Custom Controller -1
https://velog.io/@sawa1989/Custom-Controller-1 의 다음글 입니다.
CronJob 만들기
깃허브 위치 : 너무 어렵다 싶으면, github에서 코드 가져와서 쓰시면 될것같아요!
cronjob tutorial 코드가 포함되어있습니다 🙂
https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubebuilder
https://book.kubebuilder.io/cronjob-tutorial/cronjob-tutorial
초기화
kubebuilder init --domain tutorial.kubebuilder.io --repo tutorial.kubebuilder.io/project
kubebuilder create api --group batch --version v1 --kind CronJob
# Press y for “Create Resource” and “Create Controller”.아래와같이 파일 두개가 만들어진다.
api/v1/cronjob_types.go
internal/controllers/cronjob_controller.go
cronjob_types.go 분석
cronjob_types.go 분석을 먼저 시작하자~!
batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io/v1 와같은 api 가 만들어짐 {domain}/{apiversion}
차례로 내려가면 meta데이터 설정
package v1
import (
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
)spec, status를 설정하자 ( configmap은 status가 없음, 참고로 없어야함 )
// CronJobSpec defines the desired state of CronJob
type CronJobSpec struct {
// INSERT ADDITIONAL SPEC FIELDS - desired state of cluster
// Important: Run "make" to regenerate code after modifying this file
// Foo is an example field of CronJob. Edit cronjob_types.go to remove/update
Foo string `json:"foo,omitempty"`
}
// CronJobStatus defines the observed state of CronJob
type CronJobStatus struct {
// INSERT ADDITIONAL STATUS FIELD - define observed state of cluster
// Important: Run "make" to regenerate code after modifying this file
}참고 : API 제약
camelCase : 단어가 합쳐진 부분마다 맨 처음 글자를 대문자로 표기
omitempty struct 태그를 사용하여 필드가 비어 있을 때 직렬화에서 생략
- 직렬화? 예를 들어,
Examplestruct의 인스턴스가 다음과 같다면:example := Example{ Name: "Alice", Email: "", }example을 JSON으로 직렬화하면 다음과 같은 결과가 나옵니다:{ "name": "Alice" }age와email필드는 비어 있기 때문에 JSON 출력에서 생략
cronjob_types.go 코드 추가
- A schedule (the cron in CronJob)
- A template for the Job to run (the job in CronJob)
import (
batchv1beta1 "k8s.io/api/batch/v1beta1"
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
)// +kubebuilder:object:root=true
// +kubebuilder:subresource:status
// CronJob is the Schema for the cronjobs API
type CronJob struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Spec CronJobSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"`
Status CronJobStatus `json:"status,omitempty"`
}
// +kubebuilder:object:root=true
// CronJobList contains a list of CronJob
type CronJobList struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ListMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Items []CronJob `json:"items"`
}
func init() {
SchemeBuilder.Register(&CronJob{}, &CronJobList{})
}
실제 Kind에 해당하는 타입인 CronJob ( root타입 )과 CronJobList를 정의
- root타입이란?
- "루트 타입"이란 해당 객체가 Kubernetes에서 하나의 최상위 리소스 유형(Kind)을 나타낸다는 의미
- 다른 리소스에 종속되거나 포함되는 것이 아니라, 자체적으로 독립된 리소스라는 것을 의미함
- root타입이 아닌 객체는 ?
- Container: PodSpec 안에서 정의되는 Container는 루트 타입이 아니며, Pod 안에서 정의됨
- EnvVar: ContainerSpec 안에서 사용되는 환경 변수 정의
TypeMeta(버전과 Kind를 설명), ObjectMeta(이름, 네임스페이스, 라벨 등을 포함)를 포함
CronJobList는 단순히 여러 CronJob을 담는 리스트 컨테이너
( spec, status는 사실 잘 수정할 일이 없다고함.. )
+kubebuilder:object:root라는 작은 주석은 마커라고 불리는데
추가 메타데이터로 작용하여 controller-tools(코드 및 YAML 생성기)에 추가 정보를 전달하는 역할을 함
⇒ 이 타입이 Kind를 나타낸다고 알려줌 → object generator가 runtime.Object 인터페이스의 구현을 생성 ( 결과적으로 모든 Kind를 나타내는 타입이 구현해야 하는 표준 인터페이스를 생성해주는 것 )
마지막으로 init으로 스키마를 등록해줌
+kubebuilder:object:root=true 이런 root타입은 건들이지않는다.
// CronJobSpec defines the desired state of CronJob
type CronJobSpec struct {
// +kubebuilder:validation:MinLength=0
// The schedule in Cron format, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cron.
Schedule string `json:"schedule"`
// +kubebuilder:validation:Minimum=0
// Optional deadline in seconds for starting the job if it misses scheduled
// time for any reason. Missed jobs executions will be counted as failed ones.
// +optional
StartingDeadlineSeconds *int64 `json:"startingDeadlineSeconds,omitempty"`
// Specifies how to treat concurrent executions of a Job.
// Valid values are:
// - "Allow" (default): allows CronJobs to run concurrently;
// - "Forbid": forbids concurrent runs, skipping next run if previous run hasn't finished yet;
// - "Replace": cancels currently running job and replaces it with a new one
// +optional
ConcurrencyPolicy ConcurrencyPolicy `json:"concurrencyPolicy,omitempty"`
// This flag tells the controller to suspend subsequent executions, it does
// not apply to already started executions. Defaults to false.
