Spring Data JPA
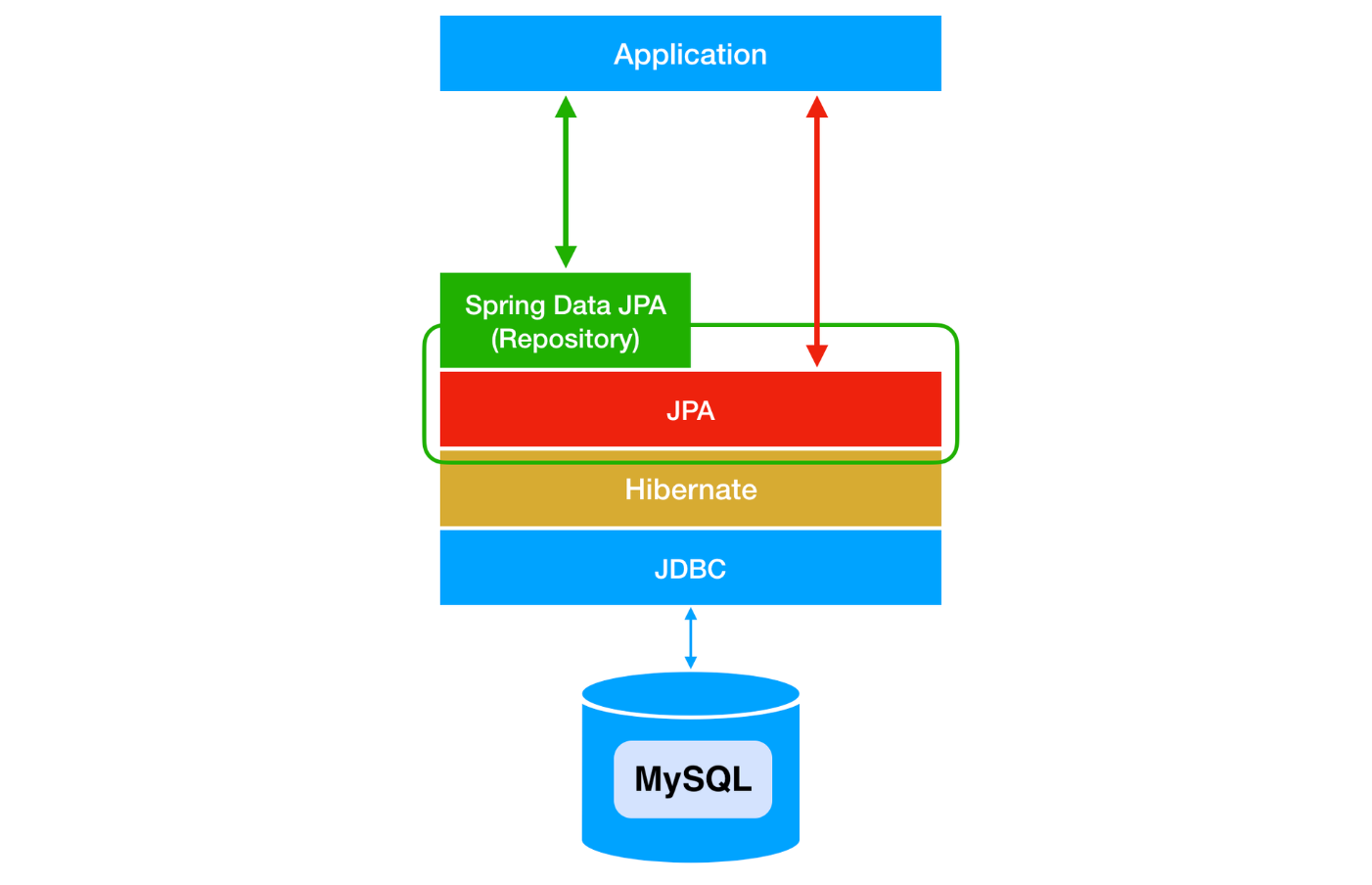
Spring Data JPA is just one of the module written to make use of JPA easier.
Using the entity manager
There is two, high and low levels of interacting with the database in JPA.
Method 1 (high-level)
The interface of JpaRepository<"@Entity class", "@Id data type"> needs to be declared. Because you are using predefined methods from the JpaRepository, you can excute most basic database operations without adding new methods in the class repository.

