❗️ Arguments vs Rest ❗️
let restFunction = function (...rest) {
console.log(arguments);
console.log(rest)
};
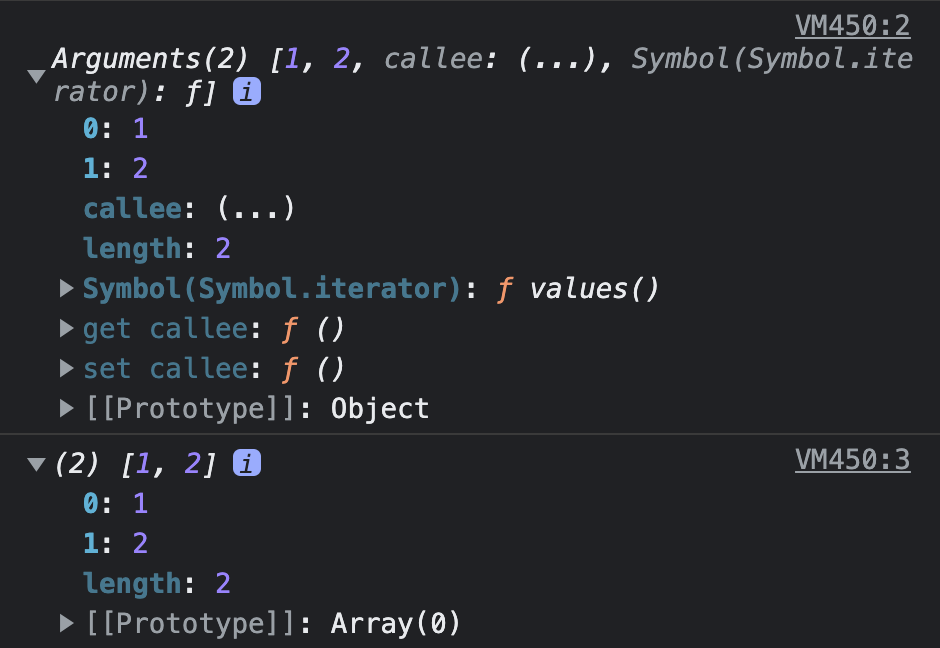
restFunction(1, 2); 🤔 arguments와 rest파라미터의 차이점은 무엇일까?
arguments는 유사 배열 객체고 rest는 배열이다.
유사 배열 객체(array-like object)는 간단하게 순회가능한(iterable) 특징이 있고 length 값을 알 수 있는 특징이 있는 것이다.
즉, 배열처럼 사용할 수 있는 객체를 말한다. 하지만, arguments는 유사배열객체이기 때문에 Array 오브젝트의 메서드를 사용할 수 없다.
반면, rest는 배열이기 때문에 Array 오브젝트의 메서드를 사용할 수 있다.
✨ Spread 연산자 (Spread Operator)
연산자의 대상 배열 또는 이터러블(iterable)을
개별 요소로 분리한다.
// 배열
console.log(...[1, 2, 3]); // -> 1, 2, 3
// 문자열
console.log(...'AvenJS'); // A, v, e, n, J, S
// Map과 Set
console.log(...new Map([['a', '1'], ['b', '2']])); // [ 'a', '1' ] [ 'b', '2' ]
console.log(...new Set([1, 2, 3])); // 1 2 3let restFunction = function (num1, num2) {
console.log(num1); // 1
console.log(num2); // 2
};
const numbers = [1,2];
restFunction(...numbers); ❗️ Spread vs Rest ❗️
//Rest
function restFunction(param, ...rest) {
console.log(param); // 1
console.log(rest); // [ 2, 3 ]
}
restFunction(1, 2, 3);
//Spread호출
function spreadFunction(x, y, z) {
console.log(x); // 1
console.log(y); // 2
console.log(z); // 3
}
spreadFunction(...[1, 2, 3]);-
함수 선언문의 파라미터에 Spread(...)연산자를 이용해서 받으면
👉 가변인자를 받아배열로 만들어서 사용하는 것 -
함수 호출문의 파라미터에 Spread(...)연산자를 이용해서 호출하면
👉 배열이 해당 매개변수로각각 매핑되는 것