// +optional
Suspend *bool `json:"suspend,omitempty"`
// Specifies the job that will be created when executing a CronJob.
JobTemplate batchv1.JobTemplateSpec `json:"jobTemplate"`
// +kubebuilder:validation:Minimum=0
// The number of successful finished jobs to retain.
// This is a pointer to distinguish between explicit zero and not specified.
// +optional
SuccessfulJobsHistoryLimit *int32 `json:"successfulJobsHistoryLimit,omitempty"`
// +kubebuilder:validation:Minimum=0
// The number of failed finished jobs to retain.
// This is a pointer to distinguish between explicit zero and not specified.
// +optional
FailedJobsHistoryLimit *int32 `json:"failedJobsHistoryLimit,omitempty"`
}ConcurrencyPolicy 타입도 추가
// ConcurrencyPolicy describes how the job will be handled.
// Only one of the following concurrent policies may be specified.
// If none of the following policies is specified, the default one
// is AllowConcurrent.
// +kubebuilder:validation:Enum=Allow;Forbid;Replace
type ConcurrencyPolicy string
const (
// AllowConcurrent allows CronJobs to run concurrently.
AllowConcurrent ConcurrencyPolicy = "Allow"
// ForbidConcurrent forbids concurrent runs, skipping next run if previous
// hasn't finished yet.
ForbidConcurrent ConcurrencyPolicy = "Forbid"
// ReplaceConcurrent cancels currently running job and replaces it with a new one.
ReplaceConcurrent ConcurrencyPolicy = "Replace"
)CronJobStatus 수정
// CronJobStatus defines the observed state of CronJob
type CronJobStatus struct {
// INSERT ADDITIONAL STATUS FIELD - define observed state of cluster
// Important: Run "make" to regenerate code after modifying this file
// A list of pointers to currently running jobs.
// +optional
Active []corev1.ObjectReference `json:"active,omitempty"`
// Information when was the last time the job was successfully scheduled.
// +optional
LastScheduleTime *metav1.Time `json:"lastScheduleTime,omitempty"`
}- 참고 파일 (
groupversion_info.go,zz_generated.deepcopy.go)groupversion_info.go: 그룹 버전에 해당하는 메타 데이터 :zz_generated.deepcopy.go:runtime.Object인터페이스의 자동 생성된 구현을 포함, 루트타입 인터페이스runtime.Object인터페이스의 핵심은 깊은 복사 메서드인DeepCopyObject입니다. controller-tools의 geneter가 각 루트 타입 및 모든 하위 타입에 대해DeepCopy와DeepCopyInto라는 두 가지 유용한 메서드도 생성해줌!DeepCopy메서드는 새로운 객체를 생성하고, 원본 객체의 모든 데이터를 이 새로운 객체에 복사하여 반환! 이렇게 하는 이유는 기존 객체에 영향을 안가게 하려고~!
controller 구성
reconciling
- 주어진 객체에 대해서 actual state, potentially external state → desired state 로 같게 만드는걸 목표로함
- 각 컨트롤러는 하나의 루트 Kind만 보지만, 경우에 따라서 다른 Kind와 상호 작용도 가능함
⇒ reconciler가 제일 중요함.
- 특정 Kind에 대한 조정을 구현하는 로직
- Reconciler는 객체의 이름을 받아오며, 다시 시도해야 하는지 여부(예: 오류 발생 시 또는 HorizontalPodAutoscaler와 같은 주기적인 컨트롤러의 경우)를 반환함.
controller 분석
package controllers
import (
"context"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime"
ctrl "sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime"
"sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/client"
"sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/log"
batchv1 "tutorial.kubebuilder.io/project/api/v1"
)
// CronJobReconciler reconciles a CronJob object
type CronJobReconciler struct {
client.Client
Scheme *runtime.Scheme
}대부분의 컨트롤러는 결국 클러스터에서 실행되므로, RBAC 권한이 필요
이러한 권한은 controller-tools의 RBAC 마커를 사용하여 지정함
ClusterRole 매니페스트는 다음 명령어를 통해 controller-gen을 사용하여 config/rbac/role.yaml에 생성
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io,resources=cronjobs,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io,resources=cronjobs/status,verbs=get;update;patchReconcile은 실제로 단일 명명된 객체에 대한 조정을 수행함
func (r *CronJobReconciler) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) {
_ = log.FromContext(ctx)
// your logic here
return ctrl.Result{}, nil
}컨텍스트
- 요청을 취소하거나 트레이싱과 같은 작업을 가능하게 함
- Background 컨텍스트는 추가 데이터나 시간 제한이 없는 기본 컨텍스트
Request
- 요청(Request)의 경우 클라이언트를 사용하여 캐시에서도 해당 객체를 가져올수있음 .
