다익스트라 문제는 처음 풀어보았다.
다익스트라의 로직을 이해한 후 직접 구현해보았다.
👨💻 문제
✍️ 풀이
📘 Node 클래스
간선의 역할을 하는 Node 클래스
도착지의 인덱스와 비용을 저장
private static class Node {
int index;
int cost;
public Node(int index, int cost) {
this.index = index;
this.cost = cost;
}
public String toString() {
return String.format("( -> %d : %d )", index, cost);
}
}toString() 메소드는 로깅을 위한 메소드
🧮 다익스트라 알고리즘
다익스트라 알고리즘은 임의의 출발 정점을 기준으로 모든 정점들의 최단 거리를 구하는 알고리즘이다.
[1]
모든 정점까지의 거리를 저장하는 배열을 만든다.
초기화는 모두 무한대값으로 지정하였다.
[2]
이미 방문한 정점은 이후에 방문하지 않는다.
이를 확인하기 위한 부울 상수 배열을 만들었다.
[3]
임의의 출발점으로부터 방문을 시작한다.
정점들의 수만큼 방문을 반복한다.
private static void dijkstra() {
// [1]
costs = new int[cityCnt + 1];
for (int i=1; i<=cityCnt; i++) {
costs[i] = INF;
}
// [2]
visited = new boolean[cityCnt + 1];
// [3]
costs[startingPoint] = 0;
for (int i=0; i<cityCnt; i++) {
visit(getMinDistanceUnvisitedCityIndex());
}
}🚪 방문
방문한 정점으로부터 연결된 모든 정점까지 거리를 측정한다.
기록되어 있는 거리보다 짧다면 갱신한다.
private static void visit(int from) {
visited[from] = true;
for (Node root : roots.get(from)) {
int to = root.index;
int entireCost = root.cost + costs[from];
if (costs[to] > entireCost) {
costs[to] = entireCost;
}
}
}🔎 다음에 방문할 정점
다음에 방문할 정점은 아직 방문하지 않은, 출발점으로부터 거리가 가장 짧은 정점이다.
private static int getMinDistanceUnvisitedCityIndex() {
int minDistUnvisitedCityIndex = 0;
int minDistUnvisitedCityDist = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i=1; i<=cityCnt; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
if (minDistUnvisitedCityDist > costs[i]) {
minDistUnvisitedCityIndex = i;
minDistUnvisitedCityDist = costs[i];
}
}
return minDistUnvisitedCityIndex;
}
📄 전체 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Main {
private static int cityCnt;
private static int busCnt;
private static List<List<Node>> roots = new ArrayList<>();
private static int startingPoint;
private static int destination;
private static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private static int[] costs;
private static boolean[] visited;
private static class Node {
int index;
int cost;
public Node(int index, int cost) {
this.index = index;
this.cost = cost;
}
public String toString() {
return String.format("( -> %d : %d )", index, cost);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
input();
dijkstra();
System.out.println(costs[destination]);
}
private static void input() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
cityCnt = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
busCnt = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
roots = Stream.generate(() -> new ArrayList<Node>()).limit(cityCnt + 1).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (int i = 0; i < busCnt; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int cost = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
roots.get(from).add(new Node(to, cost));
}
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
startingPoint = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
destination = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
private static void dijkstra() {
costs = new int[cityCnt + 1];
for (int i=1; i<=cityCnt; i++) {
costs[i] = INF;
}
visited = new boolean[cityCnt + 1];
costs[startingPoint] = 0;
for (int i=0; i<cityCnt; i++) {
visit(getMinDistanceUnvisitedCityIndex());
}
}
private static int getMinDistanceUnvisitedCityIndex() {
int minDistUnvisitedCityIndex = 0;
int minDistUnvisitedCityDist = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i=1; i<=cityCnt; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
if (minDistUnvisitedCityDist > costs[i]) {
minDistUnvisitedCityIndex = i;
minDistUnvisitedCityDist = costs[i];
}
}
return minDistUnvisitedCityIndex;
}
private static void visit(int from) {
visited[from] = true;
for (Node root : roots.get(from)) {
int to = root.index;
int entireCost = root.cost + costs[from];
if (costs[to] > entireCost) {
costs[to] = entireCost;
}
}
}
}❓ 의문
해당 소스코드의 다음 정점을 찾는 메소드는 선형으로 구현되어 있다.
이 부분에 있어서, 가장 거리가 짧은이라는 우선순위가 정해져 있기에 우선순위 큐를 사용하면 더 빠를 것이라고 생각하였지만,
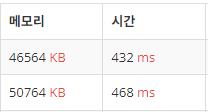
위 : 선형
아래 : 우선순위 큐우선순위 큐를 사용한 제출에서 더 많은 메모리와 시간을 소모하였다.
이는 정점의 수와 간선의 수의 비율에 따른 차이로 보인다.
정점이 많아지고 간선이 적어진다면 우선순위 큐를 통한 탐색이 더 좋은 효율을 보일 것으로 생각된다.
📄 우선순위 큐를 사용한 소스코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Main {
private static int cityCnt;
private static int busCnt;
private static List<List<Node>> roots = new ArrayList<>();
private static int startingPoint;
private static int destination;
private static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
private static int[] costs;
private static boolean[] visited;
private static PriorityQueue<Node> nextNodes;
private static class Node {
int index;
int cost;
public Node(int index, int cost) {
this.index = index;
this.cost = cost;
}
public String toString() {
return String.format("( -> %d : %d )", index, cost);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
input();
dijkstra();
System.out.println(costs[destination]);
}
private static void input() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
cityCnt = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
busCnt = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
roots = Stream.generate(() -> new ArrayList<Node>()).limit(cityCnt + 1).collect(Collectors.toList());
for (int i = 0; i < busCnt; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int cost = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
roots.get(from).add(new Node(to, cost));
}
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
startingPoint = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
destination = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
private static void dijkstra() {
costs = new int[cityCnt + 1];
for (int i=1; i<=cityCnt; i++) {
costs[i] = INF;
}
visited = new boolean[cityCnt + 1];
nextNodes = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.cost - o2.cost);
costs[startingPoint] = 0;
nextNodes.add(new Node(startingPoint, 0));
for (int i=0; i<cityCnt && !nextNodes.isEmpty(); i++) {
Node node = nextNodes.poll();
int from = node.index;
if (visited[from]) {
i--;
continue;
}
visit(from);
// System.out.println(costs);
}
}
private static void visit(int from) {
for (Node root : roots.get(from)) {
int to = root.index;
int entireCost = root.cost + costs[from];
if (costs[to] > entireCost) {
costs[to] = entireCost;
if (!visited[to]) {
visited[from] = true;
nextNodes.add(new Node(to, entireCost));
}
}
}
}
}