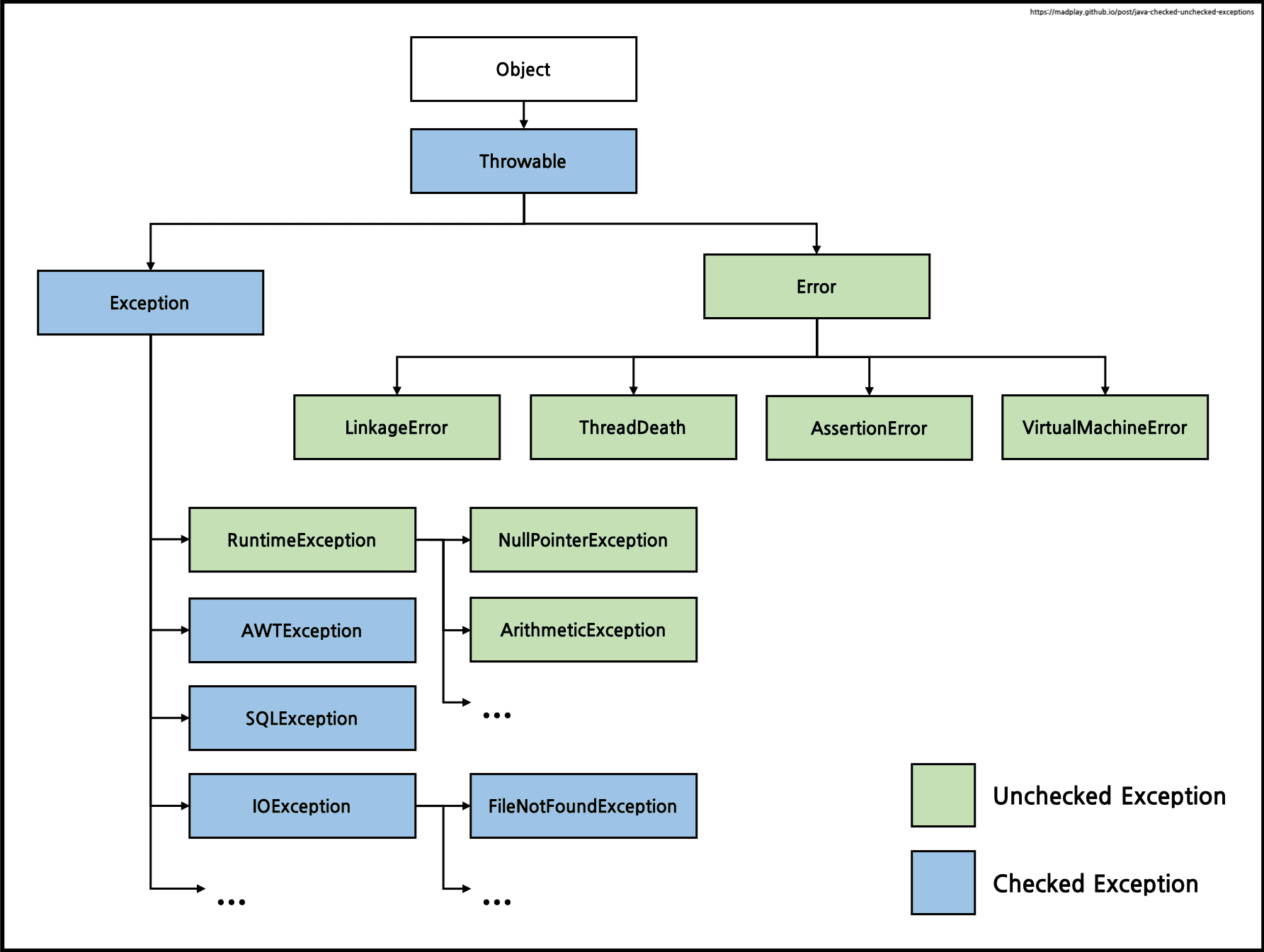
Java에는 Checked Exception과 Unchecked Exception(Runtime Exception)이 있다.
Exception 처리
- 예외 복구
- 예외 처리 회피
- 예외 전환
예외 복구
- 예외 상황 파악 후 문제를 해결하는 방법
- 예외를
catch해서 일정 시간, 조건만큼 대기 후 다시 재시도 반복 - 최대 재시도 횟수를 넘길 경우 예외 발생
예외 처리 회피
- 예외 처리를 직접 담당하지 않고 호출한 쪽으로
throws하는 방법 - 보통의 경우 예외를 그냥 던지는 것은 무책임한 방법일 수 있다. (로그라도 출력하는 것을 권장)
예외 전환
- 예외 회피와 비슷하게
throws를 하지만, 적절한 예외로 전환하여 던지는 방식 - 더 명확한 의미로 전달하기 위해 전환
- 단순하게 만들기 위해 wrap할 수도 있다.
Checked vs Unchecked
| checked | unchecked | |
|---|---|---|
| 예외 처리 | 필수 | 필수 아님 |
| 트랜잭션 롤백 | 안됨 | 기본값으로 들어 있어서 진행 |
| 검증 | 컴파일 단계 | 런타임 단계 |
Checked Exception
- 예외 처리 필수
try~ catch~로 예외 처리를 하거나 상위 메소드로throw필요 - 트랜잭션 기본 롤백 대상 x
롤백 처리하려면 추가 처리가 필요,@Transactional의rollbackFor옵션 - 컴파일 단계에서 체크
- 예시
- FileNotFoundException
- ClassNotFoundException
Unchecked Exception
RuntimeException을 상속하는 예외를 말한다.
- 예외 처리 필수 x
예측을 하지 못하기 때문에 예외 처리를 할 수 없다. - 트랜잭션 기본 롤백 대상
@Transactional의rollbackFor옵션이 기본이라 예외 발생 시 롤백 처리됨 - 런타임 단계에서 체크
- 예시
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException
- NullPointException
언제 써야할까?
일반적으로 로직을 처리하는 Service 클래스의 경우 예외를 복구할 수 없는 checked exception은 회피나 무시보다는 unchecked exception으로 wrap하여 처리하는 것이 좋다.
다만, 특정 메소드에서 어떤 예외가 발생하는지 명시적으로 알려줘야 할 때에는 checked exception을 그대로 사용하는 것이 나은 경우도 있다.
Oracle :: unchecked exceptions
Here's the bottom line guideline: If a client can reasonably be expected to recover from an exception, make it a checked exception. If a client cannot do anything to recover from the exception, make it an unchecked exception.
