백준 21939, 문제 추천 시스템 Version 1 - HashMap, TreeSet / PriorityQueue
알고리즘
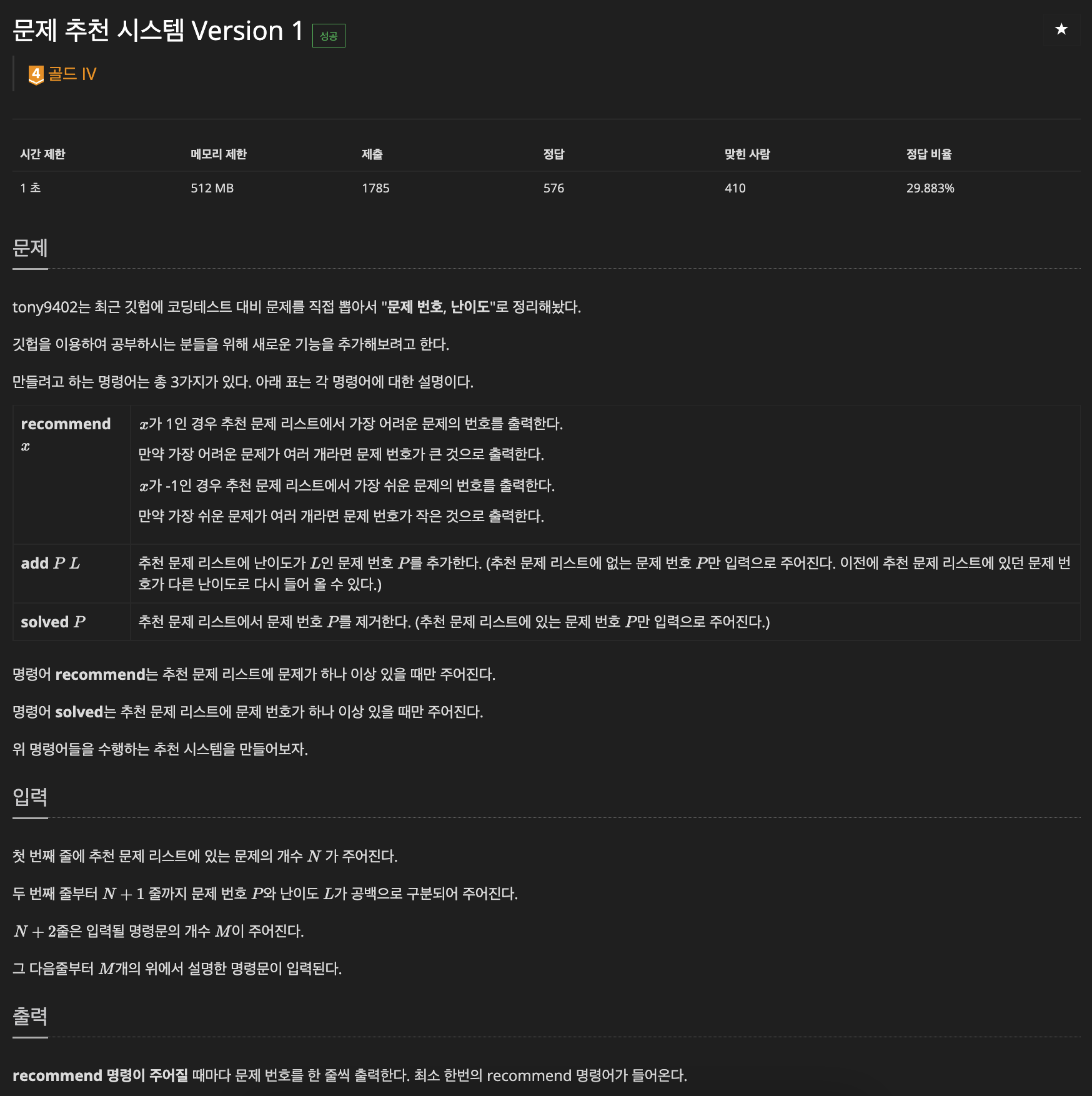
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/21939
풀이 ① - HashMap, 2개 PriorityQueue
1. 아이디어
- 문제 리스트의 문제 정보 입력 양식: "문제 번호, 난이도"
=> '문제 번호'가 중복되는 문제 존재 X 하므로, '문제 번호'가Key
1) recommend x
-
x == 1이면, 가장 어려운 문제 번호 출력 (다수일 경우, 문제 번호 큰 것 출력)
=>PriorityQueue<Problem>: 문제 난이도 높은 순 정렬 -
x == -1이면, 가장 쉬운 문제 번호 출력 (다수일 경우, 문제 번호 작은 것 출력)
=>PriorityQueue<Problem>: 문제 난이도 낮은 순 정렬
2) add P L
- 난이도가 L 인 문제 번호 P 추가
- 단, 이전에 추천 문제 리스트에 있던 문제 번호가 다른 난이도로 다시 입력 가능
=>HashMap에는 그대로put가능
=>PriorityQueue<Problem>에는 기존에 있던 문제 삭제하고 새로 추가
3) solved P
- 문제 번호 P 제거
2. 자료구조
-
HashMap<Integer, Problem>: 문제 번호 p 가 Key, 문제가 Value
=> 문제Problem: 문제 번호, 문제 난이도 -
PriorityQueue<Problem>2개: 문제 난이도 높은 순 / 낮은 순 정렬
=> "recommend 1", "recommend -1" 각각PriorityQueue<Problem>사용
3. 시간 복잡도
1) 초기 입력, 추천 문제 리스트 저장
HashMap에 저장: O(n)PriorityQueue2개에 저장: O(2n log_2 n)
=> 저장 전체 O(n log_2 n)
2) 입력 명령어 수행
HashMap: O(m)PriorityQueue: O(n log_2 n)
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Problem {
public int pIdx, level; // 문제 번호, 난이도
public Problem(int pIdx, int level) {
this.pIdx = pIdx;
this.level = level;
}
}
public class Main {
static int n; // 추천 문제 리스트의 문제 개수
static int m; // 명령어 개수
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static Map<Integer, Problem> map = new HashMap<>(); // 문제 추천 리스트 저장
static PriorityQueue<Problem> easyProblems = new PriorityQueue<>(
// 난이도 낮은 순으로 저장 (다수일 경우, 문제 번호 작은 순)
new Comparator<Problem>() {
@Override
public int compare(Problem o1, Problem o2) {
if (o1.level != o2.level)
return o1.level - o2.level;
else
return o1.pIdx - o2.pIdx;
}
}
);
static PriorityQueue<Problem> hardProblems = new PriorityQueue<>(
// 난이도 높은 순으로 저장 (다수일 경우, 문제 번호 큰 순)
new Comparator<Problem>() {
@Override
public int compare(Problem o1, Problem o2) {
if (o2.level != o1.level)
return o2.level - o1.level;
else
return o2.pIdx - o1.pIdx;
}
}
);
static void add(int pIdx, int level) {
Problem newProblem = new Problem(pIdx, level);
// 추천 문제 리스트에 없던 새로운 문제 번호 입력
if (!map.containsKey(pIdx)) {
easyProblems.add(newProblem);
hardProblems.add(newProblem);
}
// 추천 문제 리스트에 있던 문제 번호가 새로운 난이도로 입력
else {
Problem oldProblem = map.get(pIdx); // 2개의 우선순위 큐에서 기존 문제 삭제
easyProblems.remove(oldProblem);
hardProblems.remove(oldProblem);
