thread
#define THREAD_MAGIC 0xcd6abf4b
stack overflow를 방지한다.
4 kB +---------------------------------+
| kernel stack |
| | |
| | |
| V |
| grows downward |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
sizeof (struct thread) +---------------------------------+
| magic |
| intr_frame |
| : |
| : |
| status |
| tid |
0 kB +---------------------------------+thread 구조체
struct thread {
/* Owned by thread.c. */
tid_t tid; /* Thread identifier. */
enum thread_status status; /* Thread state. */
char name[16]; /* Name (for debugging purposes). */
int priority; /* Priority. */
/* Shared between thread.c and synch.c. */
struct list_elem elem; /* List element. */
#ifdef USERPROG
/* Owned by userprog/process.c. */
uint64_t *pml4; /* Page map level 4 */
#endif
#ifdef VM
/* Table for whole virtual memory owned by thread. */
struct supplemental_page_table spt;
#endif
/* Owned by thread.c. */
struct intr_frame tf; /* Information for switching */
unsigned magic; /* Detects stack overflow. */
};thread_status는 상태이다.
enum thread_status {
THREAD_RUNNING, /* Running thread. */
THREAD_READY, /* Not running but ready to run. */
THREAD_BLOCKED, /* Waiting for an event to trigger. */
THREAD_DYING /* About to be destroyed. */
};다음과 같이 정의되는데 thread의 life cycle과 매칭해보자면 이러하다.
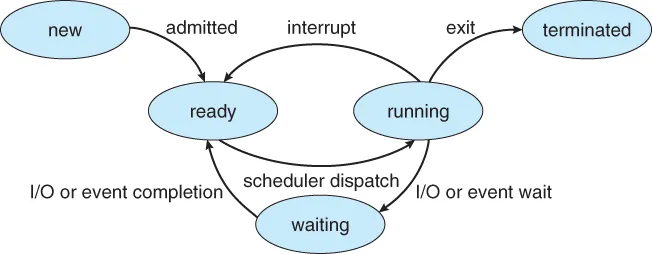
- THREAD_RUNNING == running
- THREAD_READY == ready
- THREAD_BLOCKED == waiting
- THREAD_DYING == terminated
thread의 life cycle을 칭하는 명칭이 주석과 enum이 달라서 약간의 혼동이 올 수 있으니, 이를 꼭 기억하자.
위의 thread 구조체는 아무 쓰레드도 없는 상태, 즉 idle 상태에도 idle_thread 를 둔다. 그리고 최초의 쓰레드의 초기화 initail_thread 를 둔다.
thread 관련 함수
extern bool thread_mlfqs;
void thread_init (void);
void thread_start (void);
void thread_tick (void);
void thread_print_stats (void);
typedef void thread_func (void *aux);
tid_t thread_create (const char *name, int priority, thread_func *, void *);
void thread_block (void);
void thread_unblock (struct thread *);
struct thread *thread_current (void);
tid_t thread_tid (void);
const char *thread_name (void);
void thread_exit (void) NO_RETURN;
void thread_yield (void);
int thread_get_priority (void);
void thread_set_priority (int);
int thread_get_nice (void);
void thread_set_nice (int);
int thread_get_recent_cpu (void);
int thread_get_load_avg (void);
void do_iret (struct intr_frame *tf);하나씩 간단하게 짚고 넘어가자.
thread_init
쓰레드 초기화 - 쓰레드 구조체, 쓰레드 이름, 우선순위를 인자로 받아 초기화한다.thread_start
최초에는 idle 상태로 *쓰레드를 생성하고, semaphore도 초기화해준다.
※ thread_create를 통해 쓰레드 이름, 우선순위, 실행 함수(rdi), 세마포어 주소(rsi)를 인자로 생성한다.thread_tick
아래에서 자세히 알아보자.thread_print_stats
현재 쓰레드의 상태를 출력한다.thread_create
새로운 쓰레드를 생성하여 메모리에 할당한다. 새로운 쓰레드에서 실행할 프로그램과 인자를 받고ready상태로 대기시킨다.thread_block
현재 running 중인 쓰레드를 sleep(=blocked, wait) 상태로 변경하고, 그 다음 쓰레드를 사용하겠다는 신호이다. 다음 대기열 쓰레드에게 running 상태를 부여한다.(schedule())thread_unblock
인자로 받은 쓰레드를 blocked thread(대기열 쓰레드)상태에서 ready 상태로 만들어준다.thread_current
현재 수행 중인 쓰레드를 반환한다.thread_tid
현재 쓰레드의 고유 식별자를 반환한다.thread_exit
쓰레드를 종료한고 소멸시킨다.thread_yield
현재 실행 중인 쓰레드를 ready_list 끝으로 보낸다.
