자바가 제공하는 다양한 연산자를 학습하세요.
학습할 것
산술 연산자
비트 연산자
관계 연산자
논리 연산자
instanceof
assignment(=) operator
화살표(->) 연산자
3항 연산자
연산자 우선 순위
(optional) Java 13. switch 연산자
연산자(operator)란
주어진 식을 계산하여 결과를 얻어내는 과정을 연산이라고 한다.
연산을 수행하는 기호를 연산자라고 한다.
연산을 수행하기 위해서는 대상이 있어야 하는, 이 대상을 피연산자(operand) 라고 부른다
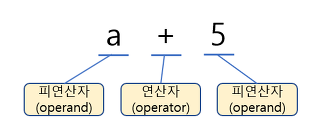
연산자(operator) : 연산을 수행하는 기호(+,-,*,/ 등)
피연산자(operand) : 연산자의 작업 대상(변수, 상수, 수식)
1. 산술연산자
(+, -, *, /, %)
| 산술연산자 | |
|---|---|
| + | 더하기 연산 |
| - | 뺄셈 연산 |
| * | 곱하기 연산 |
| / | 나누기 연산 |
| % | 나머지 연산 |
public void calcOperation() {
int num1 = 5;
int num2 = 3;
System.out.println(num1 + num2); // 8
System.out.println(num1 - num2); // 2
System.out.println(num1 * num2); // 15
System.out.println(num1 / num2); // 1 (실수형이라면 1.666 이지만 정수형이므로 내림으로 1이 나온다.)
}2. 비트 연산자
비트 연산자는 데이터를 비트 단위로 연산한다.
0과1로 표현이 가능한 정수 타입만 비트 연산이 가능.
0은 거짓, 그 외의 값은 참을 의미
대표적인 비트 연산자로는 ~(not), &(and), |(or), ^(xor)이 있음
public void bitOperation() {
int num1 = 10; // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001010
int num2 = 15; // 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001111
System.out.println(~num1) // -11
// 11111111 11111111 11111111 11110101
System.out.println(num1 & num2) // 10
// 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001010
System.out.println(num | num2) // 15
// 00000000 00000000 00000000 00001111
System.out.println(num ^ num2) // 5
// 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000101
}3. 관계 연산자
이항 연산자로 피연산자의 크기를 비교하는 연산자
연산의 결과는 true, false로 알려줌
| 연산자 | 이름 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| == | 같음 | 양쪽이 같으면 참, 아니면 거짓 |
| != | 다름 | 양쪽이 다르면 참, 같으면 거짓 |
| > | 보다큼 | 왼쪽이 크면 참, 아니면 거짓 |
| >= | 보다 크거나 같음 | 왼쪽이 크거나 같으면 참, 아니면 거짓 |
| < | 보다 작음 | 왼쪽이 작으면 참, 아니면 거짓 |
| <= | 보다 작거나 같음 | 왼쪽이 작거나 같으면 참, 아니면 거짓 |
public void relationOperation() {
System.out.println(10 > 5); // true
System.out.println(10 < 5); // false
System.out.println(9 >= 8); // true
System.out.println(9 >= 9); // true
System.out.println(8 >= 9); // false
System.out.println(8 == 8); // true
System.out.println(8 != 9); // true
}4. 논리 연산자
대상이 boolean 타입의 논리 값이다.
!은 부정을 의미 &&(and) ||(or) 연산은 비트 연산자와 비슷한 개념을 가진다.
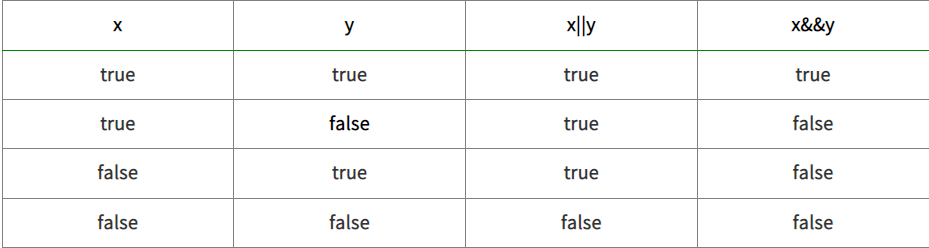
public void relativeOperation() {
boolean boo_true = true;
boolean boo_false = false;
System.out.println(!boo_true); // false;
System.out.println(!boo_false); // true;
System.out.println(boo_true && boo_false); // false;
System.out.println(boo_true || boo_false); // true;
System.out.println(boo_true && boo_true); // true;
}5. instanceof
레퍼런스 타입 변수가 레퍼런스 타입의 데이터 타입인지 확인해 보는 연산
일반적으로는 레퍼런스 타입 변수가 레퍼런스 타입으로 변환이 가능한지 확인하기 위해 사용한다.