- 참고로 빈 결과와 오류가 없음을 반환하면, 이는 controller-runtime에게 이 객체를 성공적으로 조정했고, 변경 사항이 발생할 때까지 다시 시도할 필요가 없음을 나타냄
대부분의 컨트롤러는 로깅 핸들과 컨텍스트가 필요하므로 여기서 설정
로깅 핸들은 로깅을 가능하게 합니다. controller-runtime은 logr라는 라이브러리를 통해 구조화된 로깅을 사용로깅은 키-값 쌍을 정적 메시지에 연결하는 방식으로 작동
조정 메서드의 상단에서 일부 키-값 쌍을 미리 할당하여 Reconciler의 모든 로그 라인에 연결하게 해줌
매니져에 Reconciler를 추가하는 걸 넣어줌!
katib도 보면 이렇게 되있음
Controller.go 로직 추가
-
명명된 CronJob을 로드
-
모든 활성화된 잡을 목록화하고 상태를 업데이트
-
히스토리 제한에 따라 오래된 잡을 정리
-
중지 상태인지 확인, 할꺼 없으면 PASS
-
다음 예약된 실행 시간을 확인
-
스케줄에 맞고, 마감 시간을 넘지않는 상태로 동시성 정책에 의해 차단되지 않은 경우 새로운 잡을 실행
-
실행 중인 잡을 보거나(자동으로 처리됨) 다음 예약된 실행 시간이 되었을 때 다시 큐에 넣기
import 추가
package controller
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"sort"
"time"
"github.com/robfig/cron"
kbatch "k8s.io/api/batch/v1"
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime"
ref "k8s.io/client-go/tools/reference"
ctrl "sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime"
"sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/client"
"sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/log"
batchv1 "tutorial.kubebuilder.io/project/api/v1"
)reconciler에 clock 추가 ( 테스트 가짜 타이밍 허용 하게 해줌 )
// CronJobReconciler reconciles a CronJob object
type CronJobReconciler struct {
client.Client
Scheme *runtime.Scheme
Clock
}
type realClock struct{}
func (_ realClock) Now() time.Time { return time.Now() }
// Clock knows how to get the current time.
// It can be used to fake out timing for testing.
type Clock interface {
Now() time.Time
}RBAC 권한 추가
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io,resources=cronjobs,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io,resources=cronjobs/status,verbs=get;update;patch
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io,resources=cronjobs/finalizers,verbs=update
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=batch,resources=jobs,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=batch,resources=jobs/status,verbs=getReconciler 구현
var (
scheduledTimeAnnotation = "batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io/scheduled-at"
)
// Reconcile is part of the main kubernetes reconciliation loop which aims to
// move the current state of the cluster closer to the desired state.
// TODO(user): Modify the Reconcile function to compare the state specified by
// the CronJob object against the actual cluster state, and then
// perform operations to make the cluster state reflect the state specified by
// the user.
//
// For more details, check Reconcile and its Result here:
// - https://pkg.go.dev/sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime@v0.18.2/pkg/reconcile
func (r *CronJobReconciler) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, req ctrl.Request) (ctrl.Result, error) {
log := log.FromContext(ctx)Cronjob가져오기
var cronJob batchv1.CronJob
if err := r.Get(ctx, req.NamespacedName, &cronJob); err != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to fetch CronJob")
// we'll ignore not-found errors, since they can't be fixed by an immediate
// requeue (we'll need to wait for a new notification), and we can get them
// on deleted requests.
return ctrl.Result{}, client.IgnoreNotFound(err)
}job 나열하기
var childJobs kbatch.JobList
if err := r.List(ctx, &childJobs, client.InNamespace(req.Namespace), client.MatchingFields{jobOwnerKey: req.Name}); err != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to list child Jobs")
return ctrl.Result{}, err
}Job을 가져왔으면 이제 상태(active, success, fail)에 따라서 저장해두기
바로 읽어서 처리하는건 좋지않다고하네용
- docs gen이란? API 문서화:
- Kubebuilder는 API 타입을 정의할 때,
kubebuilder:docs-gen마커를 사용하여 해당 타입과 필드에 대한 설명을 추가함 - 이를 통해, API 스펙에 대한 자동 문서화가 이루어지며, 개발자는 이를 기반으로 API를 이해하고 사용할수있음
- Kubebuilder는 API 타입을 정의할 때,
// find the active list of jobs
var activeJobs []*kbatch.Job
var successfulJobs []*kbatch.Job
var failedJobs []*kbatch.Job
var mostRecentTime *time.Time // find the last run so we can update the status
/*
We consider a job "finished" if it has a "Complete" or "Failed" condition marked as true.
Status conditions allow us to add extensible status information to our objects that other
humans and controllers can examine to check things like completion and health.
*/
isJobFinished := func(job *kbatch.Job) (bool, kbatch.JobConditionType) {
for _, c := range job.Status.Conditions {
if (c.Type == kbatch.JobComplete || c.Type == kbatch.JobFailed) && c.Status == corev1.ConditionTrue {
return true, c.Type
}
}
return false, ""
}
// +kubebuilder:docs-gen:collapse=isJobFinished
/*
We'll use a helper to extract the scheduled time from the annotation that
we added during job creation.
