❗️ 계속해서 업데이트 될 예정...
잘못된 부분이 있다면 알려주세요 🙏
스택과 큐
스택과 큐 모두 파이썬에서는 리스트로 연산이 가능하다. 다만, 리스트는 동적 배열로 되어있어 제일 앞에 요소를 pop하기에는 효율적이지 않기 때문에, 데크(Deque)라는 별도의 자료형을 사용하면 더 효율적으로 연산할 수 있다. 물론 데크를 이용해 스택 또한 연산할 수 있다.
기본 연산
- push(): 요소를 추가한다.
- pop(): 가장 최근에 삽입한 요소를 제거한다.
스택(Stack)
LIFO(Last-In-First-Out).
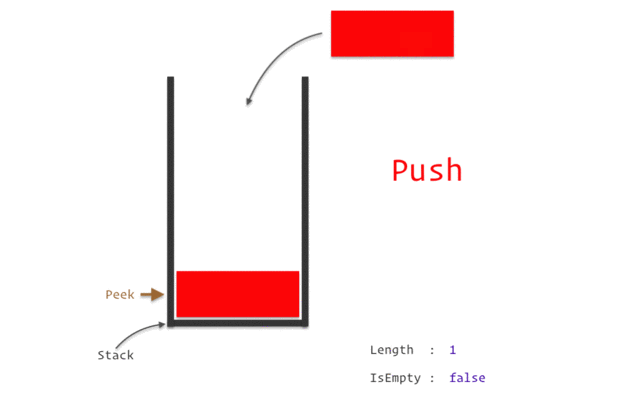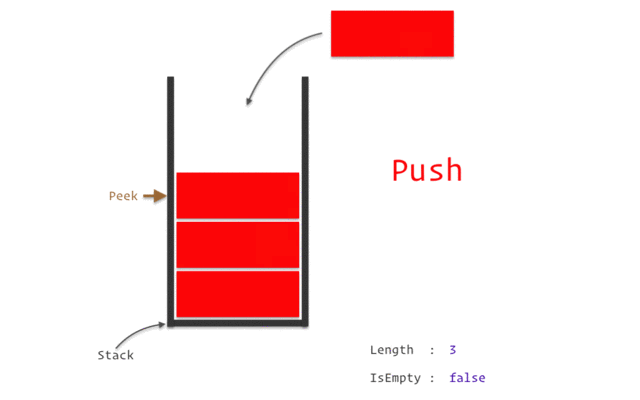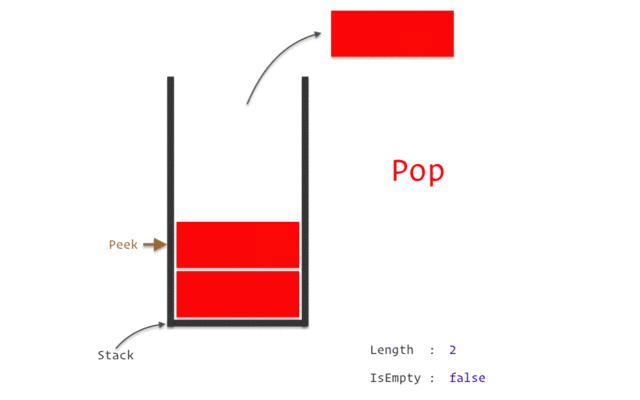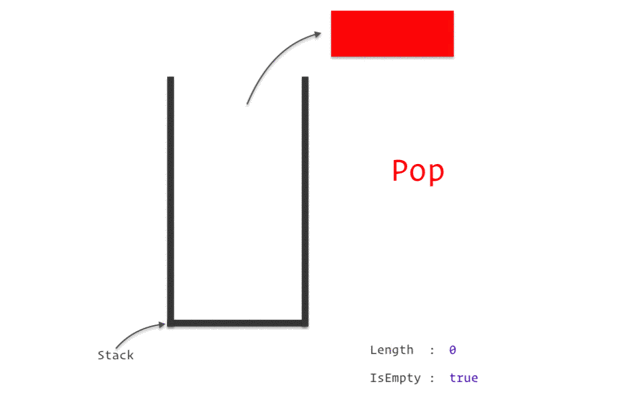
스택 구현 with Python
- 단일 연결 리스트로 구현함.
