해커톤 프로덕트로 개발 중이던 웹앱에 Firebase 실시간 데이터베이스에서 불러온 상점 데이터를 목록으로 보여주는 기능이 필요했다.
그런데 한번에 불러올 수 있는 데이터 양이나 횟수에 제한이 있는지, 상점 개수가 너무 많으면 GET 에러가 나면서 불러오는 데 실패했다.
그때 인터넷프로그래밍 수업에서 배운 무한스크롤이 떠올랐다. 라이브러리를 찾아서 적용해보려다가 원하는 대로 동작이 잘 안 돼서 그냥 직접 구현해보기로 했다.
🙄 무한스크롤이란
사용자가 페이지 하단에 도달했을 때, 콘텐츠가 계속 로드되는 방식을 무한스크롤이라고 한다. 원리는 간단하다.
- 목록의 일부만 렌더링한다.
- 사용자가 목록의 끝까지 스크롤하면 아이템을 추가로 렌더링한다.
- 목록의 아이템이 전부 렌더링될 때까지 반복한다.
🔨 구현
🧱 스크롤 감지
우선 사용자가 스크롤바를 끝까지 내렸을 때 이를 감지하는 코드가 필요하다. 사용자가 페이지 하단에 도달했는지 확인하는 가장 간단한 방법은 해당 요소의 clientHeight, scrollHeight, scrollTop을 확인하는 것이다.
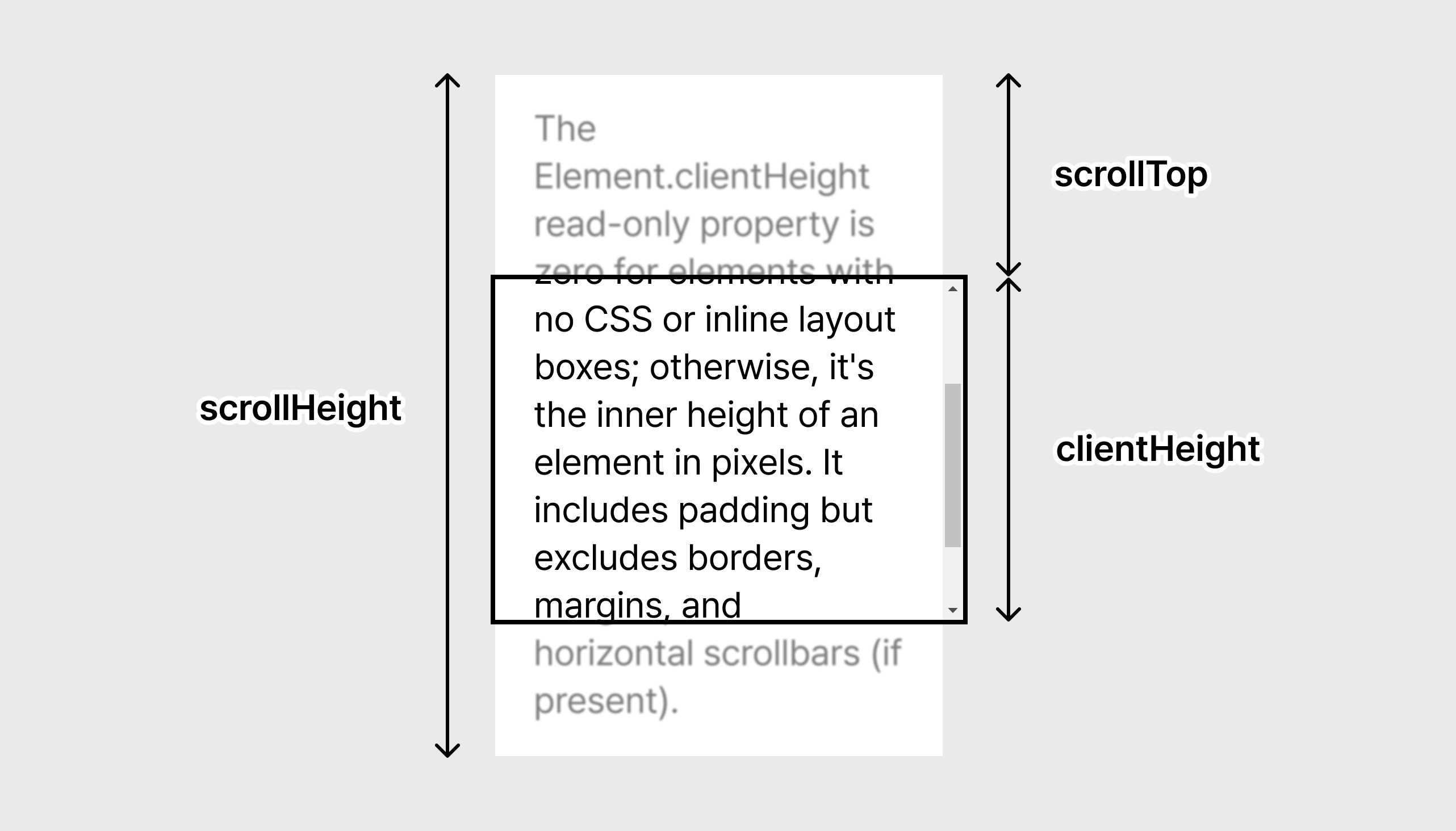
-
clientHeight: 요소의 내부 높이 (padding 포함, border, margin, scroll bar 미포함) -
scrollHeight: overflow로 보이지 않는 부분까지 포함한 요소의 content 전체 높이 -
scrollTop: 요소의 content가 수직 방향으로 얼마나 스크롤되었는지 나타내는 값
👉 clientHeight + scrollTop >= scrollHeight일 때 사용자가 스크롤을 끝까지 내렸다고 볼 수 있다.
목록 컴포넌트에 해당하는 DOM 요소에 스크롤 이벤트 리스너를 등록하고, 위 방법으로 목록 끝까지 스크롤됐을 때 다음 아이템들을 추가로 렌더링해주면 된다!
🧱 useRef로 DOM에 접근
React의 useRef를 이용해 DOM에 접근하고 조작할 수 있다. ref 객체를 만든 뒤 접근하려는 DOM 요소의 JSX에 ref 속성으로 넣어주면 된다.
function InfiniteScroll() {
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
// ...
return <div ref={scrollRef} />;
}이 방법으로 DOM 요소에 스크롤 이벤트 리스너를 등록하고 clientHeight, scrollHeight, scrollTop 값을 가져올 수 있다.
