들어가며
계속 관련 문제를 풀다보니 정리하고 싶어졌다. 같은 탐색 알고리즘이지만 우선순위가 달라서 특정 상황에서 더 효율적인 경우가 있다.
공통점
- 이전에 방문한 노드를 저장할 배열이 있어야된다.
- 각 노드는 하위 노드와 노드 값을 가지고 있다.
- BFS는 Queue 를 이용해서 우선순위 배열을 가지고 있다.
가장 나중에 들어온 노드가 가장 먼저 처리되는 속성이 Queue와 같다. - DFS는 Stack을 이용해서 우선순위 배열을 가진다.
가장 최근에 들어온 노드가 가장 먼저 처리되는 속성이 Stack과 같다.
BFS
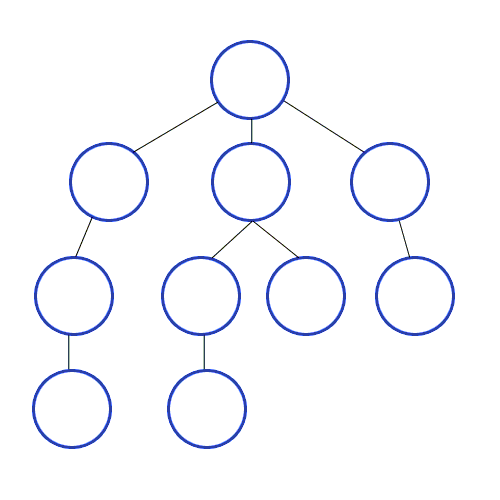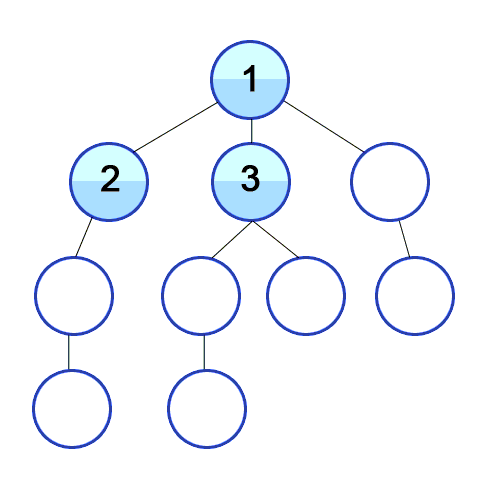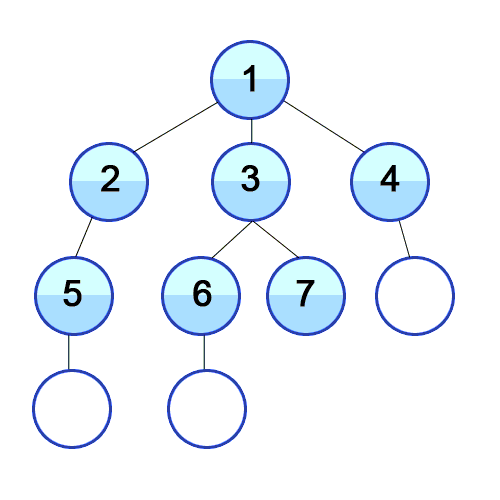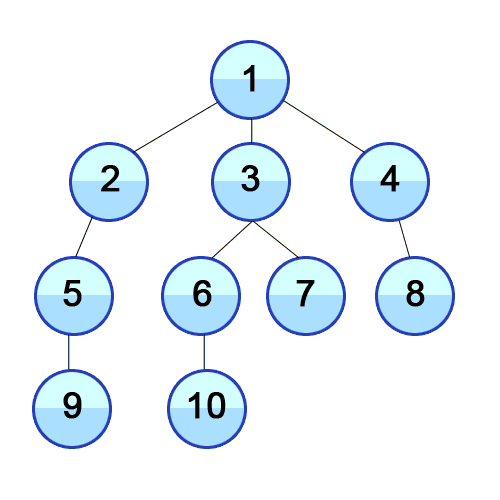
너비 우선 탐색이다. 우선 가장 가까운 노드부터 탐색한 다음 그 다음 레벨의 가까운 노드를 탐색한다.
나와 가까울 확률이 높은 경우 유용하다. 끝까지 확인해야 답이 나오는 문제는 비효율적이다.
let bfs = function (node) {
// TODO: 여기에 코드를 작성합니다.
const visited = [];
let queue = [node];
let count = 0;
let result = [];
while (queue.length !== 0) {
let target = queue.shift();
if (visited.includes(target.value)) continue;
visited.push(target.value);
result.push(target.value);
queue = queue.concat(target.children);
}
return result;
};
// 이 아래 코드는 변경하지 않아도 됩니다. 자유롭게 참고하세요.
let Node = function (value) {
this.value = value;
this.children = [];
};
// 위 Node 객체로 구성되는 트리는 매우 단순한 형태의 트리입니다.