*/
getScheduledTimeForJob := func(job *kbatch.Job) (*time.Time, error) {
timeRaw := job.Annotations[scheduledTimeAnnotation]
if len(timeRaw) == 0 {
return nil, nil
}
timeParsed, err := time.Parse(time.RFC3339, timeRaw)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &timeParsed, nil
}
// +kubebuilder:docs-gen:collapse=getScheduledTimeForJob
for i, job := range childJobs.Items {
_, finishedType := isJobFinished(&job)
switch finishedType {
case "": // ongoing
activeJobs = append(activeJobs, &childJobs.Items[i])
case kbatch.JobFailed:
failedJobs = append(failedJobs, &childJobs.Items[i])
case kbatch.JobComplete:
successfulJobs = append(successfulJobs, &childJobs.Items[i])
}
// We'll store the launch time in an annotation, so we'll reconstitute that from
// the active jobs themselves.
scheduledTimeForJob, err := getScheduledTimeForJob(&job)
if err != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to parse schedule time for child job", "job", &job)
continue
}
if scheduledTimeForJob != nil {
if mostRecentTime == nil || mostRecentTime.Before(*scheduledTimeForJob) {
mostRecentTime = scheduledTimeForJob
}
}
}
if mostRecentTime != nil {
cronJob.Status.LastScheduleTime = &metav1.Time{Time: *mostRecentTime}
} else {
cronJob.Status.LastScheduleTime = nil
}
cronJob.Status.Active = nil
for _, activeJob := range activeJobs {
jobRef, err := ref.GetReference(r.Scheme, activeJob)
if err != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to make reference to active job", "job", activeJob)
continue
}
cronJob.Status.Active = append(cronJob.Status.Active, *jobRef)
}로깅 추가
log.V(1).Info("job count", "active jobs", len(activeJobs), "successful jobs", len(successfulJobs), "failed jobs", len(failedJobs))crd 상태 업데이트
if err := r.Status().Update(ctx, &cronJob); err != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to update CronJob status")
return ctrl.Result{}, err
}history limit에 넘는 job 지우기
// NB: deleting these are "best effort" -- if we fail on a particular one,
// we won't requeue just to finish the deleting.
if cronJob.Spec.FailedJobsHistoryLimit != nil {
sort.Slice(failedJobs, func(i, j int) bool {
if failedJobs[i].Status.StartTime == nil {
return failedJobs[j].Status.StartTime != nil
}
return failedJobs[i].Status.StartTime.Before(failedJobs[j].Status.StartTime)
})
for i, job := range failedJobs {
if int32(i) >= int32(len(failedJobs))-*cronJob.Spec.FailedJobsHistoryLimit {
break
}
if err := r.Delete(ctx, job, client.PropagationPolicy(metav1.DeletePropagationBackground)); client.IgnoreNotFound(err) != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to delete old failed job", "job", job)
} else {
log.V(0).Info("deleted old failed job", "job", job)
}
}
}
if cronJob.Spec.SuccessfulJobsHistoryLimit != nil {
sort.Slice(successfulJobs, func(i, j int) bool {
if successfulJobs[i].Status.StartTime == nil {
return successfulJobs[j].Status.StartTime != nil
}
return successfulJobs[i].Status.StartTime.Before(successfulJobs[j].Status.StartTime)
})
for i, job := range successfulJobs {
if int32(i) >= int32(len(successfulJobs))-*cronJob.Spec.SuccessfulJobsHistoryLimit {
break
}
if err := r.Delete(ctx, job, client.PropagationPolicy(metav1.DeletePropagationBackground)); err != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to delete old successful job", "job", job)
} else {
log.V(0).Info("deleted old successful job", "job", job)
}
}
}중단된것 확인하기
if cronJob.Spec.Suspend != nil && *cronJob.Spec.Suspend {
log.V(1).Info("cronjob suspended, skipping")
return ctrl.Result{}, nil
}다음에 실행할 것 넣기
- 특정 CronJob에 대해 다음 실행 시간과 놓친 실행 시간을 계산하는 함수를 구현 → CronJob을 적절하게 스케줄링하는 역할
getNextSchedule := func(cronJob *batchv1.CronJob, now time.Time) (lastMissed time.Time, next time.Time, err error) {
sched, err := cron.ParseStandard(cronJob.Spec.Schedule)
if err != nil {
return time.Time{}, time.Time{}, fmt.Errorf("Unparseable schedule %q: %v", cronJob.Spec.Schedule, err)
}
// for optimization purposes, cheat a bit and start from our last observed run time
// we could reconstitute this here, but there's not much point, since we've
// just updated it.
var earliestTime time.Time
if cronJob.Status.LastScheduleTime != nil {
earliestTime = cronJob.Status.LastScheduleTime.Time
} else {
earliestTime = cronJob.ObjectMeta.CreationTimestamp.Time
}
if cronJob.Spec.StartingDeadlineSeconds != nil {
// controller is not going to schedule anything below this point
schedulingDeadline := now.Add(-time.Second * time.Duration(*cronJob.Spec.StartingDeadlineSeconds))
if schedulingDeadline.After(earliestTime) {
earliestTime = schedulingDeadline
}
}
if earliestTime.After(now) {
return time.Time{}, sched.Next(now), nil
}
starts := 0
for t := sched.Next(earliestTime); !t.After(now); t = sched.Next(t) {
lastMissed = t
// An object might miss several starts. For example, if
// controller gets wedged on Friday at 5:01pm when everyone has
// gone home, and someone comes in on Tuesday AM and discovers
// the problem and restarts the controller, then all the hourly
// jobs, more than 80 of them for one hourly scheduledJob, should
// all start running with no further intervention (if the scheduledJob
// allows concurrency and late starts).
