What is Haversine?
The haversine algorithm is used to calculate the "great-circle distance" between two points on Earth. In the given image below, it referes to the length of the red line PQ.
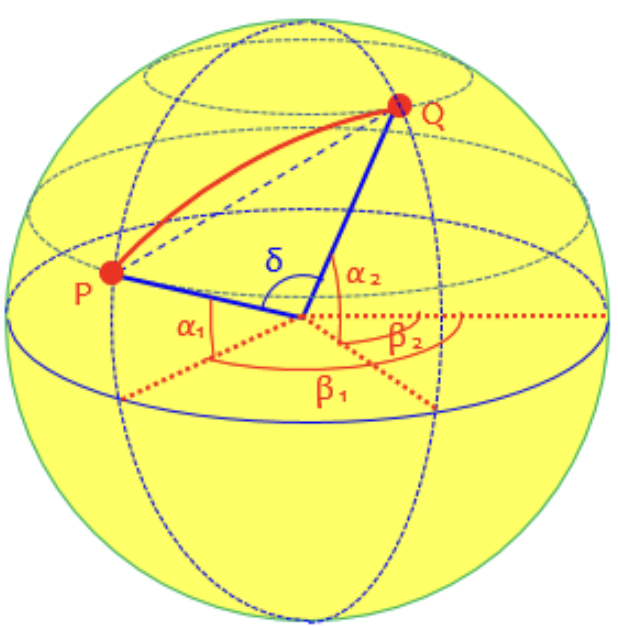
Intuitively it refers to the straight distance from one point location to another, without taking into account the shape of the roads.
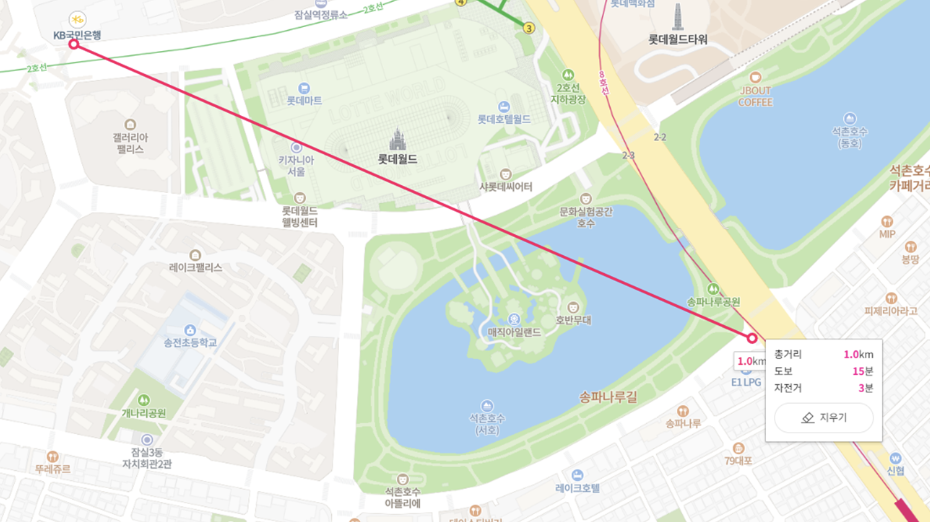
Usage
In our group project, we were developing a web app for users to reserve badminton courts and sign up for badminton clubs. We needed a search api that could filter the gyms in based how far they were from the user's registered location. Therefore, in order to calculate the distance we decided to used Haversine algorithm and create a filter for every 3, 5, 10, and 20km radius distance.
Theory & Technicals
The haversine algorithm can be broken down in to three major parts.