easyProblems.add(newProblem); // 새로 문제 추가
hardProblems.add(newProblem);
}
map.put(pIdx, newProblem);
}
static void solved(int pIdx) {
Problem removedProblem = map.remove(pIdx);
easyProblems.remove(removedProblem);
hardProblems.remove(removedProblem);
}
static void recommend(int x) {
if (x == 1) {
Problem hardProblem = hardProblems.peek();
sb.append(hardProblem.pIdx).append("\n");
}
else if (x == -1) {
Problem easyProblem = easyProblems.peek();
sb.append(easyProblem.pIdx).append("\n");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in)
);
StringTokenizer st;
// 1) HashMap, 2개 PriorityQueue 에 입력 추천 문제 리스트 저장
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int pIdx = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int level = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
Problem problem = new Problem(pIdx, level);
map.put(pIdx, problem);
easyProblems.add(problem);
hardProblems.add(problem);
}
// 2) m개 명령어 수행
m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
String command = st.nextToken();
if (command.equals("add")) {
int pIdx = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int level = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
add(pIdx, level);
}
else if (command.equals("solved")) {
int pIdx = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
solved(pIdx);
}
else if (command.equals("recommend")) {
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
recommend(x);
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}풀이 ② - HashMap, TreeSet
1. 아이디어
- 문제 리스트의 문제 정보 입력 양식: "문제 번호, 난이도"
=> '문제 번호'가 중복되는 문제 존재 X 하므로, '문제 번호'가Key
1) recommend x
x == 1이면, 가장 어려운 문제 번호 출력 (다수일 경우, 문제 번호 큰 것 출력)x == -1이면, 가장 쉬운 문제 번호 출력 (다수일 경우, 문제 번호 작은 것 출력)
=>TreeSet<Problem>: 문제 난이도 낮은 순 정렬하여first,last원소에 접근
2) add P L
- 난이도가 L 인 문제 번호 P 추가
- 단, 이전에 추천 문제 리스트에 있던 문제 번호가 다른 난이도로 다시 입력 가능
=>HashMap에는 그대로put가능
=>TreeSet<Problem>에는 기존에 있던 문제 삭제하고 새로 추가
3) solved P
- 문제 번호 P 제거
2. 자료구조
-
HashMap<Integer, Problem>: 문제 번호 p 가 Key, 문제가 Value
=> 문제Problem: 문제 번호, 문제 난이도 -
TreeSet<Problem>: 문제 난이도 낮은 순 정렬 (다수일 경우, 문제 번호 작은 순 정렬)
=>first,last원소에 접근
인터페이스인
Set<>으로 선언하면first(),last()메소드 사용 불가능
- 정렬된 원소들에서 맨 앞 / 맨 뒤 원소에 접근하려면,
TreeSet<>으로 선언할 것
3. 시간 복잡도
1) 초기 입력, 추천 문제 리스트 저장
HashMap에 저장: O(n)TreeSet에 저장: O(n log_2 n)
=> 저장 전체 O(n log_2 n)
2) 입력 명령어 수행
HashMap: O(m)TreeSet: O(m log_2 n)
