
💡 Suppressed Exception
Suppressed Exception는 억압된 예외라는 뜻으로 예외가 발생하지만 무시되는 예외를 뜻합니다.
Java에서 이 예외에 대한 가장 일반적인 예시는 try-catch-finally 문에서 finally에서 예외가 발생했을 경우입니다.
❗️ try-catch-finally에서의 Suppressed Exception
finally에서 예외가 발생하는 경우를 간단하게 살펴봅시다.
public static void demoSuppressedException(String filePath) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileIn = null;
try {
fileIn = new FileInputStream(filePath);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new IOException(e);
} finally {
fileIn.close();
}
}try-catch-finally를 활용해서 파일을 읽고 예외처리, 스트림 close 까지 모두 처리하는 코드입니다.
filePath가 정상적인 경로라면 아무런 문제없이 동작하겠지만 존재하지 않는 파일이라면 FileNotFoundException이 발생하고 finally에서 close()를 시도할 것 입니다.
하지만 존재하지 않는 파일이기에 fileIn은 null일 것이고, fineIn.close()에서는 NullPointerException이 발생할 것입니다. 의도하지 않는 동작입니다.
@Test
void givenNonExistentFileName_whenAttemptFileOpen_thenNullPointerException() {
NullPointerException exception = assertThrows(NullPointerException.class, () -> {
demoSuppressedException("/non-existent-path/non-existent-file.txt");
});
exception.printStackTrace();
}테스트를 수행해봅시다.
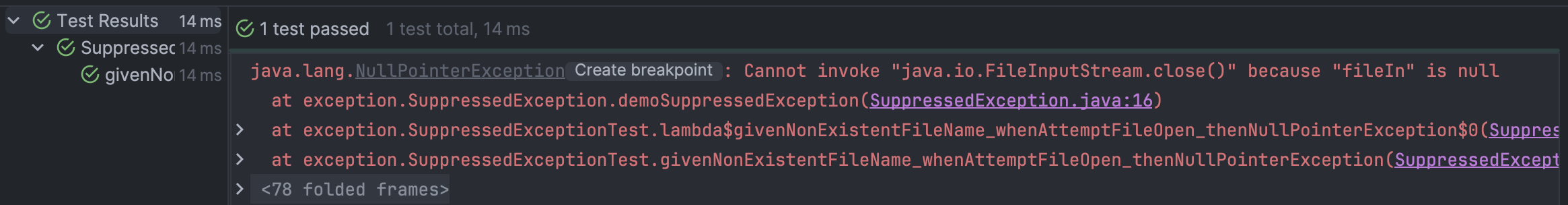
예상대로 NullPointerException이 발생했습니다. 그런데 스택 트레이스를 출력해보면 NullPointerException만 throw 되었고, 근본적인 문제인 FileNotFoundException은 throw 되지 않았습니다.
기존의 exception은 무시되고 최근의 exception만 트레이싱 되고 있는 것입니다. 이런 상황은 디버깅을 어렵게 만듭니다.
그러면 Suppressed Exception도 throw를 시킬려면 어떻게 해야할까요? Throwable.addSuppressed()를 사용하는 방법이 있습니다.
public static void demoAddSuppressedException(String filePath) throws IOException {
Throwable firstException = null;
FileInputStream fileIn = null;
try {
fileIn = new FileInputStream(filePath);
} catch (IOException e) {
firstException = e;
} finally {
try {
fileIn.close();
} catch (NullPointerException npe) {
if (firstException != null) {
npe.addSuppressed(firstException);
}
throw npe;
}
}
}finally에서 addSuppressed()를 통해 첫 번째 예외를 추가합니다.
@Test
void addSuppressedException() {
NullPointerException exception = assertThrows(NullPointerException.class, () -> {
demoAddSuppressedException("/non-existent-path/non-existent-file.txt");
});
Throwable[] suppressed = exception.getSuppressed();
assertEquals(1, suppressed.length, "Suppressed 예외는 1개여야 합니다.");
assertTrue(suppressed[0] instanceof FileNotFoundException,
"Suppressed 예외는 FileNotFoundException이어야 합니다.");
exception.printStackTrace();
}
테스트 해봅시다. Suppressed Exception은 1개이고, FileNotFoundException이어야 합니다.
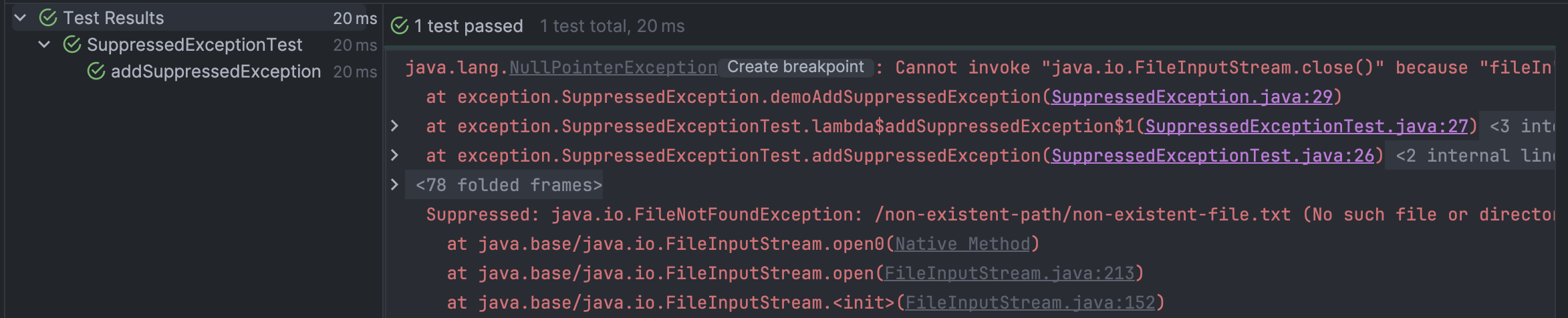
테스트도 잘 동작하고 스택 트레이스에도 FileNotFoundException이 출력되는 걸 확인할 수 있습니다.
