1. 호출 스택
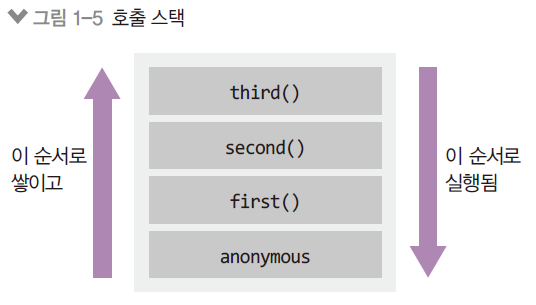
- Anoymous은 가상의 전역 컨텍스트 ( 항상 있다고 생각해 )
- 함수 호출 순서대로 쌓이고, 역순으로 실행 (stack 구조와 유사, LIFO)
2. 이벤트 루프(Event Loop)
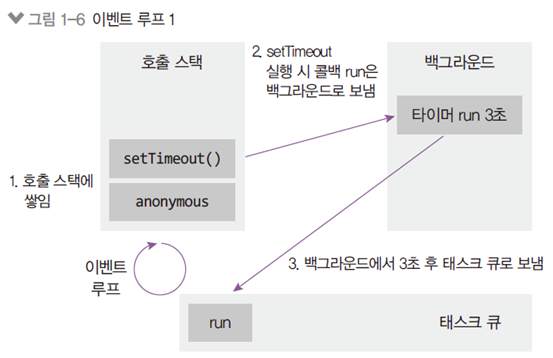
-
이벤트 루프: 이벤트 발생 시 호출할 콜백 함수들을 관리하고, 호출 순서를 결정.
-
태스크 큐: 이벤트 발생 후 호출되어야 할 콜백함수들이 순서대로 기다리는 공간.
-
백그라운드: 타이머나 I/O 작업 콜백, Event Listener들이 대기하는 공간. 여러 작업 동시 실행 OK.
- 비동기이기 때문에 백그라운드로 넘어가서 실행
- 호출스택과 백그라운드가 동시에 실행되면 멀티 스레드(multi thread)- 호출 스택, 백 그라운드, 태스크 큐 모두 비어있으면 JS 실행 종료
- 백 그라운드로 보낼 수 있는 함수 (노드에서 제한을 해 놓음)
setTimout,setInterval,네트워크 요청,HDD의 파일을 읽는 명령어(fs),암호화 명령어,압축명령어... 요정도
Ex)
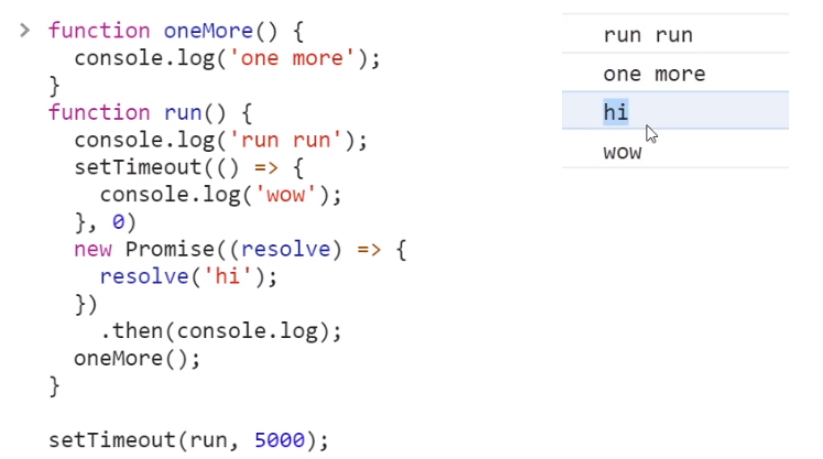
Promise의then이나catch부분은 setTimeout 이후 남아있는 익명 함수보다 우선순위가 더 높아서 'wow'보다 'hi'가 먼저 실행됨 (process.nextTick도 우선순위 높아서 새치기~)
3. var, const, let
- const 와 let은 함수 및 블록{} 에도 별도의 스코프를 가짐 (밖에선 못씀)
var은 필요 없어~ 쓰지 마!if (true) { var x = 3; } console.log(x); // 3 if (true) { const y = 3; } console.log(y); // Uncaught ReferenceError: y is not defined
- const는 값 변경 불가능
const a = 0; a = 1; // Uncaught TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. let b = 0; b = 1; // 1 const c; // Uncaught SyntaxError: Missing initializer in const declaration
4. 템플릿 문자열, 객체 리터럴
(1). 템플릿 문자열(백틱 ` 문자열) 안에 쓰면 문자와 변수 한번에 표현 가능
var num1 = 1;
var num2 = 2;
var result = 3;
var string1 = num1 + ' 더하기 ' + num2 + '는 \'' + result + '\'';
console.log(string1); // 1 더하기 2는 '3' 🔽const num3 = 1;
const num4 = 2;
const result2 = 3;
const string2 = `${num3} 더하기 ${num4}는 '${result2}'`;
console.log(string2); // 1 더하기 2는 '3'- 함수를 백틱 `` 두 개로도 호출 가능!