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Problem implements Comparable<Problem> {
public int pIdx, level; // 문제 번호, 난이도
public Problem(int pIdx, int level) {
this.pIdx = pIdx;
this.level = level;
}
// 난이도 낮은 순 (다수일 경우, 문제 번호 작은 순)
public int compareTo(Problem o) {
if (this.level != o.level)
return this.level - o.level;
else
return this.pIdx - o.pIdx;
}
}
public class Main2 {
static int n; // 추천 문제 리스트의 문제 개수
static int m; // 명령어 개수
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static Map<Integer, Problem> map = new HashMap<>(); // 문제 추천 리스트 저장
static TreeSet<Problem> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(); // 문제 난이도 낮은 순 (다수일 경우, 문제 번호 낮은 순)
static void add(int pIdx, int level) {
Problem newProblem = new Problem(pIdx, level);
// 추천 문제 리스트에 없던 새로운 문제 번호 입력
if (!map.containsKey(pIdx)) {
treeSet.add(newProblem);
}
// 추천 문제 리스트에 있던 문제 번호가 새로운 난이도로 입력
else {
Problem oldProblem = map.get(pIdx); // 기존 문제 삭제
treeSet.remove(oldProblem);
treeSet.add(newProblem); // 새로 문제 추가
}
map.put(pIdx, newProblem);
}
static void solved(int pIdx) {
Problem removedProblem = map.remove(pIdx);
treeSet.remove(removedProblem);
}
static void recommend(int x) {
if (x == 1) {
Problem hardProblem = treeSet.last();
sb.append(hardProblem.pIdx).append("\n");
}
else if (x == -1) {
Problem easyProblem = treeSet.first();
sb.append(easyProblem.pIdx).append("\n");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in)
);
StringTokenizer st;
// 1) HashMap, TreeSet 에 입력 추천 문제 리스트 저장
n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int pIdx = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int level = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
Problem problem = new Problem(pIdx, level);
map.put(pIdx, problem);
treeSet.add(problem);
}
// 2) m개 명령어 수행
m = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
String command = st.nextToken();
if (command.equals("add")) {
int pIdx = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int level = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
add(pIdx, level);
}
else if (command.equals("solved")) {
int pIdx = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
solved(pIdx);
}
else if (command.equals("recommend")) {
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
recommend(x);
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}