String과 관련된 메소드
- String 입력 : scanner.next()
- 띄어쓰기가 있는 입력 : scannex.nextLine()
- String char 접근 (인덱스로 접근) : str.chartAt(0)
- String 대,소문자로 변경 : str.toUpperCase(), str.toLowerCase()
- string -> array로 변경 : str.toCharArray()
- char[ ] -> String으로 변경 : String.valueOf(tmp); // tmp는 char [ ]
- String을 구분자를 이용하여 배열로 만들기 : str.split("구분자")
- 배열 값 String으로 한번에 확인하기 : Arrays.toString(array) // 출력문
- 특정 인덱스 찾기 : str.indexOf(" ") // 공백 위치를 앞에서부터 검색
- 부분 String으로 만들기 : String temp2=str.substring(0,idx); //substring은 마지막 인덱스 -1까지
- str=str.substring(idx+1); //다음 인덱스부터 끝까지
Character와 관련된 메소드
- Character 대 소문자 구분 (boolean) : Character.isLowerCase(c)
- char 대,소문자로 변경 : Character.toUpperCase(c)
For-Each 구문
for-each 전체는 string 안됨 -> 따라서 배열이나 arrayList등으로 변경해야 됨 for (char x:str.toCharArray()) { if (x==t) { answer+=1; } }
아스키코드를 이용한 대 소문자 변경
// 대문자 : 65~90, 소문자 : 97~122 -> 두개의 차이는 32 // char는 기본적으로 숫자(아스키 코드)로 제공되기 때문에 바로 숫자랑 비교 가능 // 하지만 캐스팅은 (char)로 붙여서 캐스팅하기 for (char c:str.toCharArray()) { if (c>=65 && c<=90) { answer+=(char)(c+32); } else { answer+=(char)(c-32); } }
알고리즘 문제 1
-
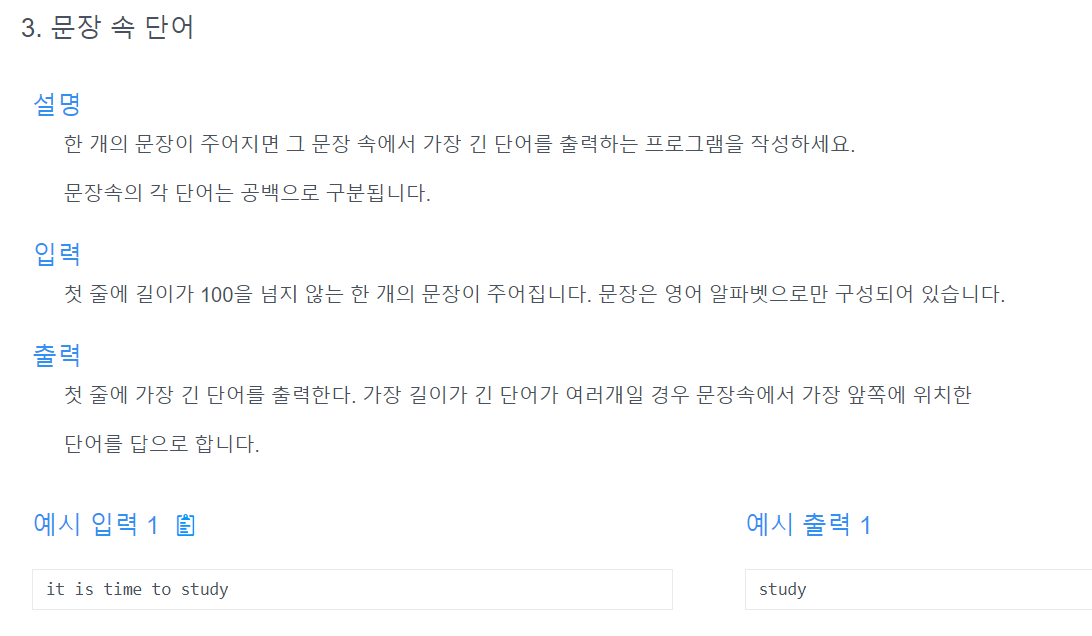
-
배운 점
- 띄어쓰기가 있는 입력 : scan.nextLine()
- 공백 구분자로 str -> 배열로 만들기 : str.split("구분자")
- String []temp =str.split(" ");
- 가장 작은 int 값 : int min=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
- 해결방법
방법 1. split()으로 배열 만들기
방법 2. indexOf()와 subString을 이용하기// indexOf는 특정 인덱스를 찾고 몇번째 인덱스인지 확인할 수 있음 (따라서 while문 조건은 -1을 붙여서 많이 사용) int idx=0; while ((idx=str.indexOf(" "))!=-1) { String temp2=str.substring(0,idx); //substring은 마지막 인덱스 -1까지 str=str.substring(idx+1); } */