class Node: # 노드 생성
def __init__(self,item,next):
self.item = item
self.next = next
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.last = None # 스택의 초기값은 None
def push(self, item):
self.last = Node(item, self.last) # push된 값을 포인터로 가리킴
def pop(self):
item = self.last.item
self.last = self.last.next # 포인터를 다음 노드로 옮김
return item큐(queue) 정의
FIFO(First-In-First-Out).
한쪽에서는 삭제, 한쪽에서는 삽입 작업이 이루어지도록 구성한 자료구조.

데크(Deque) 정의
더블 엔디드 큐(Double Ended Queue)의 줄임말. 말 그대로 양쪽 끝을 모두 추출할 수 있는 추상 자료형. 이 추상 자료형을 구현하기 위해서는 배열이나 연결 리스트 모두 가능하나, 이중 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List)로 구현하는 것이 가장 적합하다.
파이썬에서의 데크
파이썬에서는 collections 모듈을 사용하면 쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
import collections
d = collections.deque()
type(d) # <class 'collections.deque'>시간복잡도
- 스택
- 리스트로 구현
append: 시간 복잡도O(1)
pop: 시간 복잡도O(1) - 데크로 구현
리스트와 동일
- 리스트로 구현
- 큐
- 리스트로 구현
append: 시간 복잡도O(1)
pop(0): 시간 복잡도O(n)=> 제거된 값 이후를 전부 한 칸씩 당겨줘야함 - 데크로 구현
append: 시간 복잡도O(1)
popleft(): 시간 복잡도O(1)
- 리스트로 구현
스택과 큐 문제 풀이
문제 1874
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
n = int(input())
stack = []
temp = 1
result = ''
for _ in range(1, n+1):
target = int(input())
while temp <= target:
stack.append(temp)
temp += 1
result += '+'
if stack[-1] == target:
stack.pop()
result += '-'
else:
print('NO')
exit()
for i in result:
print(i)
temp에push값들을 저장하고, 결과값을result에 저장한다. 또한 조건에 맞지 않을 경우 바로exit()를 하여 프로그램을 종료시켜 시간 초과를 막아야한다.
문제 10773
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
stack = []
k = int(input())
for _ in range(k):
n = int(input())
if n > 0:
stack.append(n)
else:
stack.pop()
print(sum(stack))문제 4949
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
import re
while 1:
result = True
s = input()
if s == '.':
break
s = re.sub(r"[^(\)[\]]","", s)
stack = []
table = {')': '(', ']': '['}
for char in s:
if char not in table:
stack.append(char)
elif not stack or table[char] != stack.pop():
result = False
break
if result and not stack:
print('yes')
else:
print('no')이때동안
if not A in B이렇게만 되는 줄 알았는데if A not in B도 같은 결과를 반환한다.
정규표현식을 통해[]()가 아닌 경우는 모두 없앴다.
문제 2504
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
import re
while 1:
result = True
s = input()
if s == '.':
break
s = re.sub(r"[^(\)[\]]","", s)
stack = []
table = {')': '(', ']': '['}
for char in s:
if char not in table:
stack.append(char)
elif not stack or table[char] != stack.pop():
result = False
break
if result and not stack:
print('yes')
else:
print('no')문제 1021
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
import collections
N, M = map(int, input().split())
d = collections.deque(range(1,N+1))
select = list(map(int, input().split()))
cnt = 0
for idx in select:
while 1:
if idx == d[0]:
d.popleft()
break
elif d.index(idx) <= len(d)//2:
d.rotate(-1)
cnt += 1
else:
d.rotate(1)
cnt += 1
print(cnt)
원형 큐는rotate통해 쉽게 구현이 가능하다.
rotate(음수): 왼쪽 회전
rotate(양수): 오른쪽 회전
큐가 회전을 하면서 원하는 값과 일치하는 그 순간 그 값을 빼고(popleft()) 회전을 멈춘다.