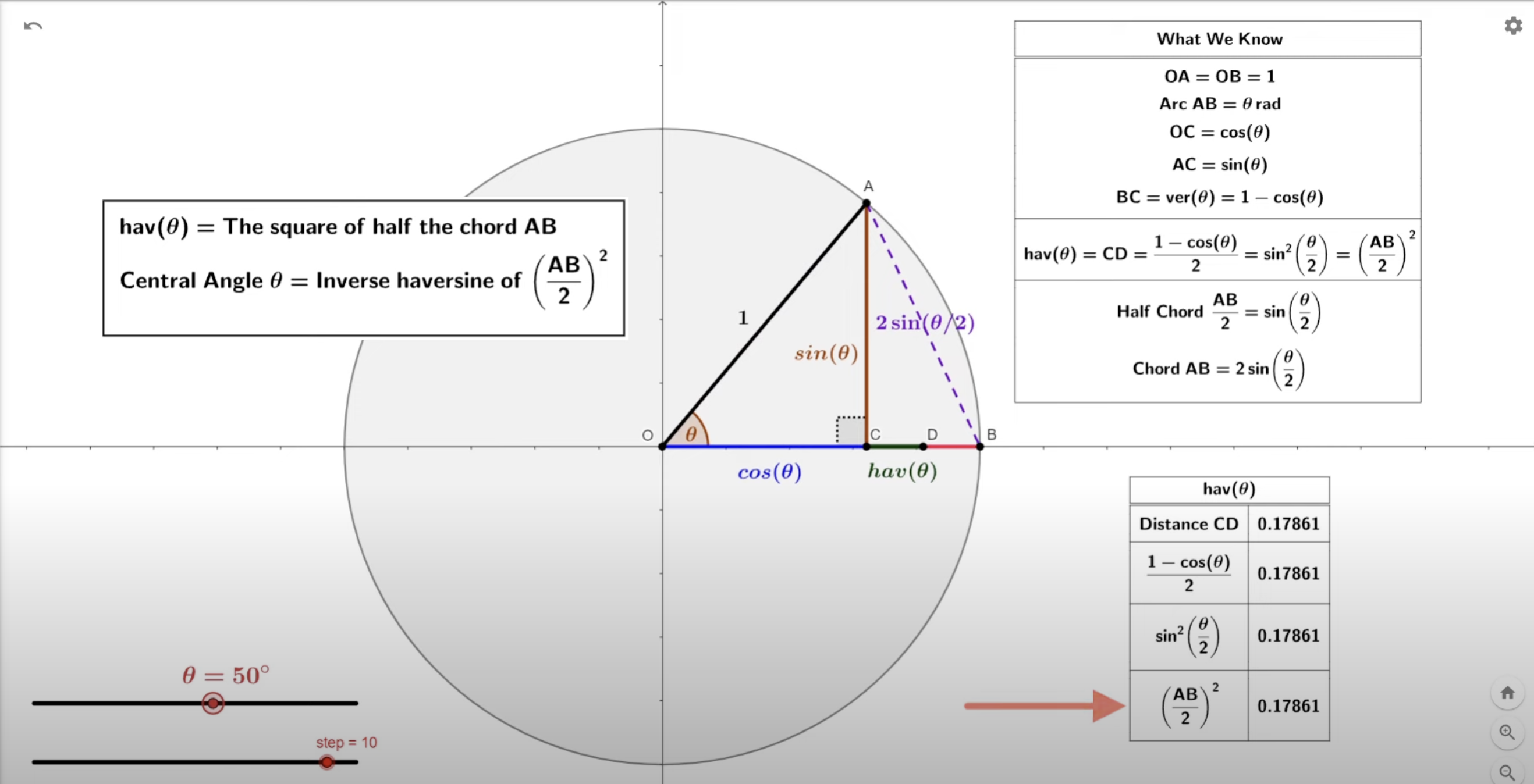
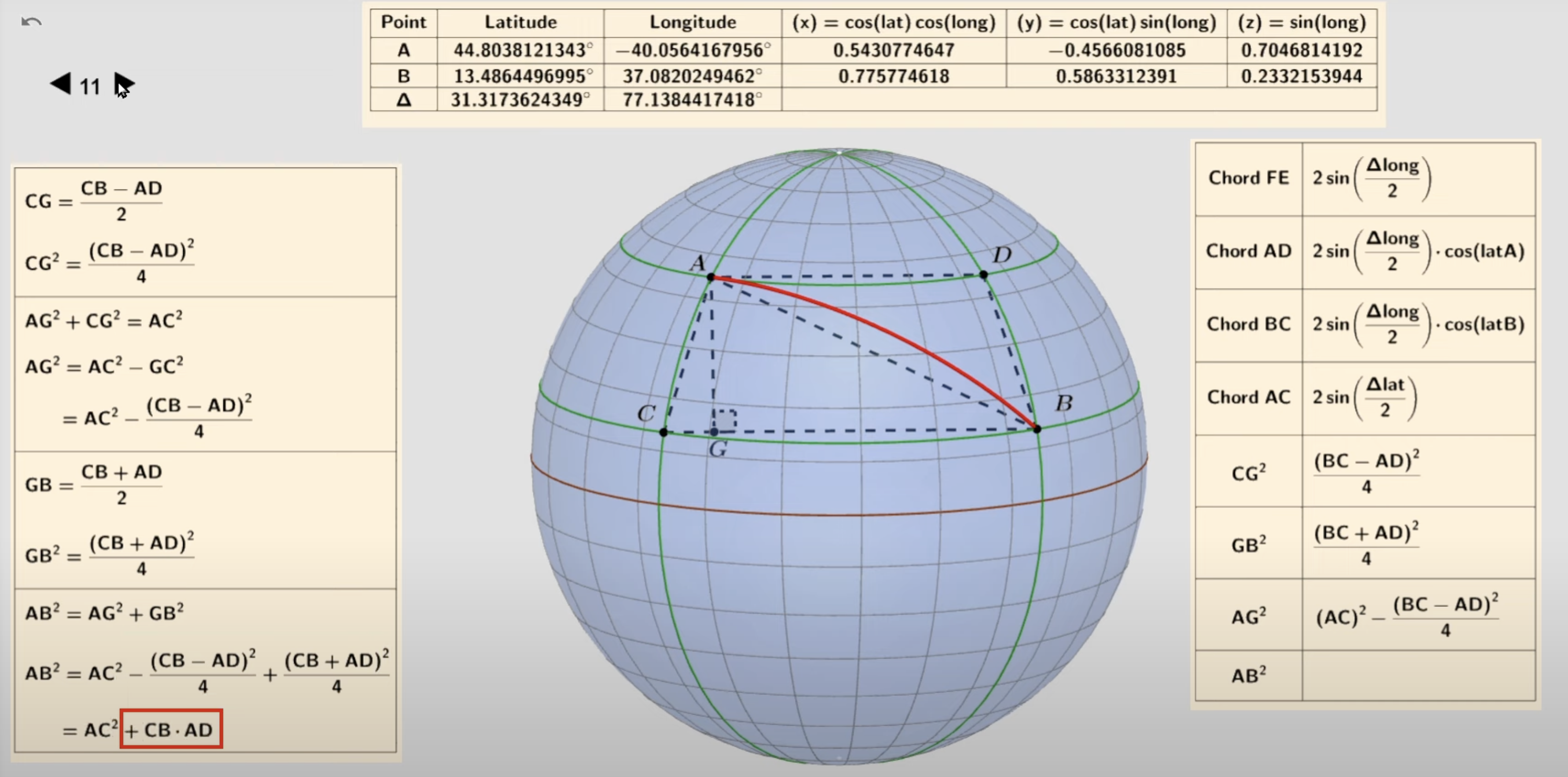
PART 1: understanding calculation of the 2D distance of AB
This step is crucial for calculating the distance between two points in the 3D space. The mathmatical derivation is shown in the image and better explained in the YouTube video that is attached.
