1. Wrapper Class 정의
- 자바의 8가지 기본 타입을 객체화하기 위해 포장한 형태로, 다양한 메소드와 필드를 사용할 수 있다.
2. Wrapper Class 종류
| Primitive type | Wrapper class |
|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
3. 박싱(Boxing)과 언박싱(UnBoxing)
- 박싱 : 기본 타입 → 래퍼 클래스 변환
- 언박싱 : 래퍼 클래스 → 기본 타입 변환
4. Wrapper Class 최대값, 최소값
public class WrapperClassEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte byteMinValue = Byte.MIN_VALUE;
byte byteMaxValue = Byte.MAX_VALUE;
int intMinValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int intMaxValue = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
long longMinValue = Long.MIN_VALUE;
long longMaxValue = Long.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.println(String.format("Byte 최소값 : %d, 최대값 : %d", byteMinValue, byteMaxValue));
System.out.println(String.format("Integer 최소값 : %d, 최대값 : %d", intMinValue, intMaxValue));
System.out.println(String.format("Long 최소값 : %d, 최대값 : %d", longMinValue, longMaxValue));
System.out.println(String.format("Byte 최소값 : %d, 값 비교 : %b", (int) -Math.pow(2, 7), Byte.MIN_VALUE == -Math.pow(2, 7)));
System.out.println(String.format("Integer 최소값 : %d, 값 비교 : %b", (int) -Math.pow(2, 31), Integer.MIN_VALUE == -Math.pow(2, 31)));
System.out.println(String.format("Integer 최대값 : %d, 값 비교 : %b", (int) (Math.pow(2, 31) - 1), Integer.MAX_VALUE == (Math.pow(2, 31) - 1)));
}
}
- MAX_VALUE, MIN_VALUE 필드는 최대값과 최소값을 표현한다.
- Math.pow( )메서드를 통해서도 최대값과 최소값을 구할 수 있다.
4.1 Byte 최대값과 최소값
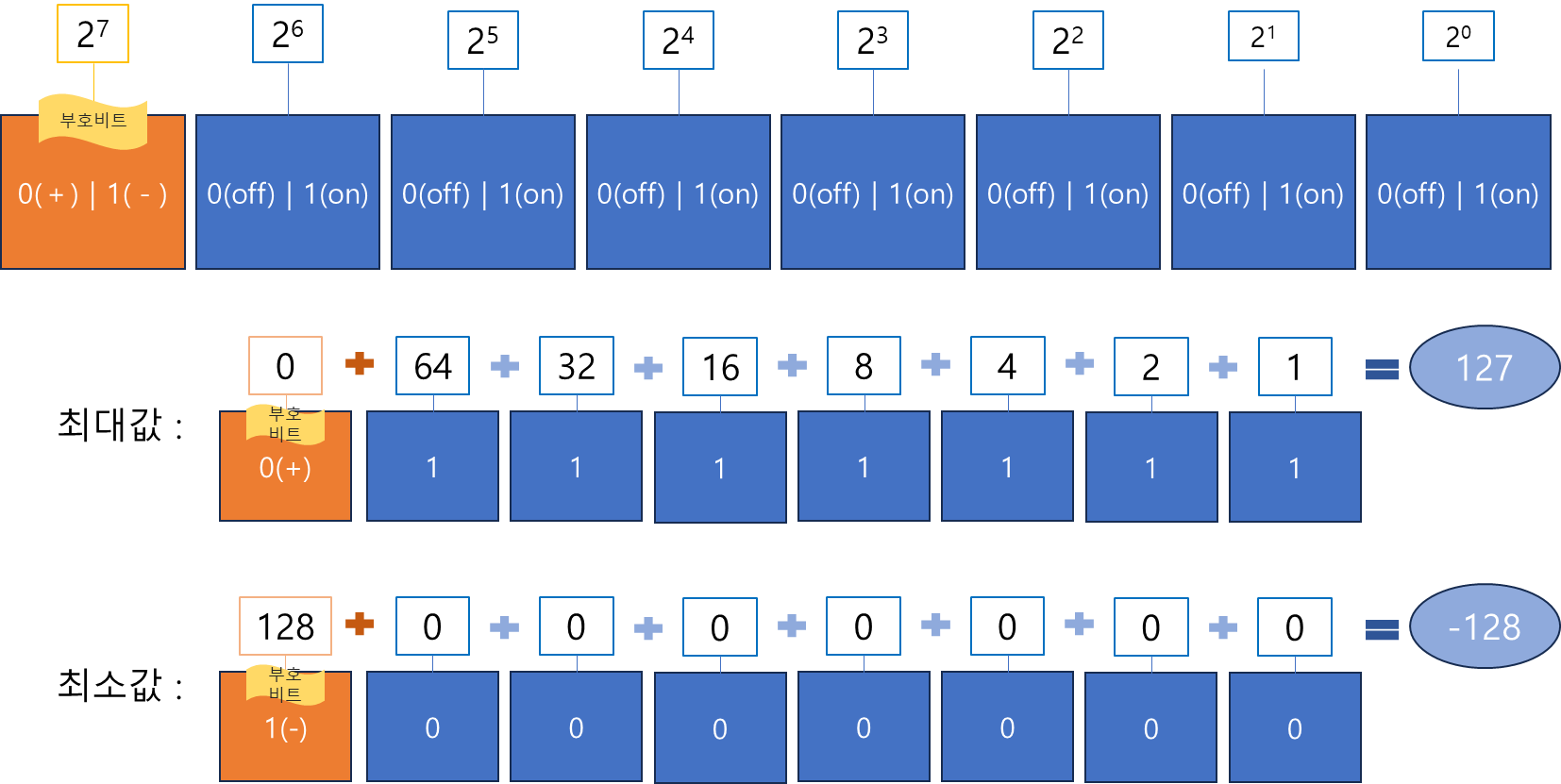
bit는 컴퓨터가 이해할 수 있는 최소 단위로 0과 1로 구성되어 있다.Byte는 컴퓨터에서 사용되는 가장 일반적인 데위터 단위로 1Byte는 8bit로 구성되고,
정수 Byte 타입은 8bit의 메모리 크기를 가진다.
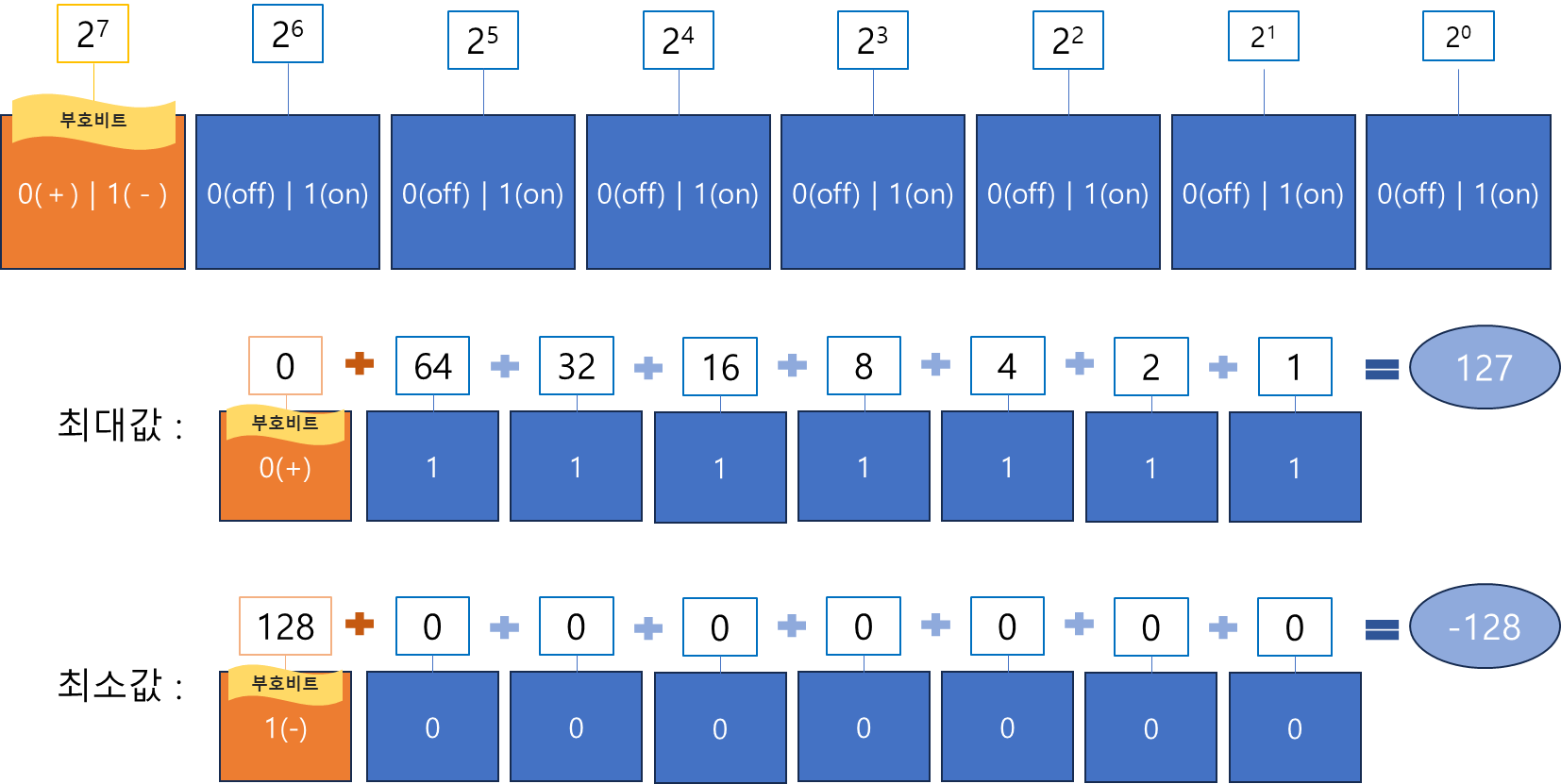
- 제일 왼쪽에 있는 비트는 부호비트로 음수를 나타낼 수 있다.