이제 Suppressed Exception 또한 트레이싱 할 수 있게 되었지만 너무 번거롭고 try-catch 또한 중첩되기에 코드가 너무 더럽습니다. 이럴 때 사용하기 좋은게 try-with-resources 입니다.
🛠️ try-with-resources 사용하기
try-with-resources는 Java 7에 추가된 구문으로, AutoCloseable 인터페이스의 구현체들의 close()를 자동으로 호출 해주는 구문입니다. 커넥션, 입출력 스트림과 같은 자원을 사용 한 후 반드시 close를 해주어야 하는데 이러한 자원들을 편하게 관리할 수 있습니다.
또한 try-with-resources는 close()를 호출하면서 exception이 발생한 경우 기존의 exception을 SuppressedException으로 자동으로 관리해줍니다.
우선 try-with-resources에 사용할 AutoCloseable 구현체를 만들어 줍시다.
public class ExceptionalResource implements AutoCloseable {
public void processSomething() {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Thrown from processSomething()");
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
throw new NullPointerException("Thrown from close()");
}
}processSomething()에서는 IllegalArgumentException을, 오버라이딩 한 close()에서는 NullPointerException를 throw 해줍니다.
public static void demoExceptionalResource() throws Exception {
try (ExceptionalResource exceptionalResource = new ExceptionalResource()) {
exceptionalResource.processSomething();
}
}try-with-resources문이 끝나고 close()가 자동으로 호출되면 NullPointerException이 throw 될 것입니다.
@Test
void tryWithResource() {
IllegalArgumentException exception = assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> {
demoExceptionalResource();
});
assertEquals("Thrown from processSomething()", exception.getMessage());
Throwable[] suppressed = exception.getSuppressed();
assertEquals(1, suppressed.length, "Suppressed 예외는 1개여야 합니다.");
Throwable suppressedException = suppressed[0];
assertInstanceOf(NullPointerException.class, suppressedException);
assertEquals("Thrown from close()", suppressedException.getMessage());
exception.printStackTrace();
}테스트 해봅시다.
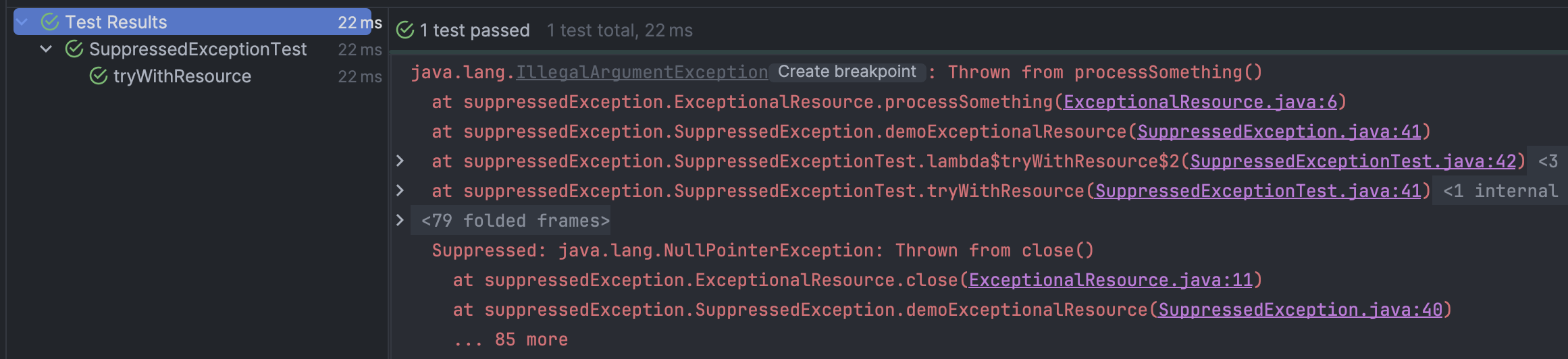
테스트도 잘 성공했고 Suppressed Exception 또한 잘 트레이싱하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. 훨씬 깔끔하고 가독성 좋은 코드로 Suppressed Exception을 관리할 수 있습니다!
⭐️ Suppressed된 Exception의 차이
주의를 해야 할 점이 있는데 Suppressed된 Exception이 다르다는 점입니다.
try-catch-finally은 기존의 Exception이 Suppressed 되었고, try-with-resources는
close()할 때 발생한 Exception이 Suppressed 되었습니다.근본 원인인 Exception이 메인이고, 그로 인해 발생한 Exception이 Suppressed 된 것입니다. 확실히 try-with-resources 쪽이 디버깅을 할 때 수월할 것 같습니다.