연산 결과로 true 또는 false를 반환.
true면 타입 변환가능
(레퍼런스 타입 변수) instance of (레퍼런스 데이터 타입)
interface interType{}
class type1 {}
class type2 extends type1 {}
class type3 implements interType {}
public class Week3 {
public void instanceOfExample() {
type1 myType1 = new type1();
type2 myType2 = new type2();
type3 myType3 = new type3();
System.out.println(myType1 instanceof interType); // false
System.out.println(myType2 instanceof interType); // false
System.out.println(myType3 instanceof interType); // true
System.out.println(myType2 instanceof type2); // true
}
}
6. assignment(=) operator
일반적으로 대입 연산자 혹은 할당 연산자라고 부른다.
오른쪽 피 연산자를 왼쪽의 피연산자에 저장 .
왼쪽에는 변수, 오른쪽에는 리터럴 이나 리터럴이 담긴 변수가 있음.
연산자 중 가장 낮은 우선수위라 나중에 수행
variable = literal
7. 화살표(->) 연산자
자바에 람다가 도입하면서 나옴.
화살표연산자는 () -> {} 의 형태를 가지고 있으며 매개변수를 받아, 메소드(함수)를 실행한다.
8. 3항 연산자
코드를 짧게 할 수 있음
(조건) ? (조건이 참일 시, 실행) : (조건이 거짓일 시, 실행)
public static void binomialOperator() {
int num1 = 10;
System.out.println((num1 > 5) ? "okay" : "no"); // okay
System.out.println((num1 < 5) ? "okay" : "no"); // no
}
Integer searchYear = request.getSalesYear() == null ? LocalDate.now().getYear() : request.getSalesYear();
Integer searchQuarter = request.getQuarter() == null ? 0 : request.getQuarter();
Integer probabilityFrom = request.getProbabilityCode() == null ? 0 : request.getProbabilityCode();
Integer probabilityTo = request.getProbabilityCode() == null ? 100 : request.getProbabilityCode();9. 연산자 우선 순위
우선수위가 앞에 있을수록 먼저 실행됨
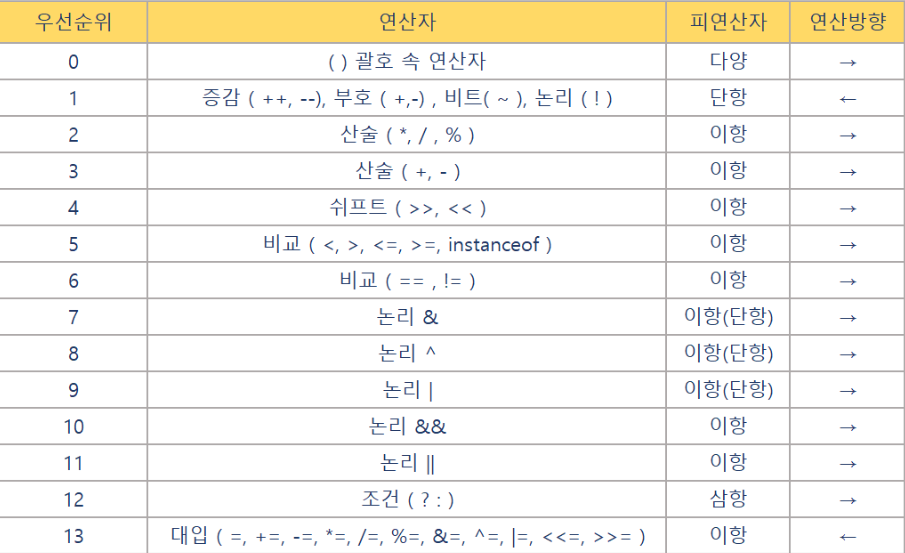
괄호를 잘 쓰는 것이 중요함
10. (optional) Java 13. switch 연산자
switch 문법은 가독성과 실행 속도를 향상 시켜준다.
switch는 statement가 아닌 operator에 더 가깝고 이미 처리된 결과를 통해서 해당 연산을 수행한다.
public static void switchOperator() {
System.out.println(swtichExample("a")); // 1
System.out.println(swtichExample("b")); // 2
System.out.println(swtichExample("c")); // 3
System.out.println(swtichExample("d")); // -1
}
public static int swtichExample(String s){
switch (s){
case "a":
return 1;
case "b":
return 2;
case "c":
return 3;
default:
return -1;
}
}