- 2진수는 0과 1로 표시하는데, 0은 전기 스위치의 on, 1은 전기 스위치 off에 기인한다.
5. 오버플로우(overflow)와 언더플로우(underflow)
- 오버플로우 : 데이터 값의 최대 표현 범위에서 벗어나는 것
- 언더플로우 : 데이터 값의 최소 표현 범위에서 벗어나는 것
- 오버플로우와 언더플로우 발생 시 해당 타입의 최소값 또는 최대값으로 되돌아가기 때문에 연산 시 주의하여야 한다.
public class WrapperClassEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte byteMinValue = Byte.MIN_VALUE;
byte byteMaxValue = Byte.MAX_VALUE;
int intMinValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int intMaxValue = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
System.out.printf("byte 최소값 : %d, 언더플로우 : %d\n", byteMinValue, --byteMinValue);
System.out.printf("byte 최소값 : %d, 오버플로우 : %d\n", byteMaxValue, ++byteMaxValue);
System.out.printf("int 최소값 : %d, 언더플로우 : %d\n", intMinValue, --intMinValue);
System.out.printf("int 최소값 : %d, 오버플로우 : %d\n", intMaxValue, ++intMaxValue);
}
}
5.1 Byte 오버플로우
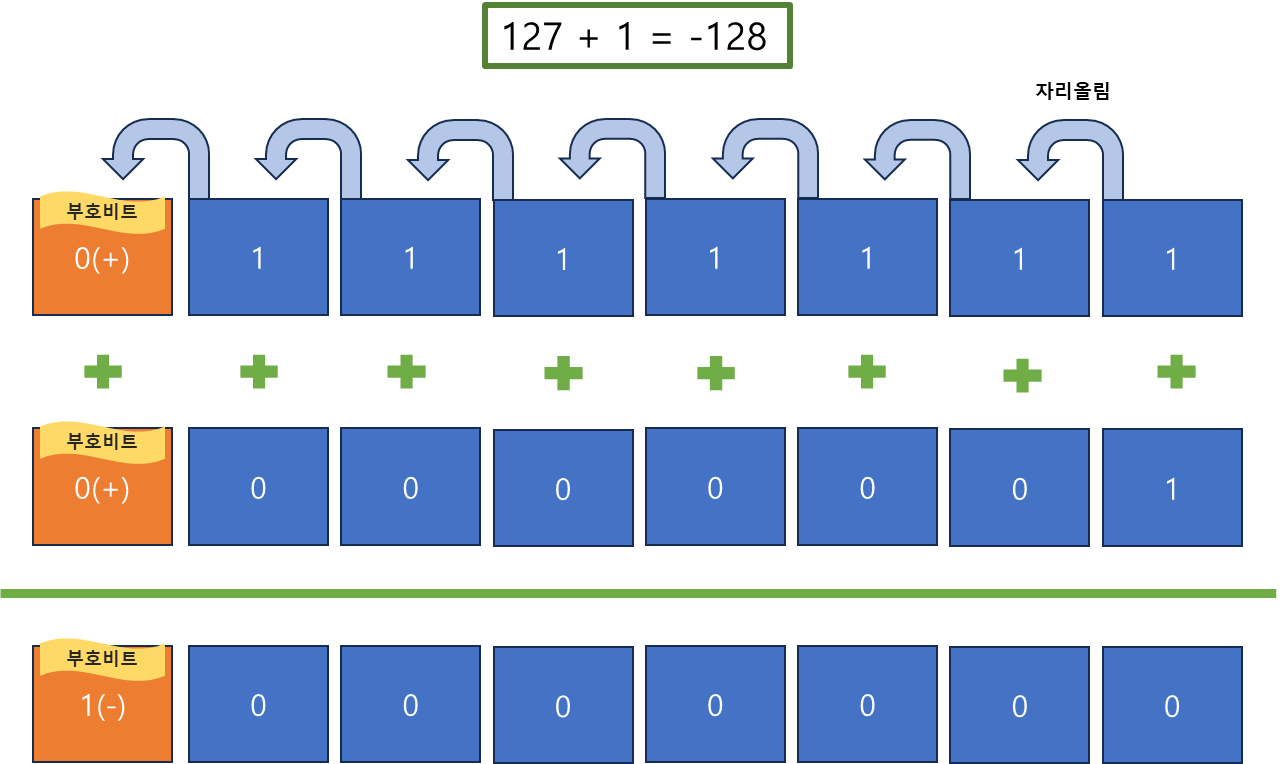
- 2진수 덧셈에서 1 + 1은 10이 된다. 왜냐하면
10진수 2 → 2진수 10으로 표현되기 때문이다.
