1. Coroutine(코루틴)
코루틴(Coroutine)은 작업을 다수의 프레임에 분산하여 처리하는 동기식 작업이다. 실행을 일시정지하고 중단한 부분부터 재개하여 처리하는 것으로 작업을 분산처리한다. 또한 코루틴은 스레드가 아니며 코루틴의 작업은 메인 스레드에서 실행한다.
[SerializeField] Rigidbody rb;
[SerializeField] float jumpPower;
private Coroutine countDownCoroutine;
private void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space))
{
countDownCoroutine = StartCoroutine(Routine());
}
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Escape))
{
StopCoroutine(countDownCoroutine);
}
}
IEnumerator Routine()
{
Debug.Log("5");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);
Debug.Log("4");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);
Debug.Log("3");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);
Debug.Log("2");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);
Debug.Log("1");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);
rb.AddForce(Vector3.up * jumpPower, ForceMode.Impulse);
}if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space))
{
StartCoroutine(Routine()); // X
}
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Escape))
{
StopCoroutine(Routine()); // X
}문법 주의 사항: 위처럼 루틴 자체를 시작 및 정지하는 것이 아닌, countDownCoroutine에게 시작 및 중지를 해야한다.
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space))
{
if (countDownCoroutine == null)
{
countDownCoroutine = StartCoroutine(Routine());
}
}위와 같이 사용하면 코루틴을 하나만 만들 수 있다. 그러나 추가적인 할당 해제가 없으면 한 번 실행된 이후 다시 실행되지 않는다.
IEnumerator Routine()
{
//...
countDownCoroutine = null;
}따라서 위와 같이 할당 해제를 해야한다
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Escape))
{
StopCoroutine(countDownCoroutine);
}또한 시작한 것을 검사하지 않고 StopCoroutine()을 호출 시 null을 호출하게 된다. 따라서 != null일 때 호출하게 해야한다.
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Escape))
{
if (countDownCoroutine != null)
{
StopCoroutine(countDownCoroutine);
countDownCoroutine = null;
}
}IEnumerator Routine()
{
Debug.Log("5");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);
Debug.Log("4");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);
Debug.Log("3");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);
Debug.Log("2");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);
Debug.Log("1");
yield return new WaitForSeconds(1f);위 상황에서 new WaitForSeconds 또한 생성을 반복하게 되는 것이다.
IEnumerator Routine()
{
WaitForSeconds delay = new WaitForSeconds(1f); // 횟수가 아주 많으면 클래스의 필드로 이동
Debug.Log("5");
yield return delay;따라서 자주 사용되는 내용은 필드에서 캐싱해두어 객체를 재사용하는 것이 좋다.
Coroutine은 Update()와 병렬로 실행되는 것이 아니다.
겉보기에는 병렬적으로 실행되는 것처럼 보일 수 있지만, 실제로는 싱글 스레드 환경에서 Update()와 마찬가지로 순차적으로 실행된다.
즉, 코루틴은 메인 스레드 안에서 실행 흐름을 일정 시점마다 나누어 처리하는 방식일 뿐, 실제 병렬 처리는 아니다.
2. UnityAction, UnityEvent
1. Unity Event
Unity Action, Unity Event 은 기존의 Delegate, Event와 별 다른 차이가 있는 것이 아닌 직렬화를 통해 유니티에서 쉽게 다룰 수 있도록 기능이 제공되는 차이가 있다.
기존에는 += 연산자, -= 연산자를 통해 추가 및 제거가 가능했었지만 유니티 이벤트에서는 메서드를 에디터 상에서 추가 및 제거가 가능하다.
public UnityEvent myEvent;
private void Update()
{
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.A))
{
myEvent.Invoke();
}
}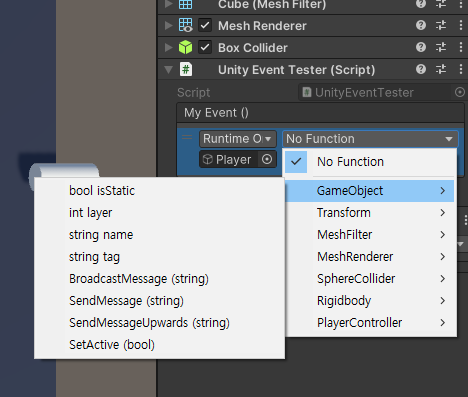
게임오브젝트를 연결하면 관련 메서드들을 선택할 수 있다.
- 주의 사항
유니티이벤트는 델리게이트를 이용한 클래스. 따라서 델리게이트 그 자체가 아니다.
엄연히 클래스이기 때문에 함수를 추가할 때+=,-=대신.AddListener()를 쓰고, 뺄 때는.RemoveListener()를 사용해서 연결 및 해제한다.
myEvent.Invoke()는 지원하지만 myEvent();는 지원하지 않는다.
+=, -= 연산자 또한 지원하지 않는다.
UnityEvent는 C#과 동일하게 UnityEvent<int, float> 매개변수를 넣을 수도 있다.
- Event와의 차이점
C#과 동일하게UnityEvent또한 소스코드에선 매개변수가 다르면 못넣는다.
그러나 UnityEvent에서는 매개변수가 달라도 에디터 상에서는 붙일 수 있다.
예를 들면 이벤트는 매개변수가 없지만 연결된 함수는 float 매개변수를 가질 때, 에디터에서 지정할 수 있다.

Dynamic float - 넘겨주는 매개변수 값을 그대로 주기
Static parameters - 에디터에서 값 넣기
2. UnityAction
public event UnityAction OnDied; // UnityAction
public event Action myDelegate; // ActionUnityAction, Action 은 아예 똑같은 기능이다. 예전 유니티 버전에서는 java 등 여러 언어를 지원했었는데 이 때 Delegate가 없는 언어가 있어서 만들어 두었던 것이 남아있다.