(2). 객체 리터럴

- 객체의 메서드에 :function을 붙이지 않아도 됨
- {sayNode: sayNode} 와 같은 것을 {sayNode}로 축약 가능
- [변수+값] 등으로 동적 속성명을 객체 속성명으로 사용 가능
5. 화살표 함수 (⇒)
function add1(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
const add2 = (x, y) => {
return x + y;
};
const add3 = (x, y) => x + y;
const add4 = (x, y) => (x + y);
function not1(x) {
return !x;
}
const not2 = x => !x;-
add 1~4 모두 같은 의미의 함수임.
-
함수 본문이 return만 있는 경우 return 생략 가능
-
객체를 리턴하는 경우는 소괄호 필수!!
```jsx const obj = (x,y) ⇒ ({x,y}); ```
// <구소스>
var relationship1 = {
name: 'zero',
friends: ['nero', 'hero', 'xero'],
logFriends: function () {
var that = this;
// relationship1을 가리키는 this를 that에 저장
this.friends.forEach(function (friend) {
console.log(that.name, friend);
});
},
};
relationship1.logFriends();- function은 자기 자신만의
this를 가지기 때문에 부모의 this를 다른 함수에서 사용하려면that같은 변수에 넣어주고 사용 해야함
// <현소스>
const relationship2 = {
name: 'zero',
friends: ['nero', 'hero', 'xero'],
logFriends() {
this.friends.forEach(friend => {
console.log(this.name, friend);
});
},
};
relationship2.logFriends();- 현재는 무조건 부모의 this를 물려받음! this.friends의
this와 this.name의this는 같음


this를 쓸 거면 function을 쓰고, this 필요 없으면 화살표 함수 쓰는 것을 권장
6. 구조 분해 할당 (=비 구조화 할당)
(1). 객체
candyMachine부터 시작해서 속성을 찾아 들어 가야 함 😣
// 구소스
var candyMachine = {
status: {
name: 'node',
count: 5,
},
getCandy: function () {
this.status.count--;
return this.status.count;
},
};
var getCandy = candyMachine.getCandy;
var count = candyMachine.status.count;// 현소스
const candyMachine = {
status: {
name: 'node',
count: 5,
},
getCandy() {
this.status.count--;
return this.status.count;
},
};
const { getCandy, status: { count } } = candyMachine;- const {
변수} =객체; 로 객체 안의 속성을 변수 명으로 사용 가능 😁- 단,
getCandy()를 실행했을 때 결과가canbyMachine.getCandy()와 는 달라지므로 주의
- 단,
count처럼 속성 안의 속성도 변수 명으로 사용 가능
[예시]
// 속성 이름을 변수로 만들어줌
const example = {a:123, b:{c:135, d:146}}
const a = example.a;
const d = example.b.d;
// 차라리 이렇게 해라!
const{a,b:{d}} = example; // ※객체는 key가 일치해야함
console.log(a); //123
console.log(d); //146(2). 배열
배열도 구조 분해 할당 가능
// 구소스
var array = ['nodejs', {}, 10, true];
var node = array[0];
var obj = array[1];
var bool = array[3];// 현소스
const array = ['nodejs', {}, 10, true];
const [node, obj, , bool] = array;- const [
변수] =배열; 형식- 각 배열 인덱스와 변수가 대응됨
- node는 array[0], obj= array[1], bool=array[3];
//배열의 경우
arr= [1,2,3,4,5];
const x= arr[0];
const y= arr[1];
const z= arr[4];
//차라리 이렇게 해라!