5.2 Byte 언더플로우
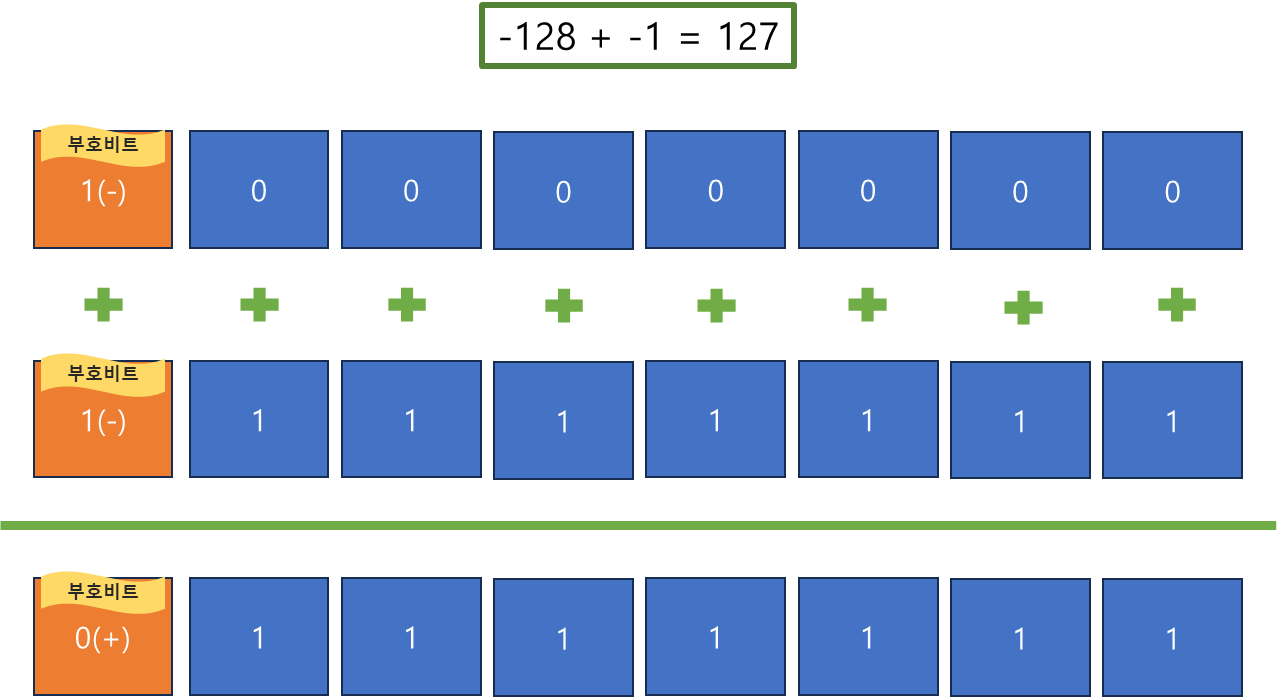
- -1은 부호비트를 사용하여
10000001 표시할 수 있는데, 이는 +0과 -0이 존재하는 문제가 있고, 양수·음수 간 연산이 어렵다.
그래서 -1은 2의 보수를 이용해 계산한다. 2의 보수란 1의 보수(자리 비트 값 반전)를 구한 값에 + 1 한 것이다.
즉, 1의 2진수 : 00000001 → 1의 보수 : 11111110 → 더하기 1 : 11111111로,
-1의 2진수는 11111111로 표현할 수 있다.(-128 + (64 + 32+ 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1) = -1)