문제코드
class Heap {
constructor(compare) {
this.heap = [];
this.compare = compare;
}
swap(a, b) {
[this.heap[a], this.heap[b]] = [this.heap[b], this.heap[a]];
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
push(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
this.upHeap();
}
pop() {
if (this.size() <= 0) {
return undefined;
}
this.swap(0, this.size()-1);
const value = this.heap.pop();
this.downHeap(0);
return value;
}
upHeap() {
let current = this.size()-1;
while (0 < current) {
const parent = Math.floor((current - 1) / 2);
if (this.compare(this.heap[parent], this.heap[current])) {
return;
}
this.swap(parent, current);
current = parent;
}
}
downHeap(i) {
let current = i;
while (current < this.size()) {
const left = current * 2;
const right = current * 2 + 1;
if (!this.heap[left]) {
break;
}
if (!this.heap[right]) {
if (this.compare(this.heap[current], this.heap[left])) {
break;
}
this.swap(current, left);
continue;
}
const next = this.compare(this.heap[left], this.heap[right]) ? right : left; // 더 작은쪽
if (this.compare(this.heap[current], this.heap[next])) {
break;
}
this.swap(current, next);
current = next;
}
}
}
function solution(n, paths, gates, summits) {
const isSummits = Array.from({length:n+1}, () => false);
const intensity = Array.from({length:n+1}, () => Infinity);
const graph = {};
const pq = new Heap((parent, child) => {
return parent[1] <= child[1];
})
for(let i=1; i<=n; i++) {
graph[i] = [];
}
paths.forEach(([ start, end, inst ]) => {
graph[start].push([end, inst]);
graph[end].push([start, inst]);
});
summits.forEach((summit) => {
isSummits[summit] = true;
});
gates.forEach((gate) => {
pq.push([gate, 0]);
intensity[gate] = 0;
});
while(0 < pq.size()) {
const [idx, inst] = pq.pop();
const nexts = graph[idx];
if (isSummits[idx] || intensity[idx] < inst) {
continue;
}
nexts.forEach(([end, nextInst]) => {
const totalInst = Math.max(inst, nextInst)
if (intensity[end] <= totalInst) {
return;
}
intensity[end] = totalInst;
pq.push([end, totalInst]);
});
}
return summits.sort((a,b) => a-b).reduce((acc, summit) => {
if (intensity[summit] < acc[1]) {
return [summit, intensity[summit]];
}
return acc;
}, [-1, Infinity]);
}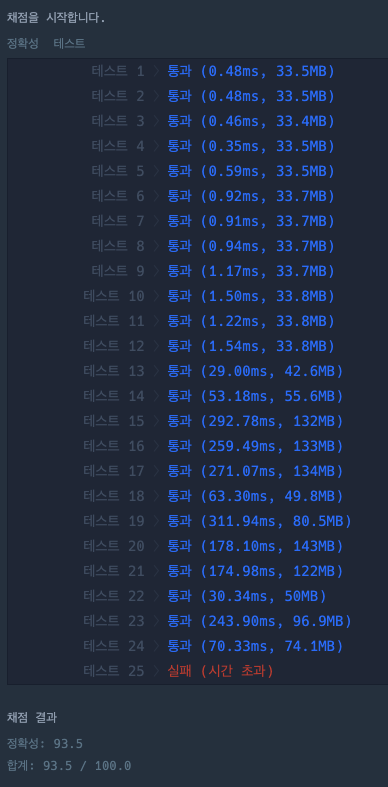
우선순위 큐를 사용한 다익스트라 알고리즘을 사용해서 해결했다. 테스트 24번까지 잘 돌아가는 걸 보고 맞았다! 싶었는데, 테스트 25에서 시간초과가 발생했고, 알고리즘 상으로는 시간복잡도가 초과하지 않아야 했다.
문제 원인과 해결
기존까지 한번 작성해둔 우선순위 큐가 큰 문제 없이 작동했기 때문에 이 부분이 문제다! 라는 생각을 늦게 했다.
확실히 C++이나 파이썬과 같이 기본으로 제공해주는 자료구조가 없다보니, 동작은 흉내내더라도 최적화된 자료구조로 사용하기에는 어려움이 있는 것 같다.
요즘 들어 이런 문제를 발견하면 사용하는 방법이 있는데, 바로 요즘 핫한 ChatGPT다.
간단하게 궁금한 점을 물어보는 것 부터, 최근에는 프론트엔드 모의 면접을 면접관 입장에서 진행해달라고 요청했더니 정말 비슷하게 진행해줬다.
그래서 이번에도 ChatGPT에게 효율적인 코드 작성을 요청했다.

