Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
It is a virtual machine where you can run java.
The following is how you run java.
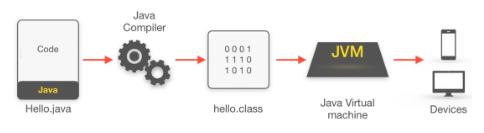
A compiler converts .java code to .class code which can be interpreted by the machine.
Components of JVM?
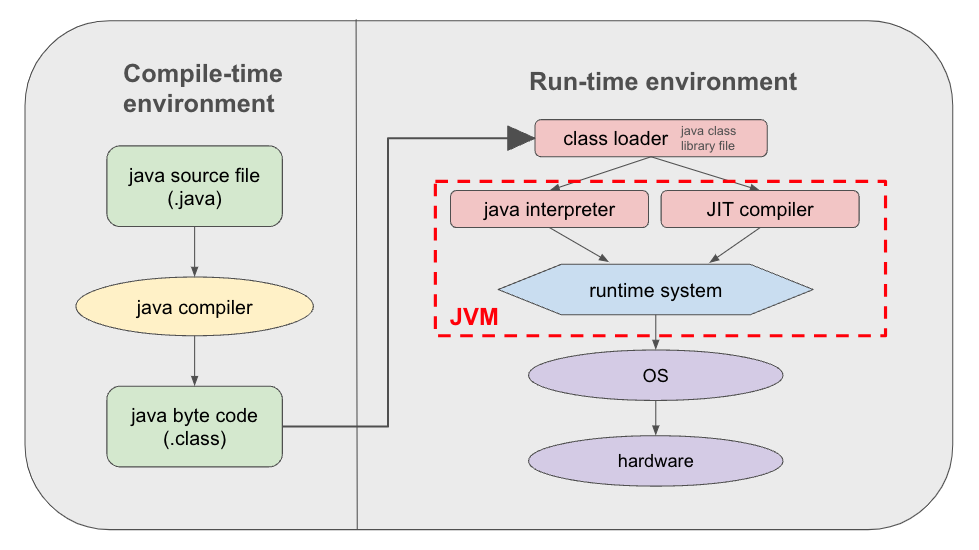
- Class Loader Subsystem is responsible for loading, linking, and initializing a Java class file (that is, “Java file”), otherwise known as dynamic class loading.
- Runtime Data Areas contain method areas, PC registers, stack areas, and threads.
- Execution Engine contains an interpreter, compiler, and garbage collection area.
Additional Explanations
Helpful YouTube Video1 (Korean, 8 min)
Helpful YouTube Video (Korean, 24 min)
- Runtime Data Areas
- Byte code is a non-runnable code generated after compilation of source code and it relies on an interpreter to get executed.
- Execution Engine
- Interpreter: converts byte code to machine assembly (=machine code).
- Just In Time (JIT) compiler: helps the interpreter (supporter)
- Garbage collection area:
Byte code vs Machine code
- Byte code is a non-runnable code generated after compilation of source code and it relies on an interpreter to get executed.
- Machine code is a set of instructions in machine language or in binary format and it is directly executed by CPU.
Running Java
JVM (compiling): converts .class file to machine language
Java Runtime Environment (JRE): converts .java to .class
Java Development Kit (JDK): does both what JVM and JRE does. It includes all the Java tools needed to run Java programs including debugging functions.
Java Language Structure/Grammar
Initial structure
Java is a programming lanugage that requires a main class and method as its basic structure. Also this outer most class's name should match the file name. For the code below the file name should be Main.java.
public class Main {
public static void main (String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}variable vs. non-variable (final)
Normally declared variable can change in value. However, when there is the key word 'final' written in front of it, the variable's value cannot be changed.
// this is an example of a non-changeable data which is like a constant
final int nbr = 10Integer variable types
- byte: numbers from -128 to 127 (8 bits, 1 byte)
- short: numbers from -32,768 to 32,767 (16 bits, 2 byte)
- int: numbers from -2147483648 to 2147483647 (32 bits, 4 byte)
- long: numbers from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to
9,223,372,036,854,775,807 (64 bits, 8 byte)
Real numbers
- float: Can express up to 3.4 * 10^38 (4 byte)
- can express more numbers than data type long.
- you have to add 'F' at the end of the number when writing it
float myFloat1 = 0.123F;
float myFloat2 = 0.123f;- double: Can express up to 1.7 * 10^308 (8 byte)
✨ All of the vairables discussed above are primitive type variables ✨
✨They also include boolean and char!✨
Reference vairables
Reference types serve as containers for memory addresses or references to objects rather than actually holding the object.
- Class Objects
- Array/List
- String
💡 For java double("") or single('') usage is unique! For example, you cannot use double quotes for char.
💡Common naming method is java is using the 🐪 camel case where the all keywords are capitalized except the very first. ex: myNumberBook
Printing an array (reference variable)
Method 1: Use java util library and convert the whole list to a string.
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}Method 2: Use a for-loop and index the array.
public class Main {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5};
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {
System.out.print(a[i]);
System.out.print(' ');
}
}
}Wrapper Class
Primitive data types such as Int, Double, and Long also exist as a Class. Because Classes have different attributes and methods, we can do so much more with our data when they are in the form of a class object rather that just the data type itself.
Boxing: Converting primitive data types to their corresponding wrapper classes.
Unboxing: Value of a wrapper class is converted back to a primitive type.
public class Main {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int nbr = 10;
Integer nbr1 = nbr; // boxing
System.out.println(nbr1.intValue()); // unboxing
}
}Memory
Stack
- static memory (fixed size/length)
- saves primitive values and the addresses/references of reference variables.
Heap
- dynamic memory (don't know the size/length)
- holds the actual contents that the reference points to.
Reference Variables
The address contained in the reference variables are saved in the stack and the actual contents are stored in the heap.
Scanner
Typecasting (examples)
double doubleNbr = 10.1212;
// convert double to int
int intNbr = (int)doubleNbr;
int intNbr = 10;
// convert int to float
float doubleNbr = (float)intNbr;
Auto Typecasting (example)
- Happens between similar data types (byte, int, long, double, float) and char to int.
- You cannot type cast a larger data type to a shorter one automatically.
- byte(1) → short(2) → int(4) → long(8) → float(4) → double(8)
char c = 'A';
int myInt = c;
System.out.println(myInt); //output is 65converting int to double
int intNbr = 200;
double doubleNbr = intNbr;⚠️ When you do division that results in a decimal and store it in int, it drops the decimals ⚠️
