1. EL Tag 기본
EL Tag는 표현 언어(Expression Language)로 내장 객체에 저장된 attribute 에 빠르게 접근하여 값을 출력하는 태그를 의미합니다.El Tag의 장점으로 JSP의 내장 스펙이므로 외부 라이브러리 없이 사용이 가능하다는 부분입니다.
<!-- quiz.jsp -->
<form action="quiz1-result.jsp">
<p><input type="text" name="userid" placeholder="ID"></p>
<p><input type="password" name="pw1" placeholder="Password"></p>
<p><input type="password" name="pw2" placeholder="Password 확인"></p>
<p><input type="text" name="name" placeholder="이름"></p>
<p><input type="number" name="yyyy" placeholder="출생년도"></p>
<p>
<select name="mm">
<%for (int i = 1; i <= 12; i++) { %>
<option><%=i %></option>
<% } %>
</select>
</p>
<p><input type="number" name="dd" min="1" max="31" placeholder="출생일"></p>
<p><input type="submit" name="" placeholder="가입신청"></p>
</form>
<!-- quiz.result -->
<jsp:useBean id="join" class="quiz.Quiz1DTO" />
<jsp:setProperty property="*" name="join"/>
<%
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// POST방식의 요청이 아니라면 quiz1.jsp로 보내기
if (request.getMethod().equals("POST") == false) {
response.sendRedirect("quiz1.jsp");
}
%>
<table>
<tr>
<th>id</th>
<th>이름</th>
<th>비밀번호</th>
<th>생년월일</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>${join.id }</td>
<td>${join.name }</td>
<td>********</td>
<td>${join.yyyy }-${join.mm }-${join.dd }</td>
</tr>
</table><※ 결과는 다음과 같습니다.>
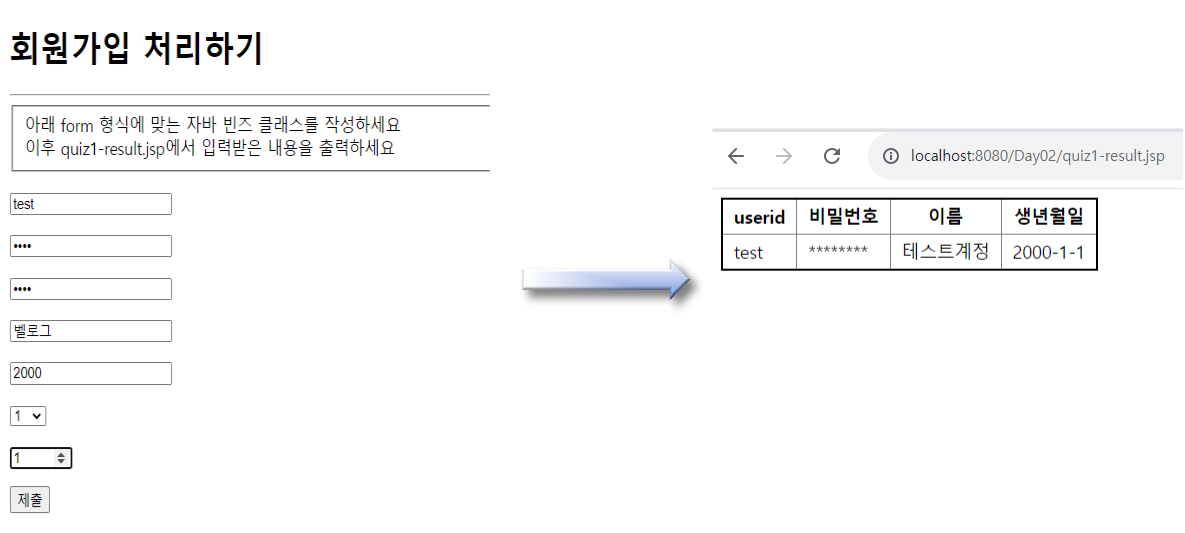
결과에서 내장 객체를 명시하지 않아도 순서대로 접근하여 attribute를 찾아서 출력하시는 모습을 보실 수 있습니다.
출력의 우선순위는
- pageContext
- request
- session
- application
public class Circle {
private double radius;
private double length;
private double square;
@Override
public String toString() {
String format = "반지름 : %.2f\n, 둘레 : %.2f\n, 넓이 : %.2f\n";
return String.format(format, radius, length, square);
}
public void calc() {
if(radius != 0) {
length = 2 * 3.14 * radius;
square = radius * radius * 3.14;
}
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getSquare() {
return square;
}
public void setSquare(double square) {
this.square = square;
}
}<jsp:useBean id="test" class="velog.Circle" />
<jsp:setProperty property="radius" name="test" value="50.7"/>
${test.calc() }
<h3>\${test } : ${test }</h3>
<h3>\${pageSope.test } : ${pageSope.test }</h3>
<h3>\${requestScope.test } : ${requestScope.test }</h3>
<h3>\${sessionScope.test } : ${sessionScope.test }</h3>
<h3>\${applicationScope.test } : ${applicationScope.test }</h3>
또한 배열, 리스트, Map에도 접근 가능한데 사용방식은 다음과 같습니다.
<%
String[] arr = {"짱구", "맹구", "훈이", "유리", "철수"};
pageContext.setAttribute("arr", arr);
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(arr);
pageContext.setAttribute("list", list);
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("나단비", 5);
map.put("john", 20);
pageContext.setAttribute("map", map);
%>
<h3>배열/리스트/맵 접근</h3>
<!-- 배열에서는 자료형을 컬렉션에서는 제네릭 타입을 맞춰주면서 출력 -->
<h3><%=((String[])pageContext.getAttribute("arr"))[1] %></h3>
<h3>\${arr[1] } : ${arr[1] }</h3>
<br>
<h3><%=((List<String>)pageContext.getAttribute("list")).get(2) %></h3>
<h3>\${list[2] } : ${list[2] }</h3>
<br>
<h3><%=((HashMap<String, Integer>)pageContext.getAttribute("map")).get("이지은") %> 살</h3>
<h3>\${map['이지은'] } : ${map['이지은'] }살</h3>
<h3>\${map.john } : ${map.john }살</h3><※ 결과는 다음과 같습니다.>

2. EL Tag 연산자
| 산술연산 | +, -, *, /, % |
|---|---|
| 비교연산 | >, <, >=, <=, ==, !=, gt, lt, ge, le, eq, ne |
| 논리연산 | and, or, not |
| null 체크 | empty, not empty |
| 삼항연산 | A ? B : C |
