분기한정법
- 되추적 기법과 같이 상태공간트리를 구축하여 최적의 해를 구한다.
- 각 마디를 검색할 때마다 bound(한계값)을 통하여 마디의 유망성을 판단한다.
- bound는 가지로 뻗어나가서(branch) 얻을 수 있는 해답값의 한계를 나타낸다.
0-1 knapsack problem
-
profit : 그 마디에 오기까지 넣었던 아이템의 가치의 합
-
weight : 그 마디에 오기까지 넣었던 아이템 무게의 합
-
bound : 마디가 수준 i에 있다고 할 때, 수준 k에 있는 마디에서 총 무게가 W를 넘는다고 가정하면
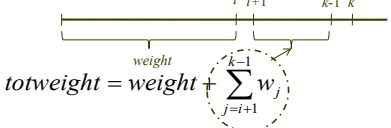

-
maxprofit : 지금까지 찾은 최선의 해답이 주는 가치
-
bound <= maxprofit이면 수준 i에 있는 마디는 유망하지 않다고 판단한다.
-
아이템을 무게당 가치가 큰 것부터 내림차순으로 정렬하여 순서대로 knapsack에 넣는다.
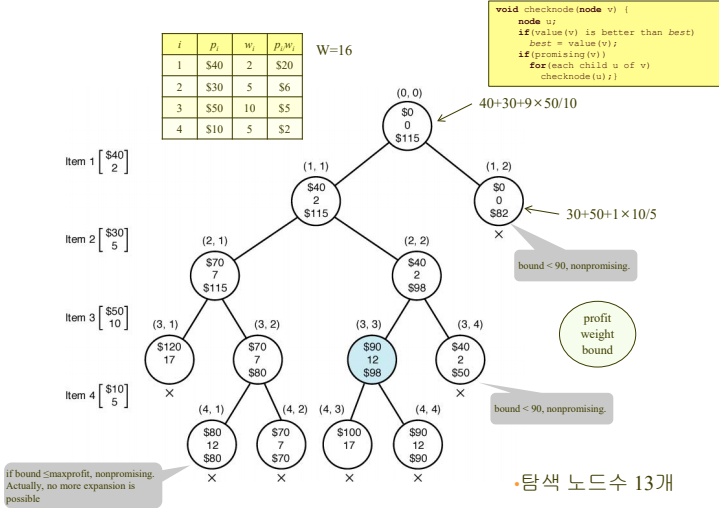
-
트리에서 왼쪽으로 가면 아이템을 넣는 경우, 오른쪽으로 가면 넣지 않는 경우로 계산하여 상태공간트리를 구축하고 profit / weight / maxprofit을 구한다.
depth-first search with branch and bound - pseudo code
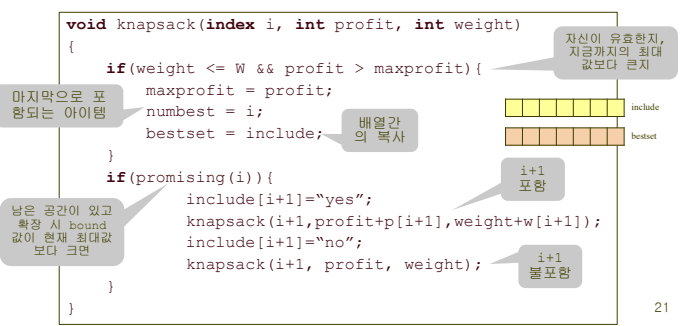
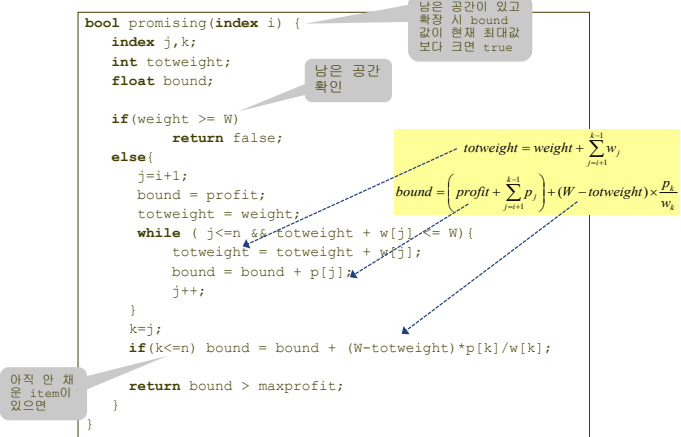
python
def promising(i, weight, profit):
global maxp
if weight > W:
return False
else:
j = i + 1
bound = profit
totweight = weight
while (j < n) and (totweight + w[j] <= W):
totweight = totweight + w[j]
bound += p[j]
j += 1
k = j
if k <= n-1:
bound = bound + (W-totweight) * (p[k] // w[k])
return bound > maxp
def kp(i, profit, weight):
global bestset
global maxp
global num_nodes
num_nodes += 1
if (weight <= W) and (profit > maxp):
maxp = profit
bestset = include[:] # Deep copy
if promising(i, weight, profit):
include[i+1] = 1
kp(i+1, profit + p[i+1], weight + w[i+1])
include[i+1] = 0
kp(i+1, profit, weight)분석
- 이 알고리즘이 점검하는 마디의 수는
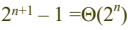
breadth-first search with branch & bound
- 뿌리마디를 먼저 검색하여 다음 수준의 모든 마디를 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 검사한다.
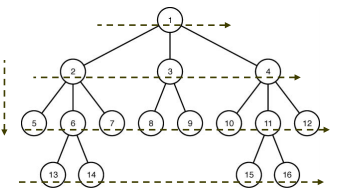
