Linked List 문제1 - Linked List Cycle
주소 : https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/description/
문제 설명 : Linked List의 head가 주어질 때 이 Linked List가 순환하는지 확인하는 문제 순환하면 true 아니면 false
풀이 1
- 방문한 것을 하나씩 저장하면서 해당 node를 갔었는지 체크하는 방식
풀이 코드1
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 방문한 것을 저장하기 위한 HashSet ->
// 이유 - visited를 한번만 방문하면 되기 때문에 여러번 방문한 것은 저장할 필요가 없음
HashSet<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<>();
// node의 header를 정해줌
ListNode cur = head;
// cur을 계속 확인하면서 visited안에 cur이 들어 있는지 확인하고 없으면 visited에 cur을 넣음
// 만약 cur이 visited에 있다면 순환해서 해당 cur에 한번더 방문한것이기 때문에 true를 리턴
// 만약 특정 노드에서 값이 null이 된다면 순환하지 않는 것이기 때문에 return false
while (cur != null) {
if (visited.contains(cur)){
return true;
}
visited.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
}- 시간 복잡도 : O(n)
풀이2
- 풀이 : 투 포인터를 이용한다. A 포인터는 B포인터보다 두발자국씩 나간다. 만약 Linked List가 순환한다면 두 포인터는 언젠가 한 노드에서 만나게 된다.
예시) 10km로 달리는 사람A 와 20km로 달리는 사람 B가 있다. 두명은 원 모형의 운동장을 끊임없이 달린다. 그렇게 된다면 20km로 달리는 사람 B가 아무리 운동장이 넓든 말든 사람 A를 따라잡아 둘이 만나게 된다.
풀이 코드2
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
// 먼저 나가는 first 포인터 , 늦게 나가는 second 포인터 정의
ListNode first = head, second =head;
// 만약 first와 first의 다음 노드가 null이 아니라면? 계속 달린다.
// 만약 first와 first.next가 null이 된다면 first.next.next를 정의할 수 없게 된다.
while (first != null && first.next!=null) {
// first는 두 발자국 먼저 나가기 위해 next.next를 하고
// second는 next로 한 발자국만 나간다.
second = second.next;
first = first.next.next;
// 만약 first와 second가 만나게 된다면 순환하는 것이기 때문에 return true
if (first == second) {
return true;
}
}
// 만약 만나지 않고 first가 null이 된다면 return false
return false;
}
}Linked List 문제2 - Linked List Cycle 2
주소 : https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
문제 설명 : 순환이 시작되는 node의 값을 반환해라!!
풀이 방법
- 투 포인터를 이용한다. 앞서 나가는 first 포인터와 천천히 나가는 second 포인터를 이용하여 만약 second와 first값이 동일해지면 fisrt를 다시 head값으로 변경한 뒤 두 포인터가 만날 때 까지 두 포인터를 값을 변경시킨다. 이것은 플로이드 주기 찾기 알고리즘으로 두 포인터가 만났을 때 만나는 지점까지의 거리와 시작점까지의 거리가 동일하다는 개념을 이용한다.
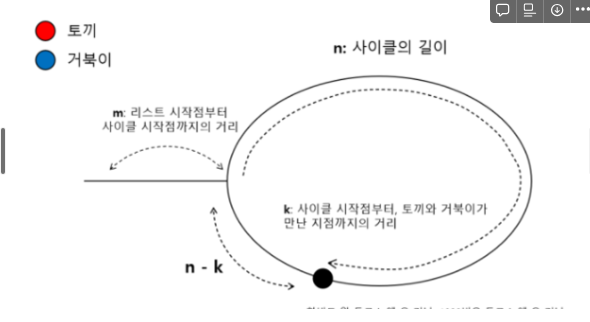
풀이 코드
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
// 투 포인터 first와 second 설정
ListNode first = head, second = head;
// first는 두 발자국 먼저 나가기 때문에 first.next와 first가 null이면 first.next.next가 성립되지 않아 체크
while (first != null && first.next!=null) {
// first는 두발자국, second는 한 발자국 먼저 나간다.
first = first.next.next;
second = second.next;
// 만약 second와 first가 만나게 되면
if (second == first) {
// first를 초기화
first = head;
//first와 second가 같아질 때 까지 한발자국씩 나가게한다.
while (first!=second) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
// 이때 first와 second가 만나면 그 점이 순환의 시작점
return first;
}
}
return null;
}
}Linked List 문제3 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists
주소 : https://leetcode.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/description/
설명 : 서로 다른 두 Linked List가 교차점에서 만나서 이어질 때 교차점을 구해라!
풀이 방법
- 두 개의 Linked List를 정의하고 nodeA와 nodeB가 같아질 때 까지 아래의 반복을 수행한다.
첫번째 nodeA가 null이 되면 nodeA는 headB로 바꿔주고 아니라면 nodeA를 전진
두번째 nodeB가 null이 되면 nodeB는 headA로 바꿔주고 아니라면 nodeB를 전진
이렇게 되면 두개의 연결 리스트가 길이가 다르더라도 어느 순간 교차점에서 만나게 된다.
풀이 코드
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
// 연결 노드를 각각 설정해준다.
ListNode nodeA = headA;
ListNode nodeB = headB;
// 위의 설명과 동일하게 각각의 연결 리스트의 행위를 수행
while (nodeA != nodeB) {
// nodeA 이동
if (nodeA == null) {
nodeA = headB;
} else {
nodeA = nodeA.next;
}
// nodeB 이동
if (nodeB == null) {
nodeB = headA;
} else {
nodeB = nodeB.next;
}
}
return nodeA;
}
}
Linked List 문제4 - Remove Nth Node From End of List
설명 : 연결 리스트에서 n번째 노드를 삭제한 연결 리스트를 반환 하는 문제
주소 : https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/description/
문제 풀이
- 투 포인터를 이용한다.
- n 번째까지 fast를 이동한다.
- 만약 fast.next가 null이 되면 head.next를 반환
- n번째까지 fast를 이동했을 때 null이 아니면 fast.next가 null이 될대까지 slow와 fast노드를 이동시킨다.
- 마지막으로 slow.next값을 slow.next.next로 매핑해주면서 연결을 바꿔준다.
문제 코드
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
if (fast == null) {
return head.next;
}
while (fast.next !=null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return head;
}
}- 시간 복잡도 : O(n)
추가 설명 : 특정 위치의 node를 삭제하기 위해서는 그 특정 노드의 바로 직전 노드와 이어지는 값이 next.next로 이동시켜주면된다.
그래서 특정 노드의 바로 직전 node를 찾는 것이 중요!!
