백준 10828번은 자료구조의 기초 중 하나인 stack에 관한 문제이다.
자료구조 스택(Stack)은 기본적으로 FILA(Fast InputmLast Output), LIFA(Last Input, First Output)의 구조를 가지고 있다. 즉, 먼저 들어오는 자료는 나중에 나가고, 나중에 들어오는 자료는 먼저 나간다는 뜻이다.
그림으로 나타내보면 다음과 같다:
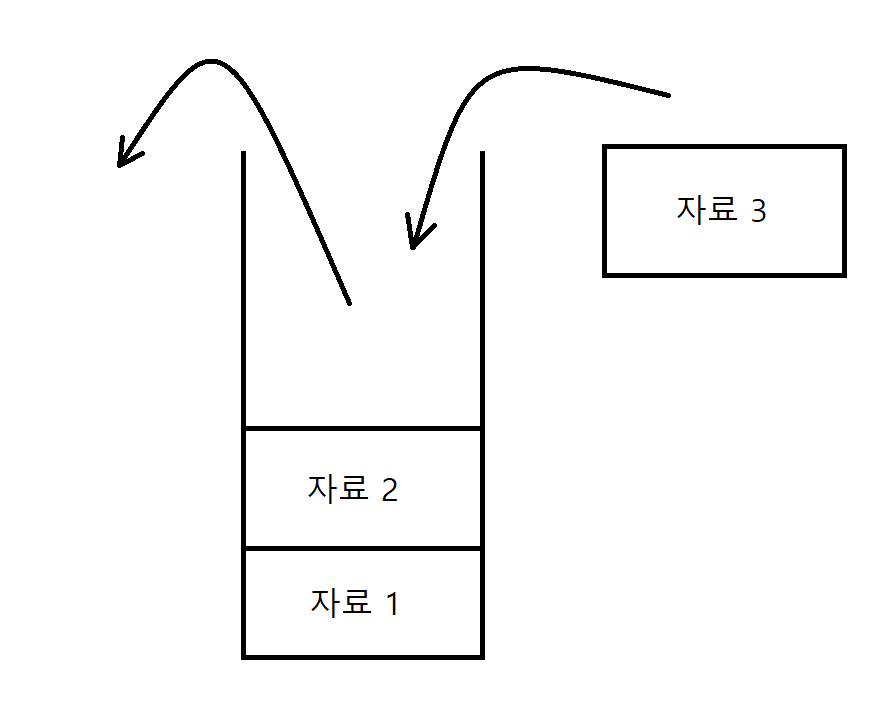
자료1은 맨 처음 들어간 자료이고, 자료2는 그 다음 들어간 자료이다. 그 이후, 자료를 순서대로 꺼내면 자료2(나중에 들어간 자료)가 나온 후 자료1(먼저 들어간 자료)이 나오게 된다.
이 문제에서 명령어는 총 5개 주어지는데, 각각
push : stack 안에 숫자를 넣는다.
pop : stack 안의 숫자를 빼고 그 수를 출력한다.
size : stack 내부의 숫자 개수를 출력한다.
empty : stack이 비었는지에 대한 여부를 조사하여 출력한다. 비었으면 1, 비지 않았으면 0을 출력한다.
top : stack의 맨 위 숫자를 출력한다. stack이 비었을 경우, -1을 출력한다.
의 의미를 가지고 있다.
stack의 기본 구조와 명령어의 사용방법만 알면 코드는 짜기 쉬워진다:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX 10000
int stack[MAX];
int top = -1;
void push(int);
int pop();
int main(void) {
int num;
scanf("%d", &num);
char order[6]; int input_num;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
scanf("%s", order);
if (strcmp(order, "push") == 0) {
scanf("%d", &input_num);
push(input_num);
}
else if (strcmp(order, "pop") == 0) {
printf("%d\n", pop());
}
else if (strcmp(order, "size") == 0) {
printf("%d\n", top + 1);
}
else if (strcmp(order, "empty") == 0) {
if (top == -1) {
printf("%d\n", 1);
}
else {
printf("%d\n", 0);
}
}
else if (strcmp(order, "top") == 0) {
if (top == -1) {
printf("%d\n", -1);
}
else {
printf("%d\n", stack[top]);
}
}
}
}
void push(int a) {
if (top < MAX) {
stack[++top] = a;
}
}
int pop() {
if (top > -1) {
return stack[top--];
}
else {
return -1;
}
}