Writing different types of data to the XLSX File
from datetime import datetime
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('Expenses03.xlsx')
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
bold = workbook.add_format({'bold': True})
money = workbook.add_format({'num_format': '$#,##0'})
date_format = workbook.add_format({'num_format': 'mmmm, d, yyyy'})
worksheet.set_column(1, 1, 15)
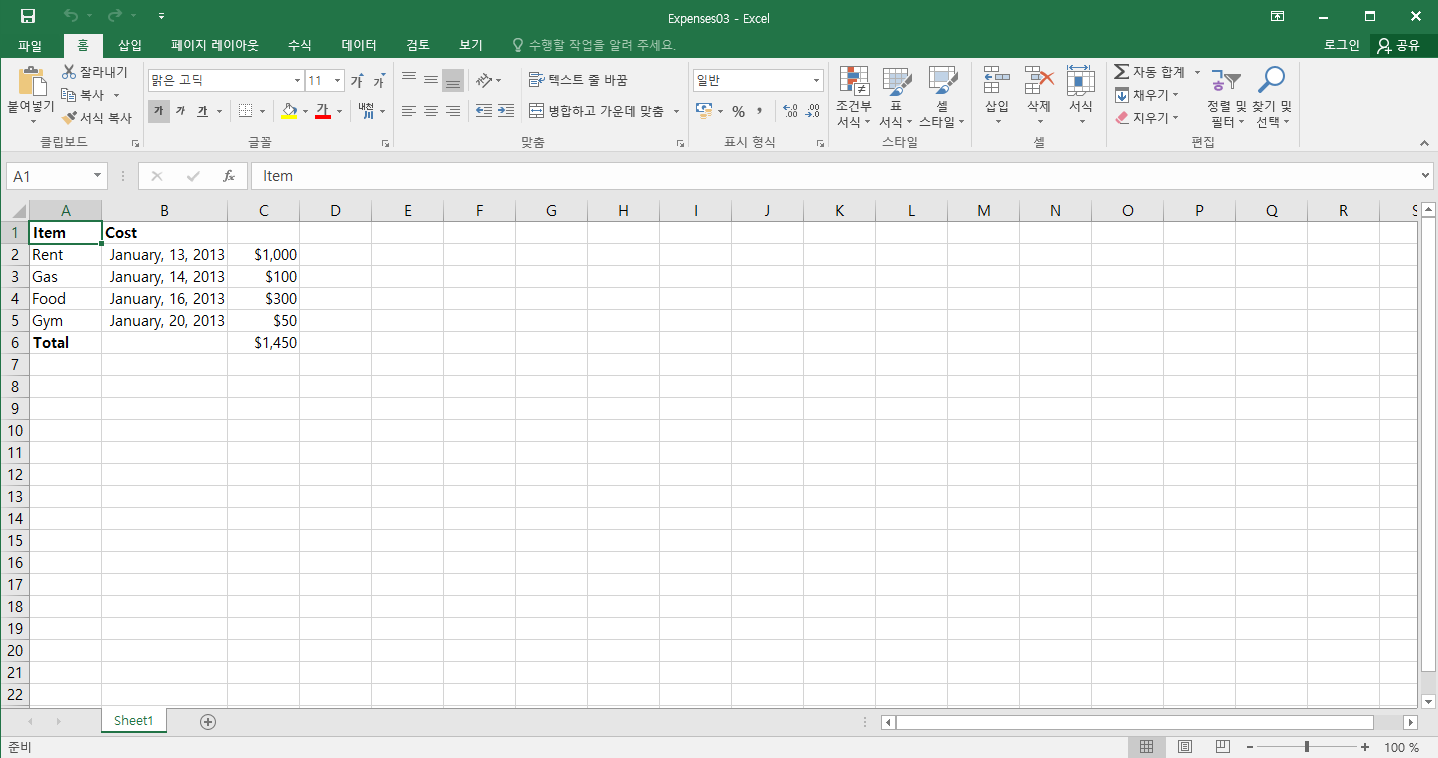
worksheet.write('A1', 'Item', bold)
worksheet.write('B1', 'Cost', bold)
expenses = (
['Rent', '2013-01-13', 1000],
['Gas', '2013-01-14', 100],
['Food', '2013-01-16', 300],
['Gym', '2013-01-20', 50]
)
row = 1
col = 0
for item, date_str, cost in expenses:
date = datetime.strptime(date_str, '%Y-%m-%d')
worksheet.write(row, col, item)
worksheet.write(row, col + 1, date, date_format)
worksheet.write(row, col + 2, cost, money)
row += 1
worksheet.write(row, 0, 'Total', bold)
worksheet.write(row, 2, '=SUM(C2:C5)', money)
workbook.close()
Note
from datetime import datetime
...
date_format = workbook.add_format({'num_format': 'mmmm d yyyy'})
...
for item, date_str, cost in (expenses):
date = datetime.strptime(date_str, "%Y-%m-%d")
...
worksheet.write_datetime(row, col + 1, date, date_format )
...
worksheet.set_column('B:B', 15)

