
안녕하세요 !
오늘은 백준 - 큐 2 문제를 가져왔습니다.
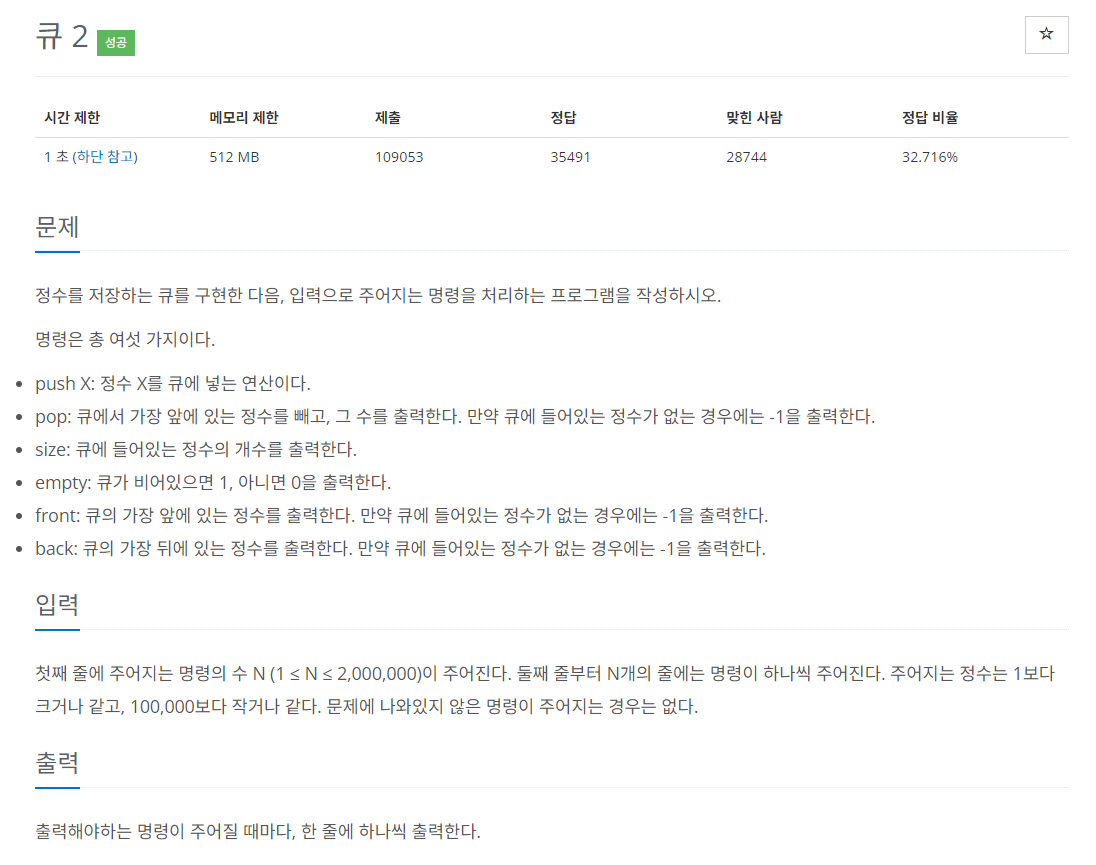
문제 설명
해결 방법
문제를 해결한 방법을 정리해보겠습니다.
- 명령의 개수를 입력받고 그 만큼 반복을 하며 명령을 입력받습니다.
- 명령이 push X일 때 큐에 요소를 넣습니다.
- 입력이 pop일 때 큐에 요소가 없으면 -1을, 있으면 큐의 첫 번째 요소를 출력하고 제거합니다.
- 입력이 size일 때 큐 요소의 개수를 출력합니다.
- 입력이 empty일 때 큐가 비었으면 1을, 아니면 0을 출력합니다.
- 입력이 front일 때 큐의 요소가 없으면 -1을, 있으면 첫 번째 요소를 출력합니다.
- 입력이 back일 때 큐의 요소가 없으면 -1을, 있으면 바지막 요소를 출력합니다.
- 명령의 개수를 입력받고 그 만큼 반복을 하며 명령을 입력받습니다.
n = int(sys.stdin.readline().strip()) for i in range(n): l = sys.stdin.readline().strip().split()
- 명령이 push X일 때 큐에 요소를 넣습니다.
if l[0] == "push": queue.append(int(l[1]))
- 입력이 pop일 때 큐에 요소가 없으면 -1을, 있으면 큐의 첫 번째 요소를 출력하고 제거합니다.
elif l[0] == "pop": if len(queue) == 0: print(-1) else: print(queue[0]) queue.popleft()
- 입력이 size일 때 큐 요소의 개수를 출력합니다.
elif l[0] == "size": print(len(queue))
- 입력이 empty일 때 큐가 비었으면 1을, 아니면 0을 출력합니다.
elif l[0] == "empty": print(int(not len(queue)))
- 입력이 front일 때 큐의 요소가 없으면 -1을, 있으면 첫 번째 요소를 출력합니다.
elif l[0] == "front": if len(queue) == 0: print(-1) else: print(queue[0])
- 입력이 back일 때 큐의 요소가 없으면 -1을, 있으면 바지막 요소를 출력합니다.
elif l[0] == "back": if len(queue) == 0: print(-1) else: print(queue[-1])
시간 초과
처음에 이 문제를 풀었을 때 큐를 리스트로 구현하였습니다.
그러다 보니 삭제할 때 queue.pop(0) 시간복잡도가 O(N)인 코드를 사용하다보니 시간 초과가 떴습니다.
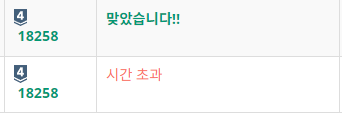
그래서 queue를 collections의 deque를 사용해서 구현했습니다.
deque를 사용하게 되면 pop과 push 연산이 매우 빨라집니다.
전체 코드
import sys
from collections import deque
queue = deque()
n = int(sys.stdin.readline().strip())
for i in range(n):
l = sys.stdin.readline().strip().split()
if l[0] == "push":
queue.append(int(l[1]))
elif l[0] == "pop":
if len(queue) == 0:
print(-1)
else:
print(queue[0])
queue.popleft()
elif l[0] == "size":
print(len(queue))
elif l[0] == "empty":
print(int(not len(queue)))
elif l[0] == "front":
if len(queue) == 0:
print(-1)
else:
print(queue[0])
elif l[0] == "back":
if len(queue) == 0:
print(-1)
else:
print(queue[-1])