- 코드
public class Main3 { public String solution(String str) { String answer=""; // 방법 1. str.split() // 공백 구분자로 단어 쪼개기 // String []temp =str.split(" "); // 배열 값 출력 // System.out.println(Arrays.toString(temp)); // int ans=0; // int ans=Integer.MIN_VALUE; // for (String s:temp) { // if (ans<s.length()) { // ans=s.length(); // answer=s; // } // } // // 방법2. indexOf, subString() /* indexOf indexOf는 특정 문자열 찾기, 없을때는 -1 return (인덱스가 -가 있는 경우는 없기 때문에) 보통 idx, while 문과 많이 사용되며, 문자열 내의 특정 부분을 추출하기 위해 사용 int idx=0; while ((idx=str.indexOf(" "))!=-1) { String temp2=str.substring(0,idx); //substring은 마지막 인덱스 -1까지 str=str.substring(idx+1); } */ // it is time to study -> 공백이 되기 전까지 it / is / time / to // 0123456789... int ans=Integer.MIN_VALUE; int idx=0; System.out.println("idx:"+str.indexOf(" ")); // 2 (공백문자 2 인덱스 발견) // 공백문자 찾기 // 주의 점은 마지막 study 뒤에는 " "가 없기 때문에 확인은 못함 -> 따라서 마지막 꺼를 추가하기 위해 공백문자를 넣는다. // 마지막꺼는 공백문자가 없다. str=str+" "; // while을 사용하여 더 이상 없으면 종료 while ((idx=str.indexOf(" "))!=-1) { System.out.println("idx"+idx); String temp2=str.substring(0,idx); //substring은 마지막 인덱스 -1까지 if (idx>ans) { answer=temp2; } // 다시 str은 다음 꺼로 // it is time to study -> is time to study -> time to study -> to study str=str.substring(idx+1); } System.out.println("answer"+answer); return answer; } public static void main(String[] args) { Main3 main =new Main3(); Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in); // 띄어쓰기가 있는 문자열은 nextLine()으로 받기 String str=scan.nextLine(); System.out.println(main.solution(str)); } }