//
// However, if there is a bug somewhere, or incorrect clock
// on controller's server or apiservers (for setting creationTimestamp)
// then there could be so many missed start times (it could be off
// by decades or more), that it would eat up all the CPU and memory
// of this controller. In that case, we want to not try to list
// all the missed start times.
starts++
if starts > 100 {
// We can't get the most recent times so just return an empty slice
return time.Time{}, time.Time{}, fmt.Errorf("Too many missed start times (> 100). Set or decrease .spec.startingDeadlineSeconds or check clock skew.")
}
}
return lastMissed, sched.Next(now), nil
}
// +kubebuilder:docs-gen:collapse=getNextSchedule
// figure out the next times that we need to create
// jobs at (or anything we missed).
missedRun, nextRun, err := getNextSchedule(&cronJob, r.Now())
if err != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to figure out CronJob schedule")
// we don't really care about requeuing until we get an update that
// fixes the schedule, so don't return an error
return ctrl.Result{}, nil
}
scheduledResult := ctrl.Result{RequeueAfter: nextRun.Sub(r.Now())} // save this so we can re-use it elsewhere
log = log.WithValues("now", r.Now(), "next run", nextRun)스케줄에 맞고, 마감 시간을 넘지않는 상태로 동시성 정책에 의해 차단되지 않은 경우 새로운 잡을 실행
if missedRun.IsZero() {
log.V(1).Info("no upcoming scheduled times, sleeping until next")
return scheduledResult, nil
}
// make sure we're not too late to start the run
log = log.WithValues("current run", missedRun)
tooLate := false
if cronJob.Spec.StartingDeadlineSeconds != nil {
tooLate = missedRun.Add(time.Duration(*cronJob.Spec.StartingDeadlineSeconds) * time.Second).Before(r.Now())
}
if tooLate {
log.V(1).Info("missed starting deadline for last run, sleeping till next")
// TODO(directxman12): events
return scheduledResult, nil
}
if cronJob.Spec.ConcurrencyPolicy == batchv1.ForbidConcurrent && len(activeJobs) > 0 {
log.V(1).Info("concurrency policy blocks concurrent runs, skipping", "num active", len(activeJobs))
return scheduledResult, nil
}
// ...or instruct us to replace existing ones...
if cronJob.Spec.ConcurrencyPolicy == batchv1.ReplaceConcurrent {
for _, activeJob := range activeJobs {
// we don't care if the job was already deleted
if err := r.Delete(ctx, activeJob, client.PropagationPolicy(metav1.DeletePropagationBackground)); client.IgnoreNotFound(err) != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to delete active job", "job", activeJob)
return ctrl.Result{}, err
}
}
}
constructJobForCronJob := func(cronJob *batchv1.CronJob, scheduledTime time.Time) (*kbatch.Job, error) {
// We want job names for a given nominal start time to have a deterministic name to avoid the same job being created twice
name := fmt.Sprintf("%s-%d", cronJob.Name, scheduledTime.Unix())
job := &kbatch.Job{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Labels: make(map[string]string),
Annotations: make(map[string]string),
Name: name,
Namespace: cronJob.Namespace,
},
Spec: *cronJob.Spec.JobTemplate.Spec.DeepCopy(),
}
for k, v := range cronJob.Spec.JobTemplate.Annotations {
job.Annotations[k] = v
}
job.Annotations[scheduledTimeAnnotation] = scheduledTime.Format(time.RFC3339)
for k, v := range cronJob.Spec.JobTemplate.Labels {
job.Labels[k] = v
}
if err := ctrl.SetControllerReference(cronJob, job, r.Scheme); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return job, nil
}
// +kubebuilder:docs-gen:collapse=constructJobForCronJob
// actually make the job...
job, err := constructJobForCronJob(&cronJob, missedRun)
if err != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to construct job from template")
// don't bother requeuing until we get a change to the spec
return scheduledResult, nil
}
// ...and create it on the cluster
if err := r.Create(ctx, job); err != nil {
log.Error(err, "unable to create Job for CronJob", "job", job)
return ctrl.Result{}, err
}
log.V(1).Info("created Job for CronJob run", "job", job)
리턴!
return scheduledResult, nil
}마지막 셋업
-
Kubernetes의 CronJob 컨트롤러를 설정하는 부분,
SetupWithManager메서드를 통해 매니저와 컨트롤러를 연결 -
CronJob 리소스와 관련된 작업을 설정하고, 매니저가 이를 관리
-
reconciler가 소유자에 따라 job을 조회할수있는 index가 필요함
-
client에서 index키를 선언해서 Index값을 추출할수있게함.
-
indexer는 네임스페이스에서 자동으로 처리해주기때문에, 소유자가있다면 소유자 이름만 처리하면됨.