문제 10828
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
import sys
N = int(input())
arr = []
for _ in range(N):
command = sys.stdin.readline()
if 'push' in command:
arr.append(command.split()[1])
elif 'pop' in command:
if not arr:
print(-1)
continue
print(arr.pop())
elif 'size' in command:
print(len(arr))
elif 'empty' in command:
if arr:
print(0)
else:
print(1)
elif 'top' in command:
if not arr:
print(-1)
continue
print(arr[-1])문제 9012
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
import sys
T = int(input())
for _ in range(T):
stack = []
arr = list(sys.stdin.readline())
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] == '(':
stack.append(i)
elif arr[i] == ')' and stack:
stack.pop()
elif arr[i] == ')' and not stack:
print('NO')
break
elif i == len(arr)-1 and stack:
print('NO')
elif i == len(arr)-1 and not stack:
print('YES')💡 흥미로운 코드
from sys import stdin
n = int(input())
for _ in range(n):
str_ = stdin.readline().strip()
stack = 0
for chr_ in str_:
if chr_ == '(':
stack += 1
else:
stack -= 1
if stack < 0:
break
if stack == 0:
print('YES')
else:
print('NO')stack의 내용을 출력하는 문제가 아니기때문에 굳이 append를 이용해 스택을 쌓지 않고도 위 코드처럼
stack+=1로 해결 할 수 있다.
append를 사용하지 않았기 때문에 속도도 빠르다.
문제 10799
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
arr = list(input())
stack = []
num = 0
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] == '(':
stack.append('(')
else:
if arr[i-1] == '(':
stack.pop()
num += len(stack)
else:
stack.pop()
num += 1
print(num)
(일때는 스택에 쌓는다.()일때는 pop을 한 뒤 stack에 쌓인(개수 만큼 정답에 더한다.)일때는 pop을 한 뒤 정답에 1을 더한다.
문제 10845
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
import sys
N = int(input())
arr = []
for _ in range(N):
command = sys.stdin.readline()
if 'push' in command:
arr.append(command.split()[1])
elif 'pop' in command:
if not arr:
print(-1)
continue
print(arr[0])
arr = arr[1:]
elif 'size' in command:
print(len(arr))
elif 'empty' in command:
if arr:
print(0)
else:
print(1)
elif 'front' in command:
if not arr:
print(-1)
continue
print(arr[0])
elif 'back' in command:
if not arr:
print(-1)
continue
print(arr[-1])
list를 이용한 풀이
문제 1406
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
import sys
s = list(input().strip())
s1 = []
N = int(input())
for _ in range(N):
cmd = sys.stdin.readline().split()
if cmd[0] == 'L':
if s: s1.append(s.pop())
elif cmd[0] == 'D':
if s1: s.append(s1.pop())
elif cmd[0] == 'B':
if s: s.pop()
else:
s.append(cmd[1])
print(''.join(s+list(reversed(s1))))처음에 커서라는 변수를 두고 리스트의 슬라이스로 문자열을 만들었는데 시간 초과가 떴다.
좀 더 시간복잡도를 낮춰야 해서append와pop의 시간복잡도가 O(1)이기 때문에 stack 을 이용했다.
Reference
문제 10845
✏️ 내가 작성한 코드
import sys
import collections
N = int(input())
deq = collections.deque()
for _ in range(N):
command = sys.stdin.readline()
if 'push_front' in command:
deq.appendleft(command.split()[1])
elif 'push_back' in command:
deq.append(command.split()[1])
elif 'pop_front' in command:
if not deq:
print(-1)
continue
print(deq.popleft())
elif 'pop_back' in command:
if not deq:
print(-1)
continue
print(deq.pop())
elif 'size' in command:
print(len(deq))
elif 'empty' in command:
if deq:
print(0)
else:
print(1)
elif 'front' in command:
if not deq:
print(-1)
continue
print(deq[0])
elif 'back' in command:
if not deq:
print(-1)
continue
print(deq[-1])
deque를 이용한 풀이