭제
객체 안의 객체 접근
객채 안의 배열 접근