const [x,y, , ,z]=arr; // ※배열은 자리가 똑같아야 함!7. 클래스(class)
클래스는 사실 프로토타입
- 구 문법에서는 생성자, 인스턴스,.. 다 따로따로 해줬음😣
var Human = function(type) {
this.type = type || 'human';
};
Human.isHuman = function(human) {
return human instanceof Human;
}
Human.prototype.breathe = function() {
alert('h-a-a-a-m');
};
var Zero = function(type, firstName, lastName) {
Human.apply(this, arguments);
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
};
Zero.prototype = Object.create(Human.prototype);
Zero.prototype.constructor = Zero; // 상속하는 부분
Zero.prototype.sayName = function() {
alert(this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName);
};
var oldZero = new Zero('human', 'Zero', 'Cho');
Human.isHuman(oldZero); // true프로토타입 문법을 깔끔하게 작성할 수 있는 Class 문법 도입
- Constructor(생성자), Extends(상속) 등을 깔끔하게 처리할 수 있음
- 코드가 그룹화 되어 가독성이 향상됨
class Human {
constructor(type = 'human') {
this.type = type;
}
static isHuman(human) {
return human instanceof Human;
}
breathe() {
alert('h-a-a-a-m');
}
}
class Zero extends Human {
constructor(type, firstName, lastName) {
super(type);
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
sayName() {
super.breathe();
alert(`${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`);
}
}
const newZero = new Zero('human', 'Zero', 'Cho');
Human.isHuman(newZero); // true- Class 내부에 관련된 코드들이 묶임
- Super로 부모 Class호출
- Static 키워드로 클래스 메서드 생성
8. 프로미스
👁🗨 프로미스 꼭 알아두기!!
프로미스: 내용이 실행은 되었지만 결과를 아직 반환하지 않은 객체
const condition = true;
// true면 resolve, false면 reject
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (condition) {
resolve('성공');
} else {
reject('실패');
}
});
// 다른 코드가 들어갈 수 있음
promise
.then((message) => {
console.log(message); // 성공(resolve)한 경우 실행
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error); // 실패(reject)한 경우 실행
})
.finally(() => { // 끝나고 무조건 실행
console.log('무조건');
});-
then을 붙이면 결과를 반환함 -
실행이 완료되지 않았으면 완료된 후에
then내부 함수가 실행됨 -
resove( 성공리턴값 ) →then으로 연결 -
reject(실패 리턴값) →catch로 연결 -
finally는 무조건 실행
promise
.then((message) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(message);
});
})
.then((message2) => {
console.log(message2);
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(message2);
});
})
.then((message3) => {
console.log(message3);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
});- 프로미스의
then연달아 사용 가능(프로미스 체이닝)then안에서 return 한 값이 다음then으로 넘어감- return 값이 프로미스면
resolve후 넘어감 - 에러가 난 경우 바로
catch로 이동 - 에러는
catch에서 한번에 처리
const promise1 = Promise.resolve('성공1');
const promise2 = Promise.resolve('성공2');
Promise.all([promise1, promise2])
.then((result) => {
console.log(result); // ['성공1', '성공2'];
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error);
});Promise.all( 배열 ): 여러 개의 프로미스를 동시에 실행- 하나라도 실패하면 catch로 감
allSettled로 실패한 것만 추려낼 수 있음
9. async/ await
Promise를 좀 더 간단하게 나타낸 것임
async function findAndSaveUser(Users) {
let user = await Users.findOne({});
user.name = 'zero';
user = await user.save();
user = await Users.findOne({ gender: 'm' });
// 생략
}async함수 안에서await를 사용할 수 있었는데, 요즘은 탑 레벨 await 로 나와서 그냥 사용 가능await은 오른쪽 → 왼쪽 순으로 실행 (Promise then의 결과 값을 좌변에 저장 느낌~)
async function main(){
try{
const result = await promise;
return result';
}catch(error){
console.log(error);
}
}
main().then((name)=> ... )
const name = await main();async함수에서 리턴 한 값은 main에서 무조건then으로 받아야 함- await를 쓸 때는 try-catch 해줘야 함
const findAndSaveUser = async (Users) => {
try {
let user = await Users.findOne({});
user.name = 'zero';
user = await user.save();
user = await Users.findOne({ gender: 'm' });
// 생략
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
};- 화살표 함수도 async/await 가능
async function findAndSaveUser(Users) {
// 생략
}
findAndSaveUser().then(() => { /* 생략 */ });
// 또는
async function other() {
const result = await findAndSaveUser();
}- async 함수는 항상 promise를 반환
10. 프론트엔드 자바스크립트
(1). Ajax
- 서버로 요청을 보내는 코드
- 라이브러리 없이는 브라우저가 지원하는 XMLHttpRequest 객체 이용
- AJAX 요청 시 Axios 라이브러리 사용하는게 편함!