scrollRef.current.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);const { clientHeight, scrollHeight, scrollTop } = scrollRef.current;이렇게 해서 완성된 코드는 대충 아래와 같다.
🏠 전체 코드
function InfiniteScroll({ allItems }) {
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const [items, setItems] = useState([]);
const itemsPerLoad = 10;
useEffect(() => {
// 처음 10개 렌더링
if (items.length <= 0) loadItems();
// 스크롤 감지
const handleScroll = () => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
const { clientHeight, scrollHeight, scrollTop } = scrollRef.current;
if (clientHeight + scrollTop >= scrollHeight) {
loadItems();
}
}
};
// 이벤트 리스너 등록
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
}
// 컴포넌트가 DOM에서 제거될 때 이벤트 리스너 삭제
return () => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
}
};
}, []);
// 현재 목록에 다음 아이템 추가
const loadItems = () => {
var newItems = allItems.slice(0, Math.min(items.length + itemsPerLoad, allItems.length));
setItems(newItems);
};
return (
<div ref={scrollRef}>
{items.map((item, index) => <Item key={index} data={item} />)}
</div>
);
}사실 이 코드는 현재 깃허브에 올라가있는 최종 코드와는 좀 다르다. 어째서인지 지금은 이게 문제없이 잘 돌아가는 것 같지만... 당시에는 몇 가지 오류가 있어서 한참을 뜯어고쳤었다. 크게 2가지 이슈가 있었는데, 이것도 간단히 기록해놓자.
