문제 1
이슈 1
- 입력 값이 nextInt() -> nextLine() 이라면 문제
- nextInt()에는 개행 문자(enter)가 포함되서 넘겨짐
- nextLine()은 앞에 enter를 확인하고 값이 입력되지 않음
-> 해결법 : nextInt() -> nextLie() 공벡 제거 -> nextLine()을 통해 입력 값을 받는다.
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=scan.nextInt();
scan.nextLine(); // 개행 문자 제거
String str=scan.nextLine();
이슈 2
nextLine()으로 입력받은 값을 배열로 저장하기 위해 split을 이용
- 입력받은 문자열을 공백 기준으로 나눈다.
String []test=str.split(" ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(test));
코드
package inflearn.section2_array;
import java.util.*;
public class Main1 {
public int[] solution(int num,String[] str) {
// Array의 첫번째 인자, string -> int
int tmp=Integer.parseInt(str[0]);
// 저장되는것은 동적이기 때문에 arrayList사용
ArrayList<Integer>arrayList=new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(tmp);
// for문 돌면서 다음꺼랑 비교
for (int i=1;i<num;i++) {
// 앞에꺼랑 비교 [1] [0]
int next=Integer.parseInt(str[i]);
if (next>tmp) {
arrayList.add(next);
}
tmp=next;
}
// arrayList -> array로 변경
int []answer=new int[arrayList.size()];
for (int i=0;i<arrayList.size();i++) {
answer[i]=arrayList.get(i);
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main1 main=new Main1();
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=scan.nextInt();
scan.nextLine(); // 개행 문자 제거
String str=scan.nextLine();
// 입력받은 문자열을 공백 기준으로 나눈다.
String []test=str.split(" ");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(test));
main.solution(num,test);
// 전달받은 인자가 array이기 때문에 for문으로 받는다.
for (int i:main.solution(num,test)) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
문제 2

이슈
에라토스테네스 체
소수를 찾는 방법. 이 방법은 마치 체로 치듯이 수를 걸러낸다고 하여 '에라토스테네스의 체'라고 부른다.
방법
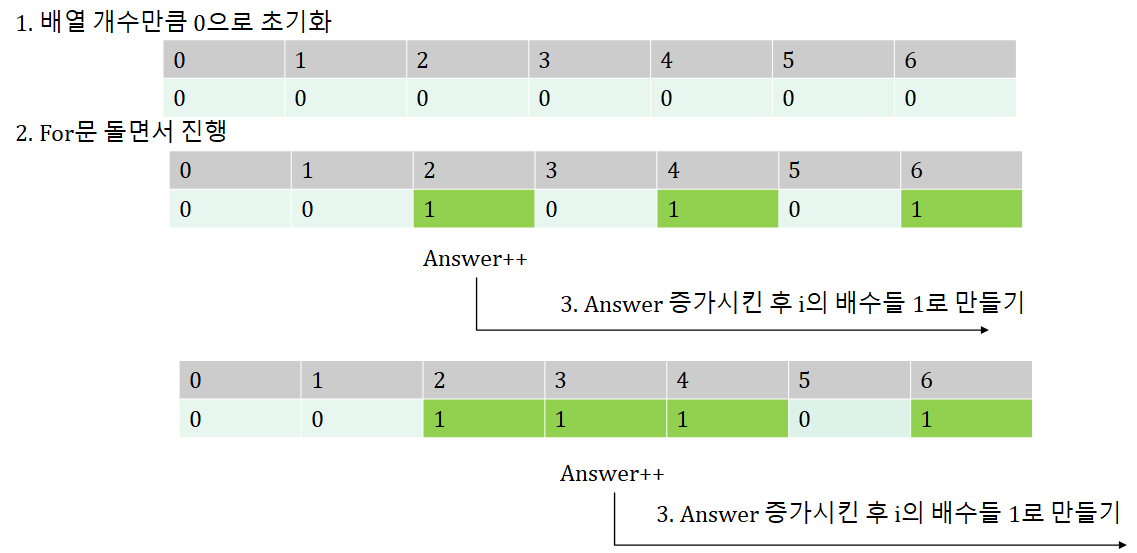
- 개수만큼 배열 생성
ex) 20이라면 21개의 배열 생성
int []=new int [21];- for 문 돌면서
2-1. If ch[i]가 0이라면 answer++ (이건 소수),
for 문 돌면서 i의 배수들 전부 1로 체크
코드
package inflearn.section2_array;
import java.util.*;
public class Main5 {
public int solution(int num) {
int answer=0;
int []ch=new int[num+1];
for (int i=2;i<=num;i++) {
if (ch[i]==0) {
answer++; // 소수
// 소수확인
// System.out.print(i+" ");
// 나머지는 1로 변경하기
for (int j=i;j<=num;j=j+i) {
ch[j]=1;
}
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main5 main=new Main5();
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(main.solution(scan.nextInt()));
}
}
문제 3
이슈 1
while과 for문을 사용하려고 했음
- 1일때만 cnt 증가 -> 하지만 0이면 더이상 진행이 안됨
- 따라서 0일때는 lt의 인덱스를 1칸 이동
- 해결은 했지만 n^2 시간복잡도
강사님 해결방법
- cnt를 0으로 초기화
- str배열의 값이 1일때만 cnt 증가하고 answer에 더해줌
- 만약 0이면 cnt를 0으로 초기화
- 이러면 시간복잡도가 n으로 계산되어질 수 있음
- 코드를 명확히
코드
package inflearn.section2_array;
import java.util.*;
public class Main7 {
public int solution(int num, String []str) {
int answer=0;
// System.out.println("string"+Arrays.toString(str));
int lt=0;
int rt=num-1;
while (lt<=rt) {
// 초기값은 0
int tmp=0;
for (int i=lt;i<=rt;i++) {
if (str[i].equals("1")) {
tmp++;
}
else {
break;
}
}
// tmp가 0이면 한칸 증가 해야됨 (핵심)
if (tmp==0) {
lt+=1;
}
else {
lt+=tmp;
}
// System.out.println("tmp:"+tmp);
int sum=0;
for (int i=1;i<=tmp;i++) {
sum+=i;
}
answer+=sum;
}
return answer;
}
// 강사님 코드
// cnt를 0으로 초기화
// str배열의 값이 1일때만 cnt 증가하고 answer에 더해줌
// 만약 0이면 cnt를 0으로 초기화
public int solution2(int num, String []str) {
int answer=0;
int cnt=0;
for (int i=0;i<num;i++) {
if (str.equals("1")) {
cnt++;
answer+=cnt;
}
// 여기가 핵심, str이 0이면 0으로 초기화
else {
cnt=0;
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main7 main=new Main7();
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=scan.nextInt();
scan.nextLine();
String []str=scan.nextLine().split(" ");
System.out.println(main.solution(num,str));
System.out.println(main.solution2(num,str));
}
}
