★ [학습목표]
Cantera 를 이용한 Heat Release Rate을 시뮬레이션 할 수 있다.
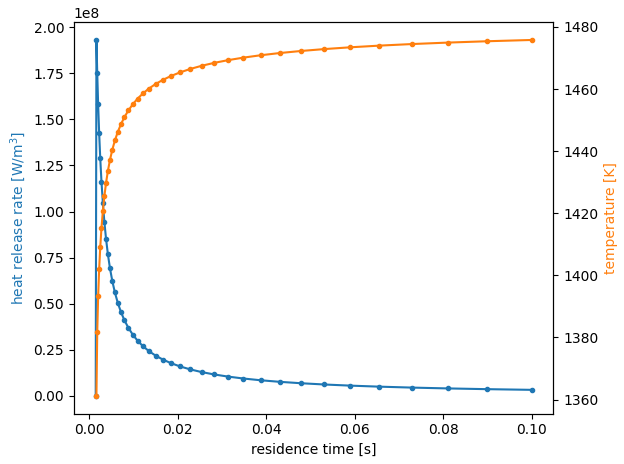
- 서로 다른 체류 시간에 대해 단일 잘 교반된 반응기(Well Stired Reactor)로 모델링된 연소기의 정상 상태 솔루션을 계산합니다. 정상상태 연소 솔루션에 관심이 있습니다. 이 예에서는 반응 완료(연소 가스 온도를 통해)와 총 열 방출 속도에 대한 체류 시간 변경의 효과를 탐구합니다.
바깥쪽 범위에서 이러한 변수를 캡처하여 질량 유량 함수가 시간 이외의 변수에 의존하는 MassFlowController의 사용을 보여줍니다. 또한 고정된 부피의 정압 반응기를 생성하기 위해 PressureController를 사용하는 방법도 보여줍니다.
요구사항: cantera >= 3.0, matplotlib >= 2.0
!pip install cantera
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cantera as ct # NumPy, Matplotlib, Cantera 라이브러리 import.
# Use reaction mechanism GRI-Mech 3.0. For 0-D simulations,
# no transport model is necessary.
gas = ct.Solution('gri30.yaml') # GRI3.0 Reaction Mechanism load 후 gas 객체를 생성
# Create a Reservoir for the inlet, set to a methane/air mixture at a specified
# equivalence ratio
equiv_ratio = 0.5 # lean combustion
gas.TP = 300.0, ct.one_atm # Temp. 300K, Pressure 1bar
gas.set_equivalence_ratio(equiv_ratio, 'CH4:1.0', 'O2:1.0, N2:3.76')
inlet = ct.Reservoir(gas) # gas 객체로 정의된 유체의 특성을 가진 입구 경계 조건을 나타내는 Reservoir 객체
# Create the combustor, and fill it initially with a mixture consisting of the
# equilibrium products of the inlet mixture. This state corresponds to the state
# the reactor would reach with infinite residence time, and thus provides a good
# initial condition from which to reach a steady-state solution on the reacting
# branch.
gas.equilibrate('HP') # 가스 상태를 열역학 평형 상태로 설정
combustor = ct.IdealGasReactor(gas) # 열역학 평형을 사용하여 'combustor' 이상 기체 반응기 객체를 생성
combustor.volume = 1.0
# Create a reservoir for the exhaust
exhaust = ct.Reservoir(gas) # 배기를 위한 exhaust 객체 생성
# Use a variable mass flow rate to keep the residence time in the reactor
# constant (residence_time = mass / mass_flow_rate). The mass flow rate function
# can access variables defined in the calling scope, including state variables
# of the Reactor object (combustor) itself.
def mdot(t):
return combustor.mass/residence_time #시간에 따라 변하는 질량 유량 mdot 함수 정의
inlet_mfc = ct.MassFlowController(inlet, combustor, mdot=mdot)
# mdot 이용 inlet에서 combustor로의 질량 유량을 제어하는 inlet_mfc를 생성
# A PressureController has a baseline mass flow rate matching the 'primary'
# MassFlowController, with an additional pressure-dependent term. By explicitly
# including the upstream mass flow rate, the pressure is kept constant without
# needing to use a large value for 'K', which can introduce undesired stiffness.
outlet_mfc = ct.PressureController(combustor, exhaust, primary=inlet_mfc, K=0.01)
# outlet_mfc를 생성하여, 'primary' 질량 유량을 기준으로하여 상수 압력을 유지
# the simulation only contains one reactor
sim = ct.ReactorNet([combustor]) # combustor 객체 하나를 포함하는 ReactorNet을 생성
# Run a loop over decreasing residence times, until the reactor is extinguished,
# saving the state after each iteration.
states = ct.SolutionArray(gas, extra=['tres'])
residence_time = 0.1 # starting residence time
while combustor.T > 500:
sim.initial_time = 0.0 # reset the integrator
sim.advance_to_steady_state()
print('tres = {:.2e}; T = {:.1f}'.format(residence_time, combustor.T))
states.append(combustor.thermo.state, tres=residence_time)
residence_time *= 0.9 # decrease the residence time for the next iteration
# combustor의 온도가 500 K보다 큰 동안 반복하여, 시간당 유입 질량을 조정하여
# 스테디 상태로 진행합니다. 스테디 상태에 도달한 후, 현재 상태를 states에 추가
# Plot results
f, ax1 = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ax1.plot(states.tres, states.heat_release_rate, '.-', color='C0')
# states.tres는 residence time, states.heat_release_rate는 열 방출율, states.T는 온도
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
ax2.plot(states.tres[:-1], states.T[:-1], '.-', color='C1')
ax1.set_xlabel('residence time [s]')
ax1.set_ylabel('heat release rate [W/m$^3$]', color='C0')
ax2.set_ylabel('temperature [K]', color='C1')
f.tight_layout()
plt.show()