pseudo code
- Queue를 이용하여 구현한다.


python
def promising(u):
if u.bound < maxProfit or u.weight > W:
return False
else:
return True
class Node:
def __init__(self, level, weight, profit, include, bound):
self.level = level
self.weight = weight
self.profit = profit
self.include = include
self.bound = bound
def kp_bfs():
global maxProfit
global bestset
global node_count
global maxqueue
# root node의 값을 할당하고 queue에 삽입합니다.
queuecount = 0
q = queue.Queue()
bound, w, i = 0, 0, 0
# root node의 bound값을 계산합니다.
while w + weight[i] <= W:
w += weight[i]
bound += profit[i]
i += 1
bound += (W - w) * (profit[i] // weight[i])
include = [0] * n
v = Node(0, 0, 0, include, bound)
q.put(v)
maxqueue += 1
queuecount += 1
while not q.empty():
v = q.get()
queuecount -= 1
node_count += 2
# promising하다고 판단된 node가 queue에 들어갑니다.
# maxProfit이 변함에 따라 후에 유망하다고 판단된 node가 유망하지 않다는 판단으로
# 바뀔 수 있기에 유망하다고 판단된 node를 고려하여 promising 조건을 검사하기 전 node 수를 증가시킵니다.
include = v.include[:]
if promising(v):
# -----왼쪽 자식의 bound 계산-----
bound = v.profit
w = v.weight
check_point = 0
# 왼쪽 자식의 무게를 더했을때 W를 넘는다면 유효하지 않기에 bound를 0으로 할당합니다
if w + weight[v.level] > W:
bound = 0
else:
for i in range(v.level, len(bestset)):
if w + weight[i] > W:
check_point = i
break
else:
w += weight[i]
bound += profit[i]
if w != W:
bound += (W - w) * (profit[check_point] // weight[check_point])
# -----왼쪽 자식의 bound 계산-----
# level의 수와 인덱스가 대응하는 요소를 넣은 경우를 가정하여 계산합니다.
u = Node(v.level + 1, v.weight + weight[v.level], v.profit + profit[v.level], include, bound)
u.include[v.level] = 1
if u.weight <= W and u.profit > maxProfit:
maxProfit = u.profit
bestset = u.include[:]