나머지는 priority, nice 관련으로 advanced 과제에서 필요한 것 같다.
여기에서 thread_tick은 도무지 뭐하는 함수인지 모르겠어서 얘만 우선 보고 넘어가자.
thread_tick()
/* Called by the timer interrupt handler at each timer tick.
Thus, this function runs in an external interrupt context. */
void thread_tick(void)
{
struct thread *t = thread_current();
/* Update statistics. */
if (t == idle_thread)
idle_ticks++;
#ifdef USERPROG
else if (t->pml4 != NULL)
user_ticks++;
#endif
else
kernel_ticks++;
/* Enforce preemption. */
if (++thread_ticks >= TIME_SLICE)
intr_yield_on_return();
}이 부분의 주석 설명이 이해가 안 되어서 좀 더 알아보니까,
타이머 인터럽트라는 것을 알아야겠더라.
tick?
컴퓨터 시스템에서 시간의 기본 단위로, 특정 시간 간격마다 발생되는 타이머 인터럽트를 의미한다.
커널이 시간 간격을 추적하는 방법이다.
다시 코드로 돌아가서, 그러면 이 thread_tick은 왜 있는 거지?
매 타이머 틱마다 타이머 인터럽트 핸들러에 의해 호출되는 함수로, 외부 인터럽트 컨텍스트에서 실행된다고 한다.
코드를 보면 현재 작업 중인 쓰레드가 뭔지 확인하고 해당하는 tick을 증가시킨다. 즉, 커널 입장에서 이 프로세스가 얼마만큼의 시간동안 CPU 자원을 점유하고 있는 지를 추적하는 것이다. 만약, 쓰레드가 점유한 시간이 개발자가 지정한 TIEM_SLICE보다 길어지면, 다른 쓰레드로 제어권을 넘겨주는 함수인 것 같다.
lock
lock 구조체
/* Lock. */
struct lock {
struct thread *holder; /* Thread holding lock (for debugging). */
struct semaphore semaphore; /* Binary semaphore controlling access. */
};lock을 가지고 있는 thread 정보와 이진세마포어 정보가 포함된다.
semaphore
semaphore 구조체
/* A counting semaphore. */
struct semaphore {
unsigned value; /* Current value. */
struct list waiters; /* List of waiting threads. */
};semaphore 구조체는 이진 세마포어 뿐 아니라, 카운팅 세마포어도 가능하도록 구현되어있는 것으로 보인다.
- value 자원의 개수
- waiters 대기열
semaphore 관련 함수
void sema_init (struct semaphore *, unsigned value);
void sema_down (struct semaphore *);
bool sema_try_down (struct semaphore *);
void sema_up (struct semaphore *);
void sema_self_test (void);semaphore에 관련된 header 파일이다. sema_down으로 lock을 획득하고, sema_up으로 작업 완료 후 lock을 반환한다.
list
list 구조체
/* List. */
struct list
{
struct list_elem head; /* List head. */
struct list_elem tail; /* List tail. */
};
/* List element. */
struct list_elem
{
struct list_elem *prev; /* Previous list element. */
struct list_elem *next; /* Next list element. */
};Doubly linked list로 구현된 list이다. 이는 커널 디렉터리에 포함되어있고, 공식 문서에서는 이를 잘 이해하기를 권장하고있다.
list head 노드와 tail 노드를 가진 이중 연결 리스트 구조체이다.
list_elem prev 노드와 next 노드를 가진 List 내 하나의 노드 구조체이다.
list 관련 함수
void lock_init (struct lock *);
void lock_acquire (struct lock *);
bool lock_try_acquire (struct lock *);
void lock_release (struct lock *);
bool lock_held_by_current_thread (const struct lock *);lock_acquire로 lock을 획득하고, lock_release 로 lock을 반환한다.
condition(Monitor)
condition 구조체
/* Condition variable. */
struct condition {
struct list waiters; /* List of waiting threads. */
};waiting threads가 담기는 Doubly Linked List 구조의 waiters이다.
(흠 공부했던 이론이랑 좀 .. 매칭이 안 되는데 나중에 사용되는 것을 보면 이해되겠지?)
그니까, 생산자-소비자 문제라고 가정한다면, 생산자 waiting threads와 소비자 waiting threads를 별도로 두는 것 같다.
condition 관련 함수
void cond_init (struct condition *);
void cond_wait (struct condition *, struct lock *);
void cond_signal (struct condition *, struct lock *);
void cond_broadcast (struct condition *, struct lock *);condition 초기화, condition 대기, condition 실행, condition broadcast
흠,, 얘네는 어떨 때 쓰이는 걸까? semaphore의 업그레이드 버전인 거 같다.