class PriorityQueue {
constructor(comparatorFunction) {
this.heap = [];
this.compare = comparatorFunction || ((a, b) => a - b);
}
enqueue(item) {
this.heap.push(item);
this.heapifyUp();
}
dequeue() {
const max = this.heap[0];
const end = this.heap.pop();
if (this.heap.length > 0) {
this.heap[0] = end;
this.heapifyDown();
}
return max;
}
heapifyUp() {
let index = this.heap.length - 1;
while (index > 0) {
const element = this.heap[index];
const parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
const parent = this.heap[parentIndex];
if (this.compare(parent, element) >= 0) {
break;
}
this.heap[index] = parent;
this.heap[parentIndex] = element;
index = parentIndex;
}
}
heapifyDown() {
let index = 0;
const length = this.heap.length;
const element = this.heap[0];
while (true) {
const leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
const rightChildIndex = 2 * index + 2;
let leftChild, rightChild;
let swap = null;
if (leftChildIndex < length) {
leftChild = this.heap[leftChildIndex];
if (this.compare(leftChild, element) > 0) {
swap = leftChildIndex;
}
}
if (rightChildIndex < length) {
rightChild = this.heap[rightChildIndex];
if (
(swap === null && this.compare(rightChild, element) > 0) ||
(swap !== null && this.compare(rightChild, leftChild) > 0)
) {
swap = rightChildIndex;
}
}
if (swap === null) {
break;
}
this.heap[index] = this.heap[swap];
this.heap[swap] = element;
index = swap;
}
}
}정답 코드
ChatGPT가 작성해준 우선순위 큐를 사용하면 아래와 같은 코드를 작성할 수 있다.
class PriorityQueue {
constructor(comparatorFunction) {
this.heap = [];
this.compare = comparatorFunction || ((a, b) => a - b);
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
enqueue(item) {
this.heap.push(item);
this.heapifyUp();
}
dequeue() {
const max = this.heap[0];
const end = this.heap.pop();
if (this.heap.length > 0) {
this.heap[0] = end;
this.heapifyDown();
}
return max;
}
heapifyUp() {
let index = this.heap.length - 1;
while (index > 0) {
const element = this.heap[index];
const parentIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
const parent = this.heap[parentIndex];
if (this.compare(parent, element) >= 0) {
break;
}
this.heap[index] = parent;
this.heap[parentIndex] = element;
index = parentIndex;
}
}
heapifyDown() {
let index = 0;
const length = this.heap.length;
const element = this.heap[0];
while (true) {
const leftChildIndex = 2 * index + 1;
const rightChildIndex = 2 * index + 2;
let leftChild, rightChild;
let swap = null;
if (leftChildIndex < length) {
leftChild = this.heap[leftChildIndex];
if (this.compare(leftChild, element) > 0) {
swap = leftChildIndex;
}
}
if (rightChildIndex < length) {
rightChild = this.heap[rightChildIndex];
if ((swap === null && this.compare(rightChild, element) > 0) ||
(swap !== null && this.compare(rightChild, leftChild) > 0)) {
swap = rightChildIndex;
}
}
if (swap === null) {
break;
}
this.heap[index] = this.heap[swap];
this.heap[swap] = element;
index = swap;
}
}
}
function solution(n, paths, gates, summits) {
const isGates = Array(n+1).fill(false);
const isSummits = Array(n+1).fill(false);
const intensity = Array(n+1).fill(Infinity);
const graph = Array.from({length: n+1}, () => []);
const pq = new PriorityQueue((a, b) => a[1] <= b[1]);
paths.forEach(([ start, end, inst ]) => {
graph[start].push([end, inst]);
graph[end].push([start, inst]);
});
gates.forEach((gate) => {
isGates[gate] = true;
pq.enqueue([gate, 0]);
intensity[gate] = 0;
});
summits.forEach((summit) => {
isSummits[summit] = true;
});
graph.map((path, start) => {
if (isSummits[start]) {
return [];
}
return path.filter(([end, inst]) => {
return !isGates[end];
});
});
while(0 < pq.size()) {
const [idx, inst] = pq.dequeue();
if (isSummits[idx] || intensity[idx] < inst) {
continue;
}
graph[idx].forEach(([end, nextInst]) => {
const totalInst = Math.max(inst, nextInst)
if (totalInst < intensity[end]) {
intensity[end] = totalInst;
pq.enqueue([end, totalInst]);
}
});
}
return summits.sort((a,b) => a-b).reduce((acc, summit) => {
if (intensity[summit] < acc[1]) {
return [summit, intensity[summit]];
}
return acc;
}, [-1, Infinity]);
}결과는 아래와 같다.
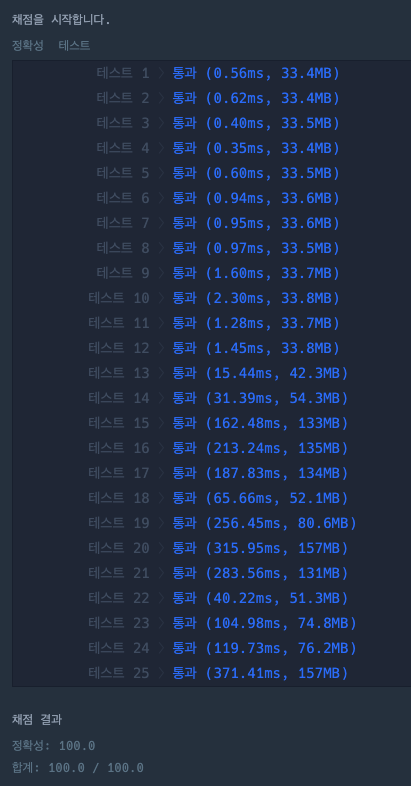
자료구조 교체 하나만으로 완전 효율적인 코드가 되어버렸다.
이걸 계기로 기존에 작성하던 알고리즘 문제풀이를 위한 자료구조를 한번 싹 정리해야겠다는 생각이 들었다.

힙을 쓸땐 조심해야겠는걸요