Here is an example of JpaRepository in use:
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Transactional
public class CommentService {
private final ScheduleService scheduleService;
private final CommentRepository commentRepository;
// Modify an existing comment
public void updateComment(Long id, CommentRequestDto requestDto) {
Comment comment = commentRepository.findById(id) // findById method
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid schedule ID: " + id));
comment.setComment(requestDto.getComment());
}
...
}
Method 2 (fundamental, low-level)
Set up process:
step1: Make entity manager factory object.
step2: Make entity manager from entity manager factory.
step3: Make a transaction from entity manager.
step4: Begin transaction.
step5: Entity Managers manage entity as needed.
step6: Commit transaction.
step6: Close transaction.
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("memo");
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
@Test
@DisplayName("변경 감지 확인")
void test8() {
EntityTransaction et = em.getTransaction();
et.begin();
try {
System.out.println("변경할 데이터를 조회합니다.");
Memo memo = em.find(Memo.class, 4);
System.out.println("memo.getId() = " + memo.getId());
System.out.println("memo.getUsername() = " + memo.getUsername());
System.out.println("memo.getContents() = " + memo.getContents());
System.out.println("\n수정을 진행합니다.");
memo.setUsername("Update");
memo.setContents("변경 감지 확인");
System.out.println("트랜잭션 commit 전");
et.commit();
System.out.println("트랜잭션 commit 후");
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
et.rollback();
} finally {
em.close();
}
emf.close();
}Sample key methods
persist(Object entity): Adds the entity to the persistence context.remove(Object entity): Removes the entity from the persistence context.find(Class<T> entityClass, Object primaryKey): Retrieves an entity from the persistence context or the database.detach(Object entity): Detaches the specific entity from the persistence context.clear(): Clears the persistence context, detaching all entities.flush(): Forces the changes in the persistence context to be converted into SQL queries.commit(): Reflects the contents of the persistence context in the database.
JPA Auditing
JPA Auditing is a feature in Java Persistence API that automatically tracks and records changes to entity fields, such as creation and modification timestamps, without requiring manual updates in the application code.
-
@MappedSuperclass
- When JPA entity classes inherit from this abstract class, the member variables declared in the abstract class, such as
createdAtandmodifiedAt, are recognized as columns.
- When JPA entity classes inherit from this abstract class, the member variables declared in the abstract class, such as
-
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
- Includes auditing functionality in the class.
-
@CreatedDate
- The time is automatically saved when the entity object is created and stored.
- Since the initial creation time is saved and should not be modified thereafter, the
updatable = falseoption is added.
-
@LastModifiedDate
- The modified time is automatically saved whenever the value of the retrieved entity object is changed.
- After the initial creation time is saved, it is updated to the corresponding modification time whenever a change occurs.
-
@Temporal
- Used when mapping date types (like
java.util.Dateandjava.util.Calendar). - In the database, there are three separate types: Date, Time, and Timestamp.
- DATE: e.g.,
2023-01-01 - TIME: e.g.,
20:21:14 - TIMESTAMP: e.g.,
2023-01-01 20:22:38.771000
- DATE: e.g.,
- Used when mapping date types (like
@Getter
@MappedSuperclass
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public abstract class Timestamped {
@CreatedDate
@Column(updatable = false)
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
@LastModifiedDate
@Column
@Temporal(TemporalType.TIMESTAMP)
private LocalDateTime modifiedAt;
}Example use
Because the Timestamped class is extened in the Relationship class and the @EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class) is added, the created and modified date will be recorded.
package com.sparta.newsfeed.entity.relation;
import com.sparta.newsfeed.entity.Timestamped;
import com.sparta.newsfeed.entity.User;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;
@Entity
@Getter
@Table(name = "relationships")
@NoArgsConstructor
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public class Relationship extends Timestamped {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "sent_id")
private User sentUser;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "received_id")
private User receivedUser;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
private RelationshipStatusEnum status = RelationshipStatusEnum.WAITING;
public Relationship(User sentUser, User receivedUser) {
this.sentUser = sentUser;
this.receivedUser = receivedUser;
}
public void update(RelationshipStatusEnum relationshipStatusEnum){
this.status = relationshipStatusEnum;
}
}
Query Methods
Query methods sound just like SQL statements and they can be used to easily work with the database.
public List<MemoResponseDto> getMemos() {
// DB 조회
return memoRepository.findAllByOrderByModifiedAtDesc().stream().map(MemoResponseDto::new).toList();
}