Q_2913) Subarrays Distinct Element Sum of Squares I
출처 : https://leetcode.com/problems/subarrays-distinct-element-sum-of-squares-i/
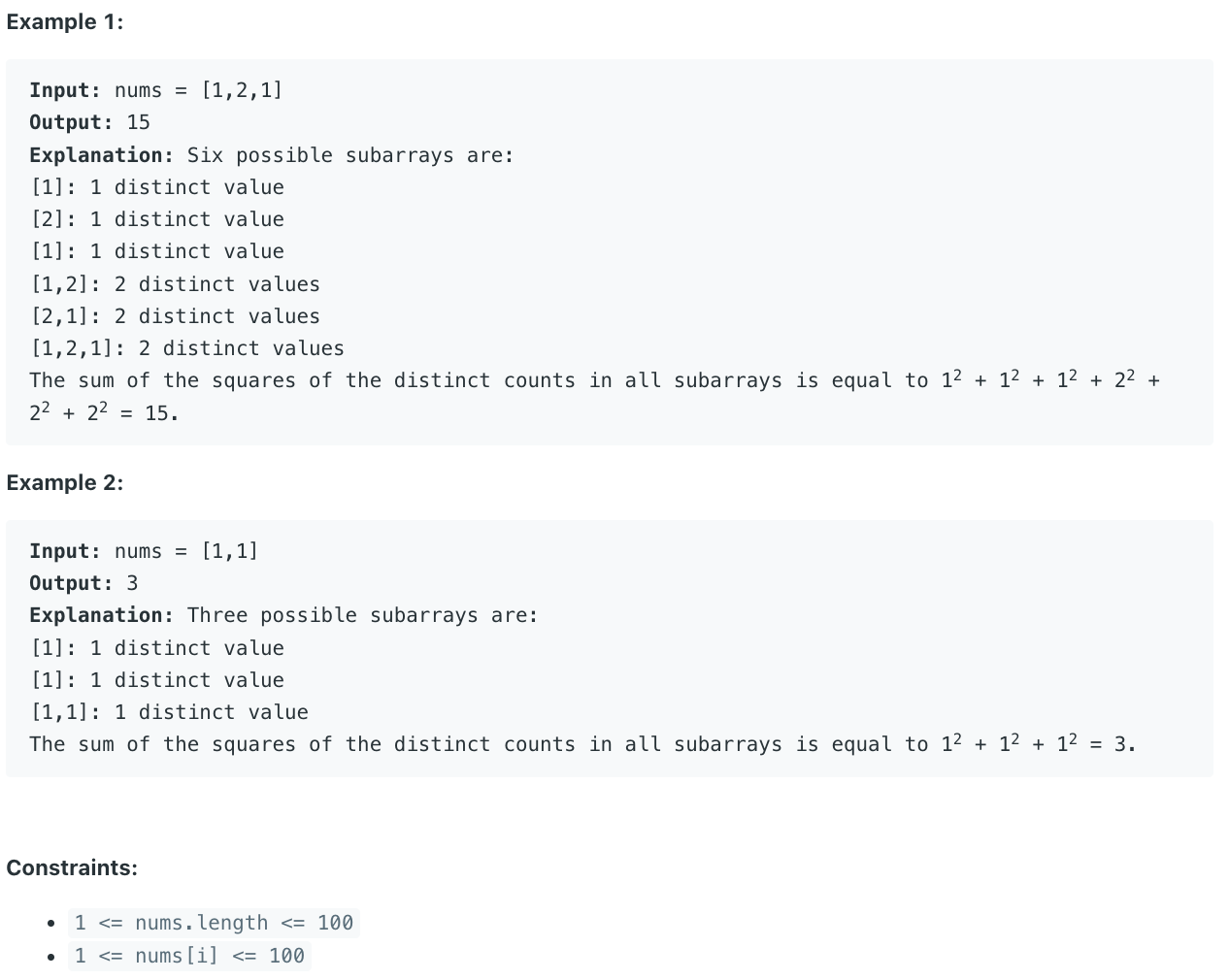
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums.
The distinct count of a subarray of nums is defined as:
Let nums[i..j] be a subarray of nums consisting of all the indices from i to j such that 0 <= i <= j < nums.length. Then the number of distinct values in nums[i..j] is called the distinct count of nums[i..j].
Return the sum of the squares of distinct counts of all subarrays of nums.
A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
class Solution {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> total = new ArrayList<>();
public int sumCounts(List<Integer> nums) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= nums.size(); i++) {
getSubArrays(nums, i, new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < total.size(); i++) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int j = 0; j < total.get(i).size(); j++) {
set.add(total.get(i).get(j));
}
sum += set.size() * set.size();
}
return sum;
}
public void getSubArrays(List<Integer> nums, int start, List<Integer> current) {
if (start == nums.size()) return;
current.add(nums.get(start));
total.add(new ArrayList<>(current));
getSubArrays(nums, start + 1, current);
current.remove(current.size() - 1);
}
}🙈 풀이 참조해서 푼 문제
-가장 일반적으로 쓰던 조합 재귀를 사용해서 풀려고 했는데 contiguous한 subarray를 구하는 부분에서 막혔다
-boolean[] visited가 당연히 필요하다고 생각했었다
-> contiguous한 subarray만 유효하기 때문에 굳이 visited[]를 통해서 tracking을 할 필요가 없다🥸
-아래는 ChatGPT가 제안한 또 다른 코드:
import java.util.*;
public class prac {
static ArrayList<List<Integer>> total = new ArrayList<>();
public static int sumCounts(List<Integer> nums) {
int sum = 0;
for (int l = 1; l <= nums.size(); l++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= nums.size() - l; j++) { //nums.size()-1의 이유 : j의 시작점을 조정해야 subarray의 크기만큼 추출해낼 수 있음
combination(new ArrayList<>(), l, 0, j, nums);
}
}
for (int a = 0; a < total.size(); a++) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int b = 0; b < total.get(a).size(); b++) {
set.add(total.get(a).get(b));
}
sum+=set.size()* set.size();
}
return sum;
}
public static void combination(ArrayList<Integer> arrayList, int limit, int count, int start, List<Integer> nums) {
if (count == limit) {
total.add(new ArrayList<>(arrayList));
} else if (start < nums.size()) {
arrayList.add(nums.get(start));
combination(arrayList, limit, count + 1, start + 1, nums);
arrayList.remove(arrayList.size() - 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 1));
System.out.println(sumCounts(list));
}
}