더 좋은 문제 풀이가 있거나 궁금하신 점이 있다면 편하게 댓글 남겨주세요!
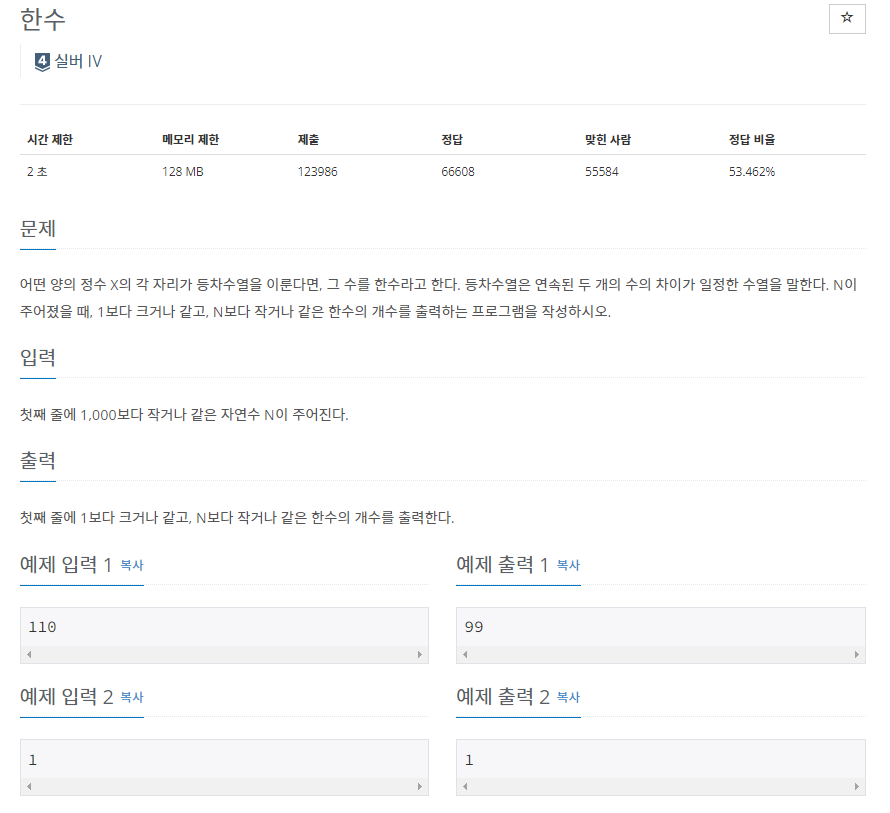
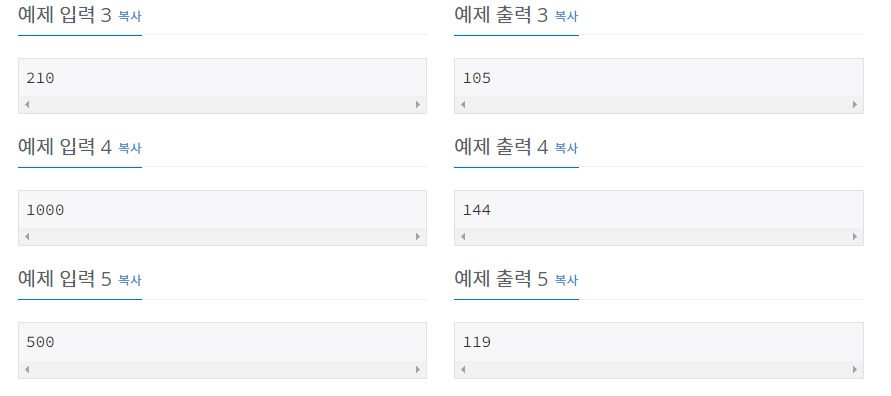
📝 문제
🤷♂️ 접근 방법
이번 문제는 등차수열을 판별하여 등차수열의 개수를 세는 문제입니다. 등차수열은 "연속하는 두 항의 차이가 모두 일정한 수열을 뜻한다." 라고 정의되어 있습니다.
즉, 수열이 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 ... 일 때 (1-3) = (3-5) = (5-7) = (7-9) 와 같이 두 항의 차이가 2로 일정한 수열을 등차수열이라고 합니다.
또한, 1-99까지는 무조건 모든 수가 같은 차이를 가지는 등비수열이라고 할 수 있습니다. 그러므로 아래의 코드와 같이 자연수 N을 입력받았을 때 99이하인 경우 한수의 개수를 N으로 설정해도 무방합니다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String arg[]){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int result = arithmetic_sequence(N);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int arithmetic_sequence(int N){
int cnt = 0 ; // 한수의 수
if(N < 100 ) return N;
else{
// N 이 100 이상일 때
}
}
}다음으로 N이 100 이상일 때는 각 자리수를 나누어 등비수열인지 판별해야 합니다. 각자리 숫자를 나누고 나눈 숫자들의 차가 같은지 확인합니다.
public static int arithmetic_sequence(int N){
int cnt = 0 ; // 한수의 수
if(N < 100 ) return N;
else{
cnt = 99;
for(int i = 100; i <= N; i++){
int num1 = i / 100;
int num2 = (i / 10) % 10;
int num3 = i % 10;
if((num1 - num2) == (num2 -num3)) cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
✍ 풀이
방법 1
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String arg[]){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int result = arithmetic_sequence(N);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static int arithmetic_sequence(int N){
int cnt = 0 ; // 한수의 수
if(N < 100 ) return N;
else{
cnt = 99;
for(int i = 100; i <= N; i++){
int num1 = i / 100;
int num2 = (i / 10) % 10;
int num3 = i % 10;
if((num1 - num2) == (num2 -num3)) cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
}
방법 2
[백준] 1065번 : 한수 - Java(자바) 의 코드를 참고하였고, 본 코드에서 99이하의 num을 count 하는 부분만 연산이 간편하게 변경하였습니다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String arg[]){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
int count = 0;
if(num <=99) count = num;
else{
for (int i = 100; i <= num; i++) {
count =99;
if (i <= 999) {
String[] num_str = Integer.toString(i).split("");
if ((Integer.parseInt(num_str[1]) - Integer.parseInt(num_str[0])) == (Integer.parseInt(num_str[2])- Integer.parseInt(num_str[1]))) count += 1;
}
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
방법2에서 num_str 배열을 선언하는 부분이 새로워 코드를 가져와 보았습니다.
String[] num_str = Integer.toString(i).split(""); // String [] num_str = {"1" , "0" , "0"} 와 같음잘 이해가 되지 않는다면 Java 배열 정리 를 참고하면 좋습니다.