❗ items가 업데이트되지 않는다
맨 처음에는 대충 위와 비슷하게 구현했었는데 스크롤이 페이지 하단에 도달했음에도 새 아이템들이 추가되지 않는 문제가 있었다. 정확히는 setItems(newItems)이 실행된 후에도 화면의 목록에는 새 아이템들이 보이지 않고, 콘솔을 찍어봐도 items 값이 그대로였다.
원인을 알 수 없어서 며칠을 끙끙대다가 결국 팀원 분한테 여쭤봤는데, React의 setState와 관련된 문제에 대해 알려주셨다. 하나의 state에 대해 setState를 연속으로 여러 번 호출하면 지나치게 잦은 리렌더링을 방지하기 위해 마지막 setState만 적용된다는 것이다. 이걸 batching이라고 한다는데, 이에 대해서는 좀 더 공부해서 따로 한번 정리해보는 게 좋을 것 같다 😊
검색으로 이 문제에 대한 해결방법을 몇 가지 찾아서 그중 하나를 적용해봤다. state를 업데이트할 때 곧바로 setState를 호출하는 대신 useEffect와 isLoading을 이용하는 방식이다.
function InfiniteScroll({ allItems }) {
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const [items, setItems] = useState([]);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true);
const itemsPerLoad = 10;
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = () => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
const { clientHeight, scrollHeight, scrollTop } = scrollRef.current;
if (clientHeight + scrollTop >= scrollHeight) {
setIsLoading(true);
}
}
};
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
}
return () => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
}
};
}, []);
// isLoading 변수를 통해 loadItems 호출
useEffect(() => {
if (isLoading) {
loadItems();
setIsLoading(false);
}
}, [isLoading]);
const loadItems = () => {
var newItems = allItems.slice(0, Math.min(items.length + itemsPerLoad, allItems.length));
setItems(newItems);
};
return (
<div ref={scrollRef}>
{items.map((item, index) => <Item key={index} data={item} />)}
</div>
);
}❗ 목록을 초기화하자
우리 서비스에서 이 목록 컴포넌트는 상점들을 한번 렌더링하고 끝나는 게 아니라 카테고리 선택에 따라 목록에 들어가는 상점들이 바뀌어야 했다. 그래서 allItems 인자 값이 바뀔 때마다 스크롤을 목록 위쪽 끝으로 올리고 목록을 초기화하는 코드를 추가했다.
function InfiniteScroll({ allItems }) {
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const [items, setItems] = useState([]);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const itemsPerLoad = 10;
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = () => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
const { clientHeight, scrollHeight, scrollTop } = scrollRef.current;
if (clientHeight + scrollTop >= scrollHeight) {
setIsLoading(true);
}
}
};
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
}
return () => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
}
};
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
if (isLoading) {
loadItems();
setIsLoading(false);
}
}, [isLoading]);
// 목록 데이터 변경 시
useEffect(() => {
// 목록 스크롤 위치 맨 위로 이동
scrollRef.current.scrollTo({
top: 0,
behavior: 'auto',
});
// 아이템 초기화
setItems([]);
// 처음 10개 아이템 렌더링
setIsLoading(true);
}, [allItems]);
const loadItems = () => {
var newItems = allItems.slice(0, Math.min(items.length + itemsPerLoad, allItems.length));
setItems(newItems);
};
return (
<div ref={scrollRef}>
{items.map((item, index) => <Item key={index} data={item} />)}
</div>
);
}📃 Reference
clientHeight, scrollHeight, scrollTop
Manipulating the DOM with a ref
React batches state updates


좋은 글 잘 보고 갑니다 :)