-
컨트롤러가 일부 작업을 소유하고 있다는 것을 매니저에게 알리면, 작업이 변경되거나 삭제되는 등의 상황에서 자동으로 기본 CronJob에 대해 Reconcile을 호출하게 됨
var (
jobOwnerKey = ".metadata.controller"
apiGVStr = batchv1.GroupVersion.String()
)
// SetupWithManager sets up the controller with the Manager.
func (r *CronJobReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error {
// set up a real clock, since we're not in a test
if r.Clock == nil {
r.Clock = realClock{}
}
if err := mgr.GetFieldIndexer().IndexField(context.Background(), &kbatch.Job{}, jobOwnerKey, func(rawObj client.Object) []string {
// grab the job object, extract the owner...
job := rawObj.(*kbatch.Job)
owner := metav1.GetControllerOf(job)
if owner == nil {
return nil
}
// ...make sure it's a CronJob...
if owner.APIVersion != apiGVStr || owner.Kind != "CronJob" {
return nil
}
// ...and if so, return it
return []string{owner.Name}
}); err != nil {
return err
}
return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr).
For(&batchv1.CronJob{}).
Owns(&kbatch.Job{}).
Complete(r)
}
web hook설정은 생략 / 아래 문서 보면서 설정하시면 됩니다~!
https://book.kubebuilder.io/cronjob-tutorial/webhook-implementation
설치및 sample 적용
make install
make run
# project/config/samples/batch_v1_cronjob.yaml
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: project
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: kustomize
name: cronjob-sample
spec:
schedule: "*/1 * * * *"
startingDeadlineSeconds: 60
concurrencyPolicy: Allow # explicitly specify, but Allow is also default.
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: busybox
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- date; echo Hello from the Kubernetes cluster
restartPolicy: OnFailure
EOF결과
yusa@YUSAui-MacBookAir project % kubectl logs cronjob-sample-1718439840-kchdg
Sat Jun 15 08:24:56 UTC 2024
Hello from the Kubernetes cluster
yusa@YUSAui-MacBookAir Everything % kubectl api-resources | grep kubebuilder
cronjobs batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io/v1 true CronJob
yusa@YUSAui-MacBookAir Everything % kubectl get crd | grep kubebuilder
cronjobs.batch.tutorial.kubebuilder.io 2024-06-15T08:18:33Z
webhook설정 하는것도 볼수있음
leader lease하는 것도 확인 가능
트러블 슈팅
- metadata.annotations: Too long: must have at most 262144 bytes
- Makefile crd:maxDescLen=0 추가 필요
- indent 한칸도 잘못 넣으면 오류를 뱉으니 확인 잘하기~!!!
- https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubebuilder/issues/2556
- Makefile crd:maxDescLen=0 추가 필요
.PHONY: manifests
manifests: controller-gen ## Generate WebhookConfiguration, ClusterRole and CustomResourceDefinition objects.
$(CONTROLLER_GEN) rbac:roleName=manager-role crd:maxDescLen=0 webhook paths="./..." output:crd:artifacts:config=config/crd/bases
- Certmanager / prometheus 배포 필요
-
https://book.kubebuilder.io/cronjob-tutorial/running-webhook
-
CRD 배포 필요
resource mapping not found for name: "project-serving-cert" namespace: "project-system" from "STDIN": no matches for kind "Certificate" in version "cert-manager.io/v1" ensure CRDs are installed first resource mapping not found for name: "project-selfsigned-issuer" namespace: "project-system" from "STDIN": no matches for kind "Issuer" in version "cert-manager.io/v1" ensure CRDs are installed first resource mapping not found for name: "project-controller-manager-metrics-monitor" namespace: "project-system" from "STDIN": no matches for kind "ServiceMonitor" in version "monitoring.coreos.com/v1" -
