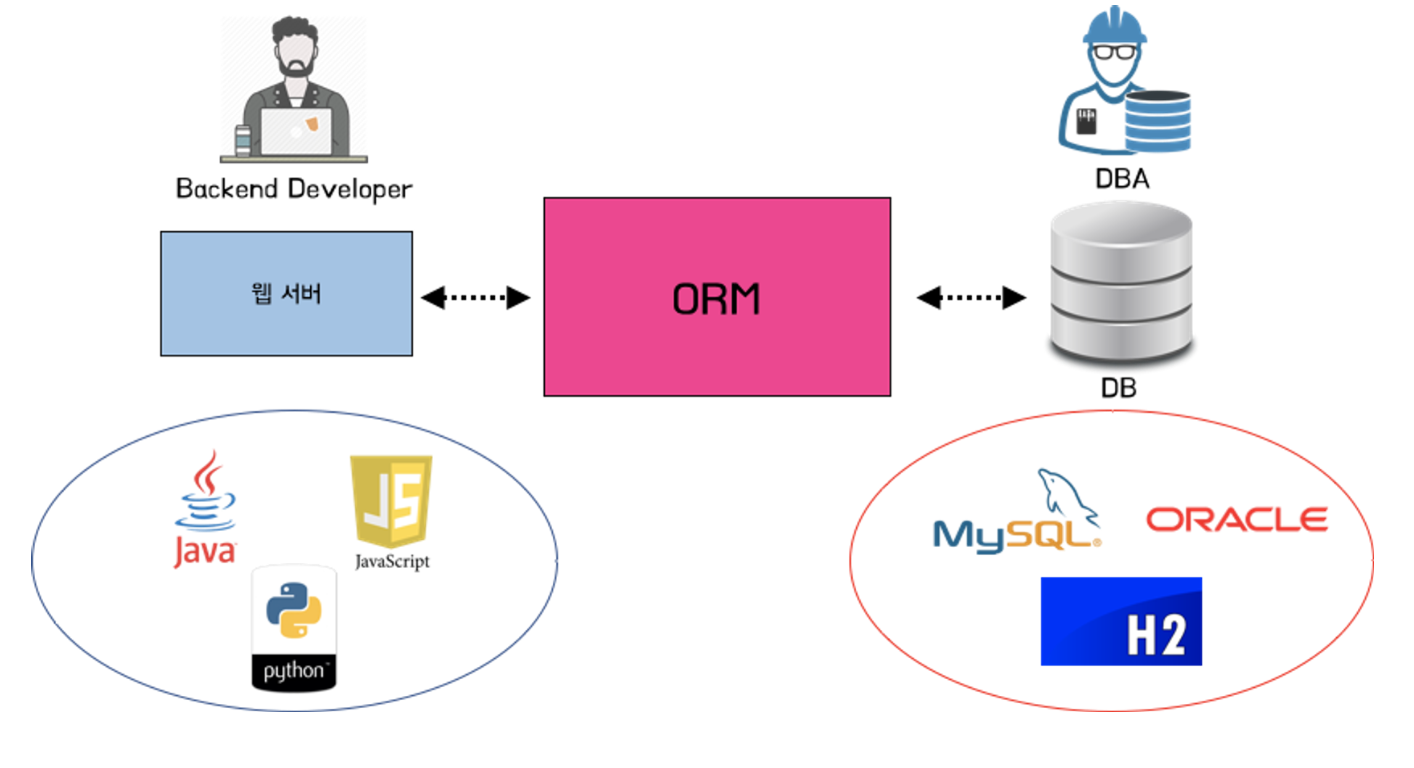
Object-Relational Mapping (ORM)
ORM is a technology that maps class objects with data points in the data base.
💡This simplifies the lengthy process we went through when using JDBC.
Java Persistence API (JPA)
JPA is one of the most well known examples of ORM.
Hybernate: a widely used Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework in Java that simplifies the development of Java applications by handling the interaction between Java objects and a relational database.
Persistence Context
The persistence context is a temporary, in-memory data store that holds entity instances managed by an EntityManager within a transactional scope. It ensures that any changes made to entities are tracked and synchronized with the database when the transaction is committed, acting as a first-level cache for improved performance.
Entity Manager
The EntityManager is the interface in JPA that handles operations such as persisting, retrieving, updating, and deleting entities in the persistence context. It is responsible for interacting with the persistence context and the database, providing the main API for managing the lifecycle of entities.
Entity Manager Factory
The EntityManagerFactory is a factory for creating EntityManager instances. It is a heavyweight object that represents a configuration and connection to the underlying database, and it should be created once per application and reused to create EntityManager instances as needed.
JPA Transaction
A JPA transaction is a series of operations performed within a transactional context, ensuring that all changes to the database are committed as a single unit. Transactions provide atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID properties), and are managed by the EntityManager in collaboration with the persistence context.
How do they all work together?
The EntityManagerFactory creates EntityManager instances, which in turn manage the Persistence Context for handling entity states. The EntityManager interacts with the persistence context to perform CRUD operations, and the JPA Transaction ensures that these operations are executed within a safe, consistent, and isolated environment, with all changes being committed to the database at the end of the transaction. Together, these components form the core of JPA's data management and transaction handling system.