알고리즘 문제 2
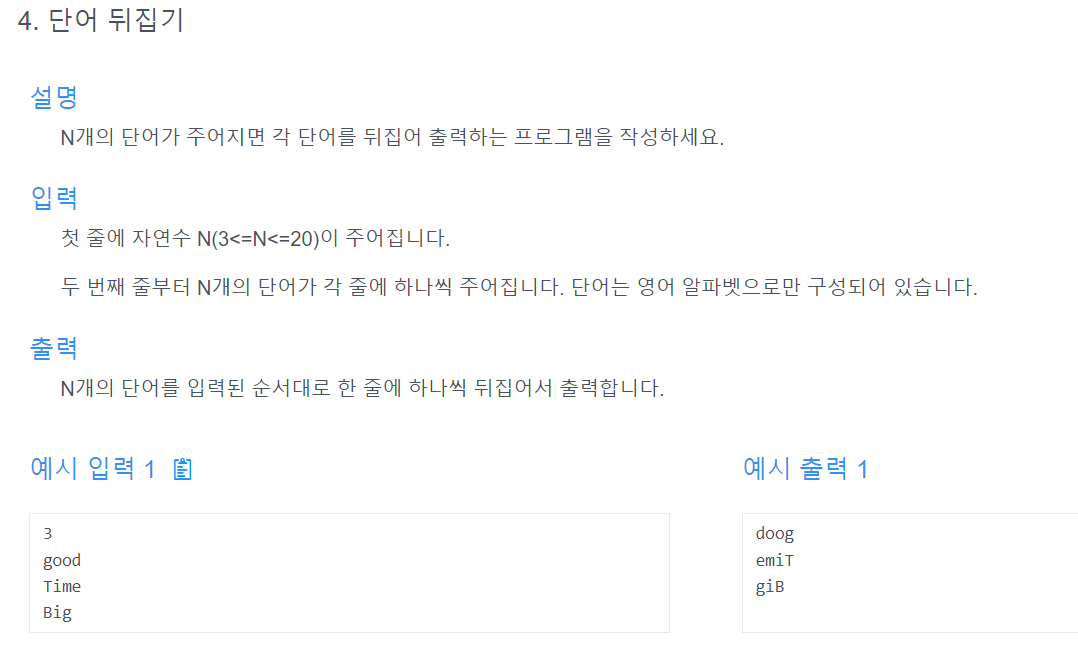
해결방법
- 방법 1. StringBuilder의 reverse 메소드를 이용하여 단어 뒤집기
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(ans).reverse();- 방법 2. 첫번째 인덱스와 마지막 인덱스를 교환하기
lt와 rt를 이용하여 증가, 빼기를 통해 교환
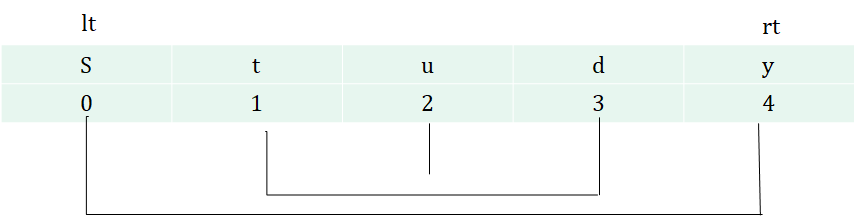
배운점
- StringBuilder 사용하면 객체를 따로 만들지 않고 만들어진 객체를 이용하기 때문에 속도 측면에서 우수
- reverse()나 append() 등 활용 메소드가 많음 - 직접 인덱스 비교하여 변경, 특정 값만 변경할 수 있음
lt와 rt의 인덱스를 이용함
코드
package inflearn.section1_string;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
public class Main4 {
public String solution(String ans) {
// 방법 1. StringBuilder의 reverse 메소드를 이용하여 단어 뒤집기
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(ans).reverse();
// 방법 2. 첫번째 인덱스와 마지막 인덱스를 교환하기
// - lt와 rt를 이용하여 증가, 빼기를 통해 교환
char [] tmp=ans.toCharArray();
int lt=0;
int rt=tmp.length-1; //study -> 길이는 5
while (lt<rt) {
// lt 인덱스, rt인덱스 교환
char temp=tmp[lt];
tmp[lt]=tmp[rt];
tmp[rt]=temp;
lt++;
rt--;
}
// char -> toString
System.out.println("tmp:"+String.valueOf(tmp));
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main4 main =new Main4();
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
int k=scan.nextInt();
String temp[]=new String[k];
for (int i=0;i<k;i++) {
temp[i]=scan.next();
}
for (String ans:temp) {
System.out.println(main.solution(ans));
}
}
}알고리즘 문제 3