// membership check(중복 확인)를 따로 하지 않습니다.
Node.prototype.addChild = function (child) {
this.children.push(child);
return child;
};
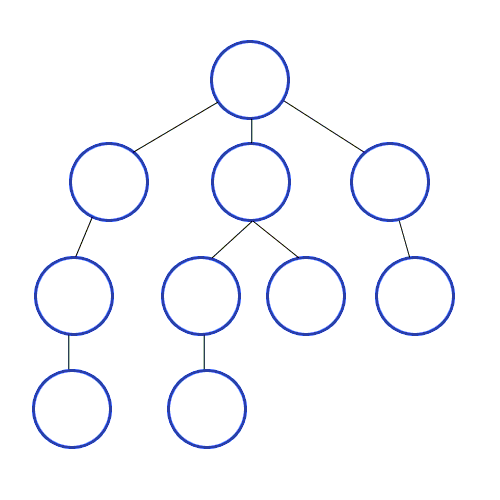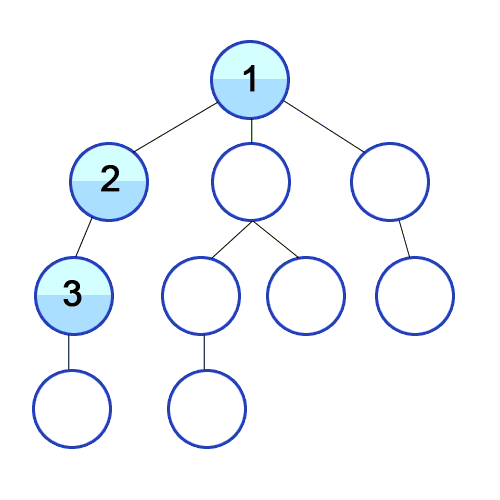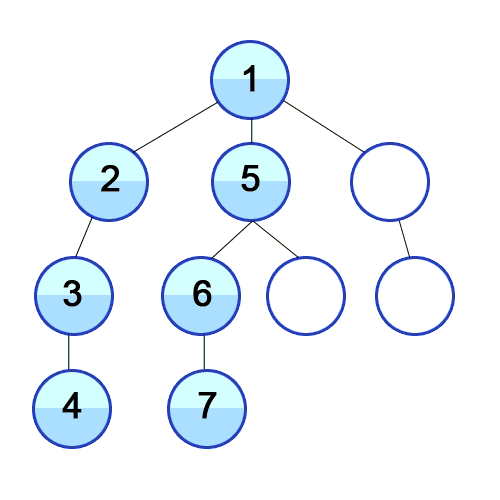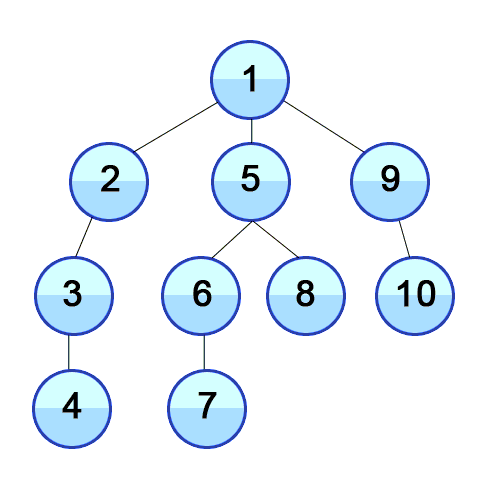
DFS
깊이 우선 탐색이다. 우선 가장 끝 노드까지 탐색한 다음 그 다음 옆 노드의 끝까지 탐색한다.
끝까지 찾아야 답이 나울 확률이 높은 경우 유용하다.
어떤 방향으로 찾는지 정할 수 있다. 가장 왼쪽 노드부터 찾고 싶은 경우, 가장 오른쪽 노드부터 찾고 싶은 경우를 정할 수 있다.
let dfs = function (node) {
// TODO: 여기에 코드를 작성합니다.
// Queue 하나, Stack 하나
let visitedQueue = [];
let nodeStack = [node];
while (nodeStack.length > 0) {
let poppedNode = nodeStack.pop();
if (visitedQueue.includes(poppedNode.value)) continue;
visitedQueue.push(poppedNode.value)
nodeStack.concat(poppedNode.children)
console.log(nodeStack)
}
return visitedQueue
};
// 이 아래 코드는 변경하지 않아도 됩니다. 자유롭게 참고하세요.
let Node = function (value) {
this.value = value;
this.children = [];
};
// 위 Node 객체로 구성되는 트리는 매우 단순한 형태의 트리입니다.
// membership check(중복 확인)를 따로 하지 않습니다.
Node.prototype.addChild = function (child) {
this.children.push(child);
return child;
};