[논문리뷰] LightGCN: Simplifying and Powering Graph Convolution Network for Recommendation (2020)
RecSys
세 줄 요약
- collaborative filtering의 성능을 저하시키는 기존 GCN 구조 (feature transformation, nonlinear activation) 의 단순화를 목적으로 함
- neighborhood aggregation과 같은 주 요소만 포함한 LightGCN을 제안
- SOTA GCN-based recommender 보다 향상된 결과를 보임
Problem definition
- GCN은 node feature가 풍부한 그래프의 node classification 태스크에 주로 이용되는 방법론
- 하지만, CF를 위한 user-item interaction graph에서 각 node는 ID embedding으로 이루어짐 (no concrete semantic)
- 따라서, GCN의 feature transformation 과 nonlinear activation은 Neural Graph Collaborative Filtering (NGCF)에 거의 기여하는 바가 없음
Solution
- LightGCN은 GCN의 가장 중요한 요소인 neighborhood aggregation 만을 포함하도록 함
Empirical Explorations on NGCF
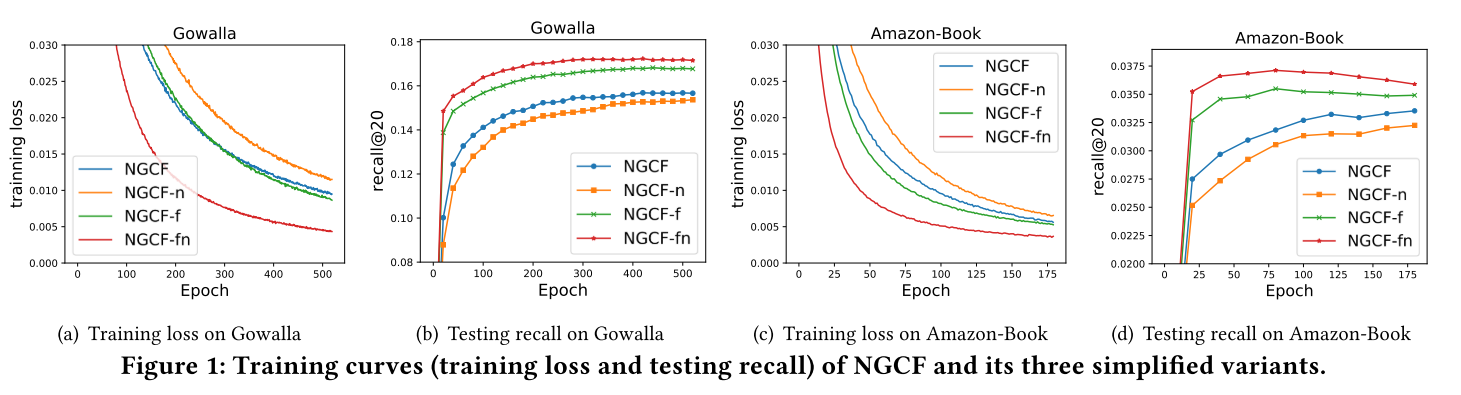
- NGCF-f(removes feature transformation)
- NGCF-n(removes non-linear activation function)
Finding
(1) Feature transformation imposes negative effect on NGCF
(2) Nonlinear activation affects slightly
(3) Removing them simultaneously improves largely (9.57% relative improvement on recall)
-> Deterioration of NGCF stems from the training difficulty, rather than overfitting
LightGCN
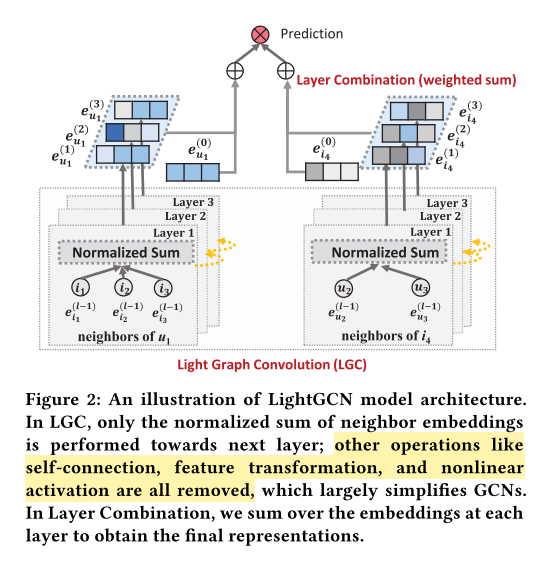
GCN에서 item or user embedding의 기본은 아래와 같음
여기서 self-connction, feature transformation, nonlinear activation을 제거함
따라서, LightGCN에서는 neighborhood aggregation은 아래와 같음
Aggregation이 단순 합이므로, trainable model parameter는 0-th layer, 과 에만 존재한다.
Final representation을 얻기 위해서 개의 layer를 합하는 layer combination을 수행하는데 이는 아래 수식과 같다.
이때 hyperparameter로 지정하는 는 k-th layer embedding의 importance이다.
본 논문에서는 layer마다 동일하게 로 설정하는 것이 전반적으로 좋은 성능을 냈다고 한다.
layer combination을 수행한 이유로는 아래의 세 가지 이유를 든다.
(1) 레이어의 수가 증가할수록 over-smoothing되는 문제를 해결하기 위해
(2) 각 레이어의 embedding이 다른 semantic을 포착하기 때문
(3) weighted sum을 이용한 layer combination이 self-connection의 효과를 내기 때문 (uniform한 alpha를 사용한다면서..)
마지막으로 model prediction을 위해 user와 item의 inner product를 수행해 recommendation을 위한 ranking score를 구한다.
이러한 과정을 matrix form으로 나타내면 아래와 같다.
user-item interaction matrix 에 대해
embedding size 에 대해
symmetrically normalized matrix 에 대해
따라서,