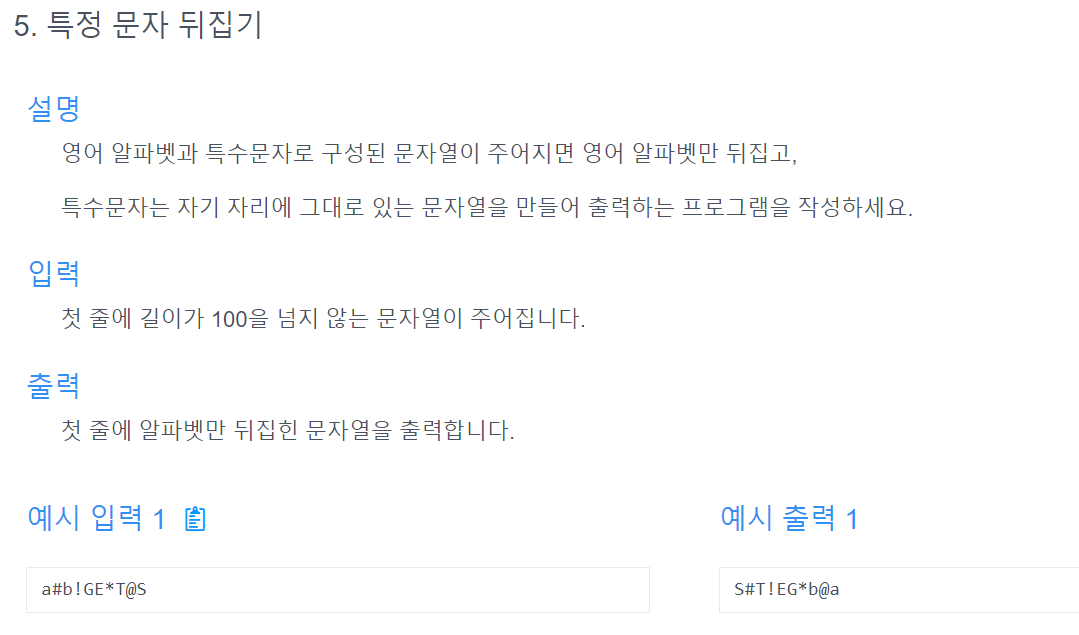
-
해결방법
while (lt <rt) { if (lt==특수문자) lt++; else if (rt==특수문자) rt--; else -> lt rt 교환 , lt++ rt -- } -
코드
package inflearn.section1_string;
// 특정 문자열만 교환
/*
알고리즘
while (lt <rt) {
if (lt==특수문자) lt++;
else if (rt==특수문자) rt--;
else -> lt rt 교환 , lt++ rt --
}
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
public class Main5 {
public String solution(String str) {
String answer="";
// String -> 인덱스 접근, 배열로 만들기
char []temp=str.toCharArray();
// 문자열을 비교하고 만약
int lt =0;
int rt=temp.length-1;
while (lt<rt) {
if (!Character.isAlphabetic(temp[lt])) {
lt++;
}
else if (!Character.isAlphabetic(temp[rt])) {
rt--;
}
else {
// 스왑
char tmp=temp[lt];
temp[lt]=temp[rt];
temp[rt]=tmp;
lt++;
rt--;
}
}
// char[] -> string으로 변환
answer=String.valueOf(temp);
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main5 main =new Main5();
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(main.solution(scan.next()));
}
}알고리즘 문제 4
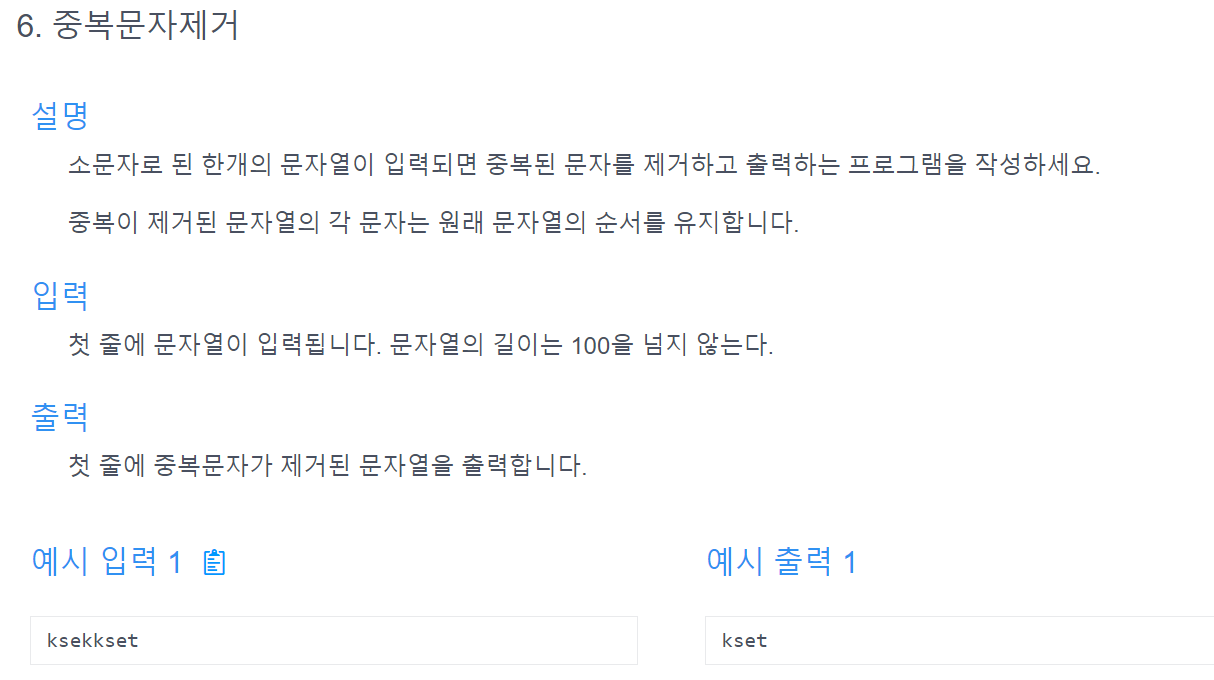
해결방법
- 인덱스와 IndexOf 이용

코드
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main6 {
public String solution(String str) {
String answer="";
for (int i=0;i<str.length();i++) {
// System.out.println(str.charAt(i)+" "+i+" "+str.indexOf(str.charAt(i)));
if (i==str.indexOf(str.charAt(i))) {
answer+=str.charAt(i);
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main6 main =new Main6();
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(main.solution(scan.next()));
}
}