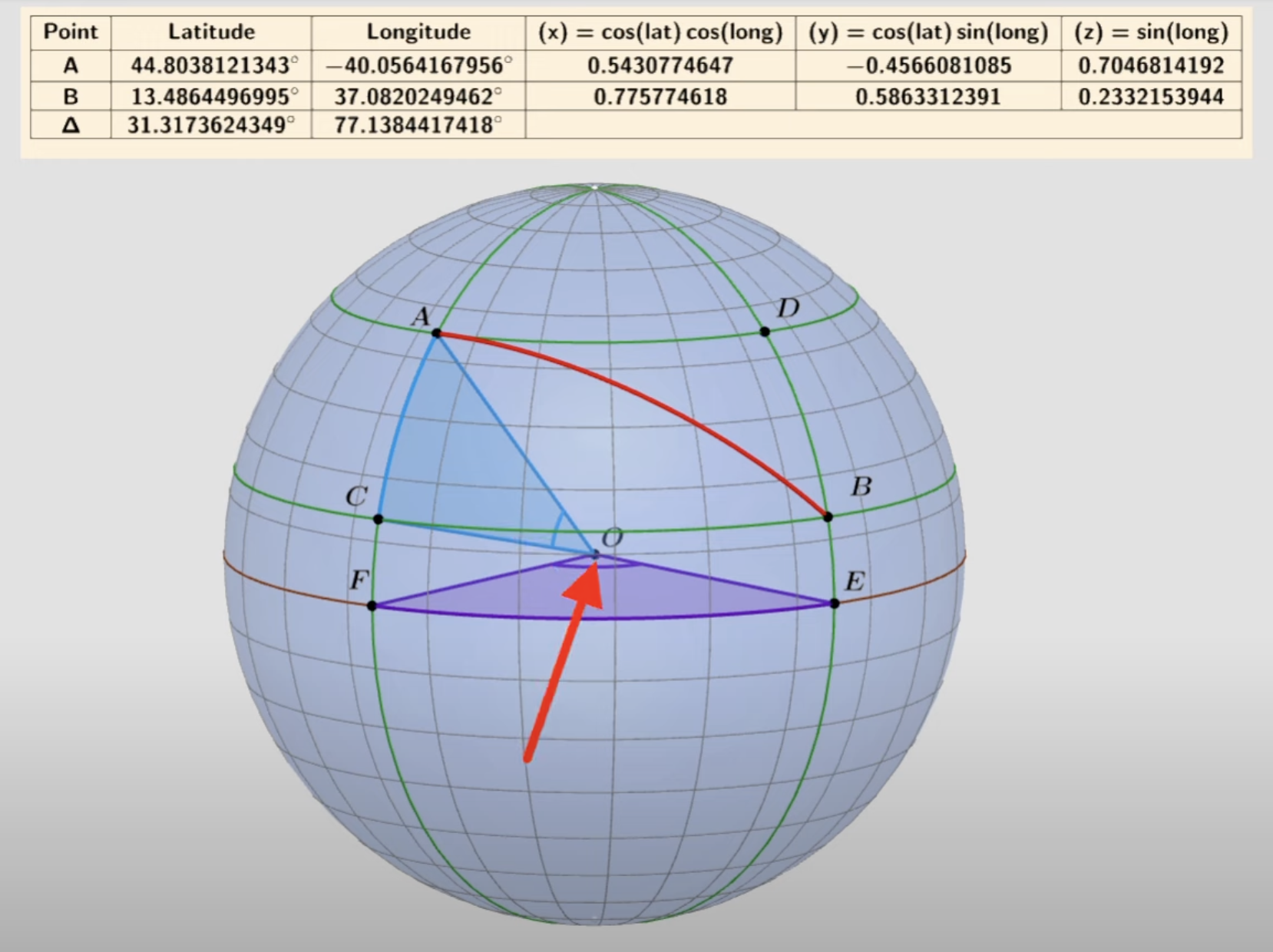
PART 2: calculating the distance of chord AC and EF in 3D context
The part is applying the calculation method from part 1.