cert manager 설치 / prometheus 설치
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/jetstack/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.9.1/cert-manager.yaml kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/prometheus-operator/prometheus-operator/main/bundle.yaml kubectl get pods -A NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE cert-manager cert-manager-7dff8ccdd7-7fc2d 1/1 Running 0 14m cert-manager cert-manager-cainjector-5bb8444c78-mlb84 1/1 Running 0 14m cert-manager cert-manager-webhook-9594fd5f-fsdj7 1/1 Running 0 14m default prometheus-operator-78d4457445-x6xjz 1/1 Running 0 14m
실제로 kubebuilder써? - katib 사례분석
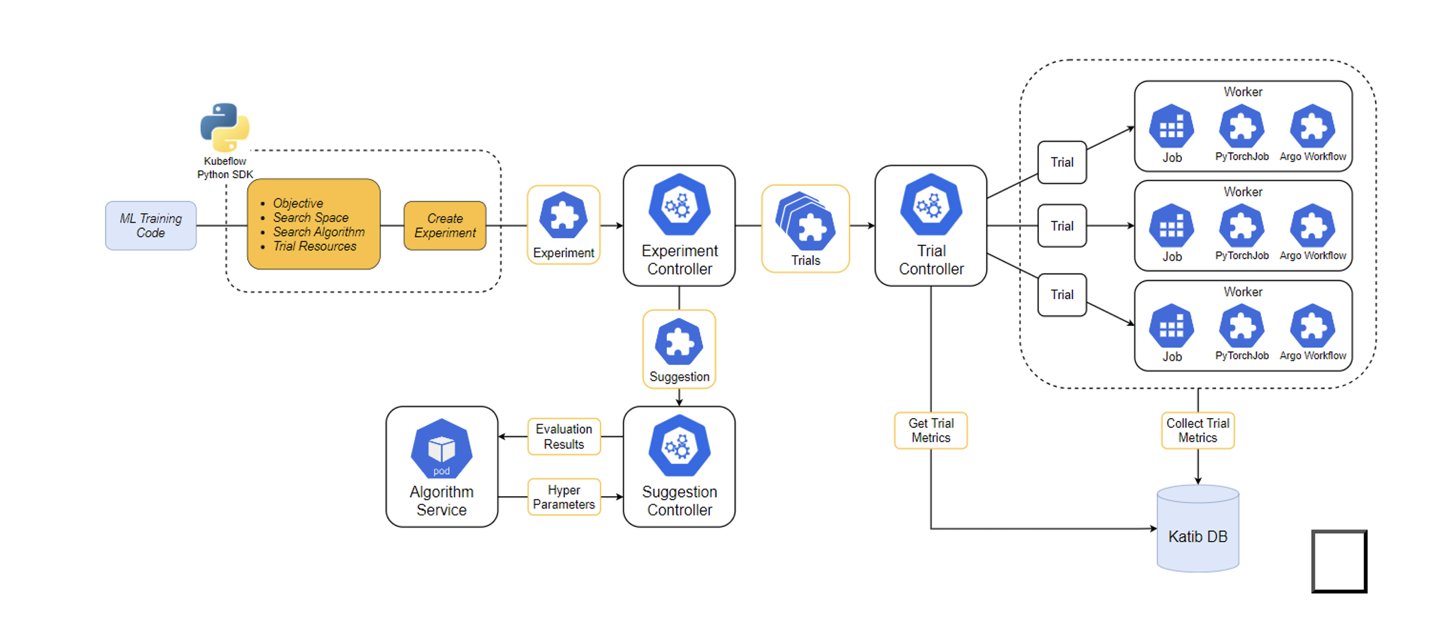
kubeflow - katib 은 하이퍼 파라미터 튜닝을 위한 시스템
- 모델을 최적화하기 위해 하이퍼파라미터를 조정하는 과정
- 학습률, 손실 함수, 배치 사이즈 이런 것들 을 조정하는 것
- Katib는 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝을 자동화하여 머신 러닝 모델의 성능을 최적화하는데 사용된다..
https://github.com/kubeflow/katib
- 배경 지식 하나만 넣고 가자…!
- Kubeflow Katib의
Experiment객체- 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝 실험을 정의하고 관리하기 위한 커스텀 리소스
Experiment객체는 어떤 하이퍼파라미터를 어떻게 튜닝할 것인지, 실험의 목표는 무엇인지, 실험의 조건은 무엇인지 등을 정의하게됨.- CRD라면…. Reconcile이 있겠지…
- Experiment (실험)
- 특정 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝 작업을 정의
- 어떤 하이퍼파라미터를 조정할지, 어떤 알고리즘을 사용할지, 목표 메트릭은 무엇인지 등을 포함
- Trial (실험 실행)
- 실험에서 정의된 하나의 하이퍼파라미터 조합에 대한 모델 학습 실행
- 여러 개의 Trial을 통해 최적의 하이퍼파라미터를 찾음
- Suggestion (제안)
- 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝 알고리즘을 사용하여 다음에 시도할 하이퍼파라미터 조합을 제안
- 예를 들어, Grid Search, Random Search, Bayesian Optimization 등의 알고리즘이 사용
- Kubeflow Katib의
- Expermient CRD
experiment_types.go
trial_types.go
여기서 struct를 보면 여기 spec, status를 참고하면 밑에 yaml과 동일한 것을 볼수있음.
katib/pkg/apis/controller/experiments/v1beta1
/experiment_types.go
// ExperimentSpec is the specification of an Experiment.
type ExperimentSpec struct {
}
// ExperimentStatus is the current status of an Experiment.
type ExperimentStatus struct {
}
// TrialTemplate describes structure of trial template
type TrialTemplate struct {
}
// TrialSpec is the specification of a Trial.
type TrialSpec struct {
}
// TrialStatus is the current status of a Trial.
type TrialStatus struct {
}- 중요한 Reconcile 객체를 보자
- 리소스의 현재 상태를 원하는 상태로 맞추기 위해 실행되는 핵심 로직을 포함
Reconciler는 리소스가 변경될 때마다 호출되어, 필요한 수정 작업을 수행
- finalizer Kubernetes에서 리소스 객체가 삭제될 때 추가적인 처리를 수행할 삭제 전처리, 삭제 보류, 재시도, 안전성 향상
// 여기서 컨트롤러가 experiments.kubeflow.org이 여러 권한을 가지는 것을 볼수있음.
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=experiments.kubeflow.org,resources=experiments,verbs=get;list;watch;create;update;patch;delete
// +kubebuilder:rbac:groups=experiments.kubeflow.org,resources=experiments/status,verbs=get;update;patch
func (r *ReconcileExperiment) Reconcile(ctx context.Context, request reconcile.Request) (reconcile.Result, error) {
// Fetch the Experiment instance
logger := log.WithValues("Experiment", request.NamespacedName)
original := &experimentsv1beta1.Experiment{}
// request.NamespacedName에 해당하는 Experiment 객체를 가져옵니다.
// 객체를 찾을 수 없으면 종료하고, 오류가 발생하면 다시 에 넣어 버림.
err := r.Get(ctx, request.NamespacedName, original)
if err != nil {
if errors.IsNotFound(err) {
// Object not found, return. Created objects are automatically garbage collected.