# 값의 변경을 막기 위해 aliasing합니다.
if u.bound > maxProfit:
q.put(u)
queuecount += 1
if queuecount > maxqueue:
maxqueue = queuecount
# -----오른쪽 자식의 bound 계산-----
bound = v.profit
w = v.weight
check_point = 0
include = v.include[:]
temp = v.weight
for i in range(v.level + 1, len(bestset)):
temp += weight[i]
# 앞의 무게가 더해지지 않은 상태에서 남은 무게를 더했을때 W보다 작다면
# 남은 profit을 모두 더하여 bound를 계산합니다.
if temp < W:
for i in range(v.level + 1, len(bestset)):
bound += profit[i]
elif v.level == len(bestset) - 2 and w + weight[v.level + 1] < W:
bound += profit[i]
else:
for i in range(v.level + 1, len(bestset)):
if w + weight[i] > W:
check_point = i
break
else:
w += weight[i]
bound += profit[i]
if w != W:
bound += (W - w) * (profit[check_point] // weight[check_point])
# -----오른쪽 자식의 bound 계산-----
# level의 수와 인덱스가 대응하는 요소를 넣지 않은 경우를 가정하여 계산합니다.
u = Node(v.level + 1, v.weight, v.profit, include, bound)
u.include[v.level] = 0
if u.bound > maxProfit:
q.put(u)
queuecount += 1
if queuecount > maxqueue:
maxqueue = queuecountbest-first search
- 주어진 마디의 모든 자식마디를 검색한 후 유망하면서 확장되지 않은 마디를 살펴보고 그 중 가장 좋은 bound를 가진 마디로 확장한다.
- 최고 한계를 가진 마디를 우선적으로 선택하기 위해서 priority-queue를 사용한다.
- heap 구조를 통하여 구현할 수 있다.
pseudo code

python
class Node2:
def __init__(self, level, weight, profit, bound, include):
self.level = level
self.weight = weight
self.profit = profit
self.bound = bound
self.include = include
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.bound < other.bound
def kp_Best_FS():
global maxProfit2
global bestset2
# root node를 생성하고 priority queue에 삽입합니다.
pq = queue.PriorityQueue()
temp = n * [0]
v = Node2(0, 0, 0, 0, temp)
v.bound = compBound(v)
pq.put(v)
while not pq.empty():
v = pq.get()
if v.bound < maxProfit2: # 마디가 유망한지 확인합니다.
# level의 수와 인덱스가 대응하는 요소를 넣은 경우를 가정하여 계산합니다.
u = Node2(v.level + 1, v.weight + weight[v.level], v.profit + profit[v.level], 0, temp)
u.include = v.include[:]
u.include[v.level] = 1
u.bound = compBound(u)
if u.weight <= W and u.profit > maxProfit2:
maxProfit2 = - u.profit # bound와의 비교 연산을 위하여 부호를 바꾸어 할당합니다.
bestset2 = u.include[:]
if u.bound < maxProfit2:
pq.put(u)
# level의 수와 인덱스가 대응하는 요소를 넣지 않은 경우를 가정하여 계산합니다.
u = Node(v.level + 1, v.weight, v.profit, 0, temp)
u.include = v.include[:]
u.bound = compBound(u)
if u.bound < maxProfit2:
pq.put(u)
maxProfit2 *= -1 # minheap계산을 위해 bound값을 계산할 때 부호를 바꾸었기 때문에 결과 출력을 위해 다시 부호를 바꿉니다.
def compBound(u): # bound를 계산합니다.
if u.weight >= W:
return 0
else:
result = u.profit
j = u.level + 1
totweight = u.weight
while j < n and totweight + weight[j] <= W:
totweight += weight[j]
result += profit[j]
j += 1
k = j
if k < n:
result += (W-totweight) * (profit[k] // weight[k])
return -result # minheap이므로 부호를 바꾸어서 처리합니다.