PART 3: calculate the distance of the arc AB based chord AB
Below is a YouTube video that explain what I have summarized above:
YouTube: Haversine Algroithm Explained
NOTE: the images I have used are screenshots from the video
Double vs. BigDecimal
Below code tests out the accuraccy of using double and BigDecimal as data types to apply the haversine algorithm. Results, show that Using BigDecimal gave 50% more accurate results.
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.MathContext;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
public class Main {
private static final BigDecimal EARTH_RADIUS = new BigDecimal("6371"); // Kilometers
private static final MathContext MATH_CONTEXT = new MathContext(10, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);
// Convert degrees to radians using BigDecimal
private static BigDecimal toRadians(BigDecimal degrees) {
BigDecimal pi = new BigDecimal(Math.PI);
return degrees.multiply(pi, MATH_CONTEXT).divide(new BigDecimal("180"), MATH_CONTEXT);
}
// Calculate the sine of an angle in radians using BigDecimal (approximation)
private static BigDecimal sin(BigDecimal radians) {
return new BigDecimal(Math.sin(radians.doubleValue()), MATH_CONTEXT);
}
// Calculate the cosine of an angle in radians using BigDecimal (approximation)
private static BigDecimal cos(BigDecimal radians) {
return new BigDecimal(Math.cos(radians.doubleValue()), MATH_CONTEXT);
}
// Calculate the arccosine of a value using BigDecimal (approximation)
private static BigDecimal acos(BigDecimal value) {
return new BigDecimal(Math.acos(value.doubleValue()), MATH_CONTEXT);
}
// BigDecimal을 사용한 계산
public static BigDecimal calculateDistance(BigDecimal lat1, BigDecimal lon1, BigDecimal lat2, BigDecimal lon2) {
BigDecimal lat1Rad = toRadians(lat1);
BigDecimal lon1Rad = toRadians(lon1);
BigDecimal lat2Rad = toRadians(lat2);
BigDecimal lon2Rad = toRadians(lon2);
BigDecimal sinLat1 = sin(lat1Rad);
BigDecimal sinLat2 = sin(lat2Rad);
BigDecimal cosLat1 = cos(lat1Rad);
BigDecimal cosLat2 = cos(lat2Rad);
BigDecimal deltaLon = lon1Rad.subtract(lon2Rad).abs();
BigDecimal cosDeltaLon = cos(deltaLon);
// Haversine formula components
BigDecimal centralAngle = sinLat1.multiply(sinLat2)
.add(cosLat1.multiply(cosLat2).multiply(cosDeltaLon));
BigDecimal distance = EARTH_RADIUS.multiply(acos(centralAngle), MATH_CONTEXT);
return distance;
}
// Double을 사용한 계산
private static double calculateDistanceDouble(double lat1, double lon1, double lat2, double lon2) {
lat1 = Math.toRadians(lat1);
lon1 = Math.toRadians(lon1);
lat2 = Math.toRadians(lat2);
lon2 = Math.toRadians(lon2);
double earthRadius = 6371; //Kilometers
return earthRadius * Math.acos(Math.sin(lat1) * Math.sin(lat2) + Math.cos(lat1) * Math.cos(lat2) * Math.cos(lon1 - lon2));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal lat1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(37.497943);
BigDecimal lon1 = BigDecimal.valueOf(127.027621);
BigDecimal lat2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(37.500586);
BigDecimal lon2 = BigDecimal.valueOf(127.036333);
BigDecimal answer = calculateDistance(lat1, lon1, lat2, lon2);
double answerDouble = calculateDistanceDouble(37.497943, 127.027621, 37.500586, 127.036333);
System.out.println("Google's calculation': 827.74");
System.out.println("BigDecimal calculation: "+answer);
System.out.println("double calculation: "+answerDouble);
}
}