// For additional cleanup logic use finalizers.
return reconcile.Result{}, nil
}
// Error reading the object - requeue the request.
logger.Error(err, "Experiment Get error")
return reconcile.Result{}, err
}
instance := original.DeepCopy()
// finalizer가 필요하다면 update함, 추가적인 정리 작업을 할수있게 됨
if needUpdate, finalizers := needUpdateFinalizers(instance); needUpdate {
return r.updateFinalizers(instance, finalizers)
}
// 실험이 완료된 상태인지 확인해서, 완료되면 관련 자원을 정리해버림
if instance.IsCompleted() {
// Cleanup suggestion after Experiment is finished.
// If ResumePolicy = Never or ResumePolicy = FromVolume, delete suggestion deployment, service and mark suggestion status succeeded.
if instance.Spec.ResumePolicy == experimentsv1beta1.NeverResume || instance.Spec.ResumePolicy == experimentsv1beta1.FromVolume {
err := r.cleanupSuggestionResources(instance)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err, "cleanupSuggestionResources error")
return reconcile.Result{}, err
}
}
// 재시작 가능여부 확인해서 재시작도 가능하게 함.
// Check if experiment is restartable and max trials is reconfigured
// That means experiment is restarting
if (util.IsCompletedExperimentRestartable(instance) &&
instance.Spec.MaxTrialCount != nil &&
*instance.Spec.MaxTrialCount > instance.Status.Trials) ||
(instance.Spec.MaxTrialCount == nil && instance.Status.Trials != 0) {
logger.Info("Experiment is restarting",
"MaxTrialCount", instance.Spec.MaxTrialCount,
"ParallelTrialCount", instance.Spec.ParallelTrialCount,
"MaxFailedTrialCount", instance.Spec.MaxFailedTrialCount)
msg := "Experiment is restarted"
instance.MarkExperimentStatusRestarting(util.ExperimentRestartingReason, msg)
// If ResumePolicy = FromVolume, suggestion must remove succeeded status and add running status when restarting
if instance.Spec.ResumePolicy == experimentsv1beta1.FromVolume {
err := r.restartSuggestion(instance)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err, "restartSuggestion error")
return reconcile.Result{}, err
}
}
} else {
// If experiment is completed with no running trials, stop reconcile
if !instance.HasRunningTrials() {
return reconcile.Result{}, nil
}
}
}
// 생성되지않은 경우 상태 업데이트, 생성된 경우 실험을 조정함.
if !instance.IsCreated() {
if instance.Status.StartTime == nil {
now := metav1.Now()
instance.Status.StartTime = &now
}
if instance.Status.CompletionTime == nil {
instance.Status.CompletionTime = &metav1.Time{}
}
msg := "Experiment is created"
instance.MarkExperimentStatusCreated(util.ExperimentCreatedReason, msg)
} else {
err := r.ReconcileExperiment(instance)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err, "Reconcile experiment error")
r.recorder.Eventf(instance,
corev1.EventTypeWarning, consts.ReconcileErrorReason,
"Failed to reconcile: %v", err)
return reconcile.Result{}, err
}
}
// 원래 상태, 현재 상태를 비교해서 변경상황 있으면 업데이트
if !equality.Semantic.DeepEqual(original.Status, instance.Status) {
//assuming that only status change
err = r.updateStatusHandler(instance)
if err != nil {
logger.Info("Update experiment instance status failed, reconciler requeued", "err", err)
return reconcile.Result{
Requeue: true,
}, nil
}
}
return reconcile.Result{}, nil
}이제 우리는 무엇을 할수있나?
Kubernetes로 클러스터 외부 자원 관리하기
https://engineering.linecorp.com/ko/blog/managing-external-resources-with-kubernetes
kubeflow/Katib의 안전한 사용과 커뮤니티를 위해 기여하기
https://makinarocks.github.io/open-source-contributions-katib/
코드 까보는 것도 가능!
https://velog.io/@sawa1989/aws-alb-controller-port-cli-ingress이슈
참고
쿠베빌더 공식문서
kubebuilderに触れてみた①概念編
https://qiita.com/shiei_kawa/items/e745f20040ad5911fcc2
Kubebuilder Intro & Deep Dive | Oshi Gupta
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QYwTRZjEyK4
Kubernetes Operator series 2 — Overview of controller-runtime
Everything you need to know about Kubebuilder: Write operators like a pro
https://youtu.be/_XUJ1HoinWA?si=_B2qMumEqNL0pNmR
Kubebuilder: SDK for Extending Kubernetes - Fan Zhang, VMware Inc & Mengqi Yu, Google
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CD33-TRYwJc
안승규 ( Custom Controller 만들기 - kubebuilder 활용)
https://devocean.sk.com/blog/techBoardDetail.do?ID=164260
안승규 ( Custom Controller 2 - Kubebuilder Architecture )
https://devocean.sk.com/blog/techBoardDetail.do?ID=165032&boardType=techBlog#none
Kubernetes Operator series 1 — controller-runtime example controller
https://nakamasato.medium.com/kubernetes-operator-series-1-controller-runtime-aa50d1d93c5c
Katib관련글
https://makinarocks.github.io/open-source-contributions-katib/
Kurly만의 MLOps 구축하기 - 쿠브플로우 도입기