- HTML에 아래 스크립트를 추가하여 사용
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> // 여기에 예제 코드를 넣으세요. </script>
- HTML에 아래 스크립트를 추가하여 사용
-
GET 요청 보내기
- axios.get 함수의 인자로 요청을 보낼 주소 넣음```jsx <script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> axios.get('https://www.zerocho.com/api/get') .then((result) => { console.log(result); console.log(result.data); // {} }) .catch((error) => { console.error(error); }); </script> ``` - 프로미스 기반 코드라 async/await 사용 가능 ```jsx <script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> (async () => { try { const result = await axios.get('https://www.zerocho.com/api/get'); console.log(result); console.log(result.data); // {} } catch (error) { console.error(error); } })(); </script> ```
-
POST 요청하는 코드 (데이터를 담아 서버로 보내는 경우)
- 두 번째 인수로 데이터를 넣어 보냄
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> (async () => { try { const result = await axios.post('https://www.zerocho.com/api/post/json', { name: 'zerocho', birth: 1994, }); console.log(result); console.log(result.data); } catch (error) { console.error(error); } })(); </script>
- 두 번째 인수로 데이터를 넣어 보냄
(2). Form Data
- Axios는 데이터를 전송할 때 form data에 넣어서 보내야 함
<script>
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('name', 'zerocho');
formData.append('item', 'orange');
formData.append('item', 'melon');
formData.has('item'); // true
formData.has('money'); // false;
formData.get('item');// orange
formData.getAll('item'); // ['orange', 'melon'];
formData.append('test', ['hi', 'zero']);
formData.get('test'); // hi, zero
formData.delete('test');
formData.get('test'); // null
formData.set('item', 'apple');
formData.getAll('item'); // ['apple'];
</script>-
append로 데이터를 하나 씩 추가
- 이미지도 가능함
-
has 로 데이터 존재 여부 확인
-
get으로 데이터 조회
-
getAll로 데이터 모두 조회
-
delete로 데이터 삭제
-
set으로 데이터 수정
-
FormData POST 요청으로 보내기
- Axios의 data자리에 formData를 넣어서 보내면 됨
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> (async () => { try { const formData = new FormData(); formData.append('name', 'zerocho'); formData.append('birth', 1994); const result = await axios.post('https://www.zerocho.com/api/post/formdata', formData); console.log(result); console.log(result.data); } catch (error) { console.error(error); } })(); </script>
- Axios의 data자리에 formData를 넣어서 보내면 됨
(3). encodeURIComponent, decodeURIComponent
- 가끔 주소 창에 한글 입력하면 서버가 처리하지 못하는 경우 발생 ⇒
encodeURIComponent로 한글 감싸서 처리 (URL아니고 URI )-
url : 서버에 있는 파일 위치
-
uri : 서버에 있는 자원의 위치 (요즘 이걸 더 많이 씀)
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script> <script> (async () => { try { const result = await axios.get(`https://www.zerocho.com/api/search/${encodeURIComponent('노드')}`); console.log(result); console.log(result.data); // {} } catch (error) { console.error(error); } })(); </script>
-
(4). data attribute와 dataset
- HTML 태그에 데이터를 저장하는 방법
- 서버의 데이터를 front-end로 내려줄 때 사용
- 태그 속성으로
data-속성명 - 자바스크립트에서
태그.dataset.속성명으로 접근 가능- data-user-job → dataset.userJob (뒤에는 - 떼고 대문자 됨)
- 반대로 자바스크립트 dataset에 값을 넣으면 data-속성이 생김
<ul> <li data-id="1" data-user-job="programmer">Zero</li> <li data-id="2" data-user-job="designer">Nero</li> <li data-id="3" data-user-job="programmer">Hero</li> <li data-id="4" data-user-job="ceo">Kero</li> </ul> <script> console.log(document.querySelector('li').dataset); // { id: '1', userJob: 'programmer' } </script>- 공개해도 되는 데이터는 html에 간단히 저장 가능!
인프런 Node.js 강의
Zerocho 님의 "Node.js 교과서 - 기본부터 프로젝트 실습까지" 강의를 기반으로 작성한 문서입니다.
