문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/9465
풀이
이 문제는 대각선 계산을 이용하면 된다.
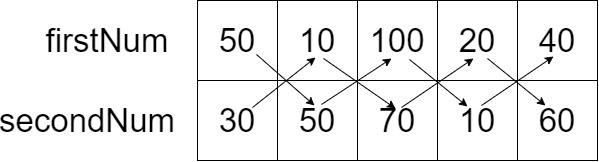
하지만 이 방법을 이용했을때 문제가 하나 발생하는데, 대각선이 아니라 한 칸 더 앞선 대각선의 경우가 값이 더 클때가 있다.
예를 들어 위의 경우 50, 50, 100, 60 의 합인 260이 최댓값이다.
.jpg)
그러므로 대각선 더하기를 고려할때 대각선 값과 다음 대각선값을 비교하여 해결하는 방향을 생각했다. 참고로 3번째 대각선의 경우는 아래 그림과 같다.
.jpg)
그림과 같이 그 다음부터는 이전 대각선들의 합이 더 클수밖에 없기 때문에 신경쓰지 않아도 된다.
이를 구현하기 위해 최대값을 나열할 배열을 생성하였다.
.jpg)
result 배열은 왼쪽 아래의 result값과 왼쪽왼쪽 아래의 result값을 비교하여 더 큰 쪽을 고르고 그 값과 firstNum 또는 secondNum 값을 더하는 구조이다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Num9465 {
public static int T;
public static int N[];
public static int firstNum[][];
public static int secondNum[][];
public static int result[][];
public static void main(String[] args) {
//input
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
T = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
N = new int[T];
firstNum = new int[T][1000001];
secondNum = new int[T][1000001];
for (int i=0; i<T; i++) {
N[i] = Integer.parseInt(scanner.nextLine());
String[] a = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
for (int j=1; j <= N[i]; j++) {
firstNum[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(a[j - 1]);
}
a = scanner.nextLine().split(" ");
for (int j=1; j <= N[i]; j++) {
secondNum[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(a[j - 1]);
}
}
//logic
for (int i=0; i<T; i++) {
result = new int[2][1000001];
result[0][0] = 0;
result[1][0] = 0;
result[0][1] = firstNum[i][1];
result[1][1] = secondNum[i][1];
for (int j=2; j <= N[i]; j++) {
result[0][j] = Math.max(result[1][j - 1], result[1][j - 2]) + firstNum[i][j];
result[1][j] += Math.max(result[0][j - 1], result[0][j - 2]) + secondNum[i][j];
}
int max = 0;
for (int j=0; j <= N[i]; j++) {
max = Math.max(max, result[1][j]);
max = Math.max(max, result[0][j]);
}
System.out.println(max);
}
//output
}
}
