Spacial Indexing Using R-Tree
Introduction
Our project 'Hi-Clear' web app has uses spacial indexing technique to filter the gym objects based on their distance from the registered location.
Application In The Code
Distance Calculation
The spatial index on the gym.location column enables quick filtering of geometries (e.g., gym points) near the given location. Without spatial indexing, this calculation would scan all rows, which is computationally expensive for large datasets.
...
BooleanExpression condition = buildSearchCondition(
name, address, gymType, userLocation, requestDistance);
NumberTemplate<Double> distanceTemplate = Expressions.numberTemplate(
Double.class,
"ST_Distance_Sphere({0}, {1})", gym.location, userLocation
);
Range Filtering
-
ST_Buffer: Creates a circular buffer (radius = requestDistance) around the user's location. -
ST_Contains: Checks if the gym's location (gym.location) lies within this buffer.
How R-tree indexing is used: -
The R-tree spatial index on gym.location optimizes the containment check. The database quickly identifies points within the buffer by narrowing down the search space to relevant areas instead of scanning the entire dataset.
...
private BooleanExpression buildSearchCondition(
String name, String address, GymType gymType,
Point userLocation, Double requestDistance) {
BooleanExpression condition = gym.isNotNull();
condition = condition.and(gym.deletedAt.isNull());
if (requestDistance != null) {
requestDistance *= 1000;
condition = condition.and(
Expressions.booleanTemplate(
"ST_CONTAINS(ST_Buffer({0}, {1}), {2})",
userLocation, requestDistance, gym.location
));
}
...Theory
Minimum Boundary Rectangle (MBR)
- MBR is the minimum size rectuangle that can fit the shape inside it.
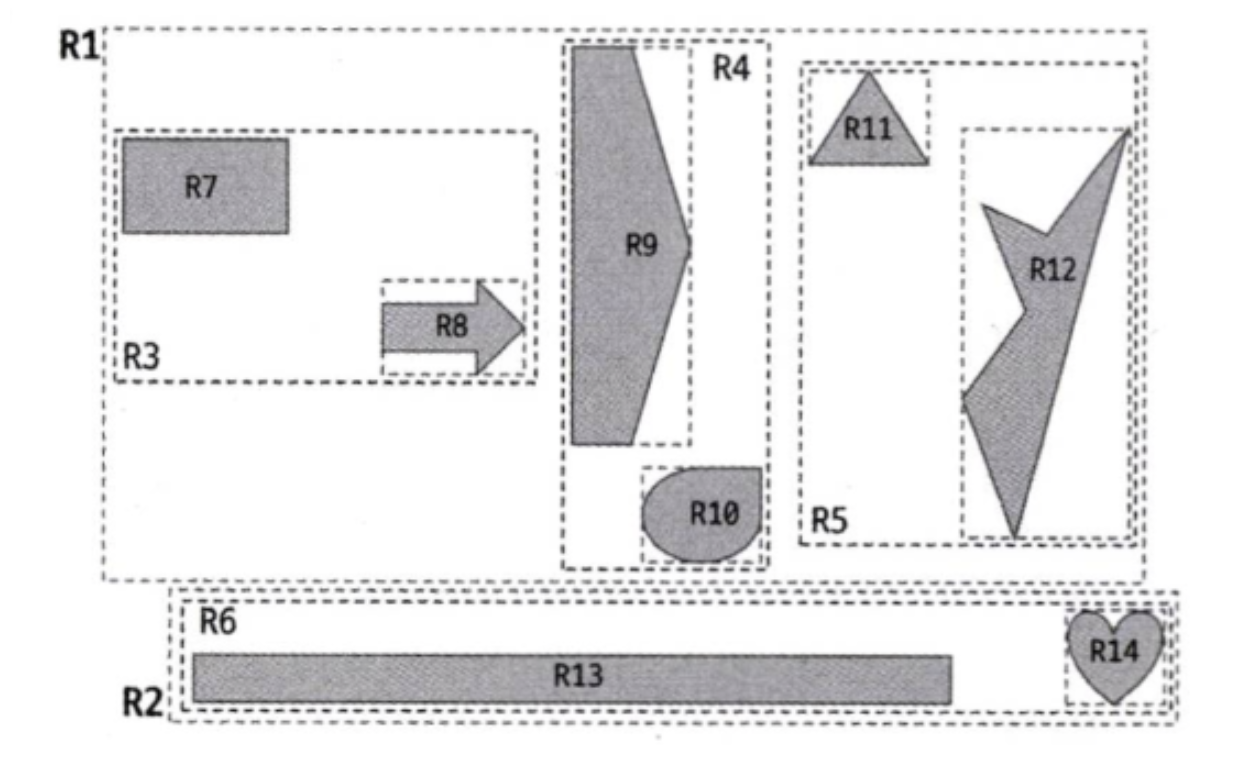
- highest level: R1~R2
- sub-high level: R3~R6
- lowest level: R7~R14
R-Tree
- root node: R1~R2
- branch node: R3~R6
- leaf node: R7~R14
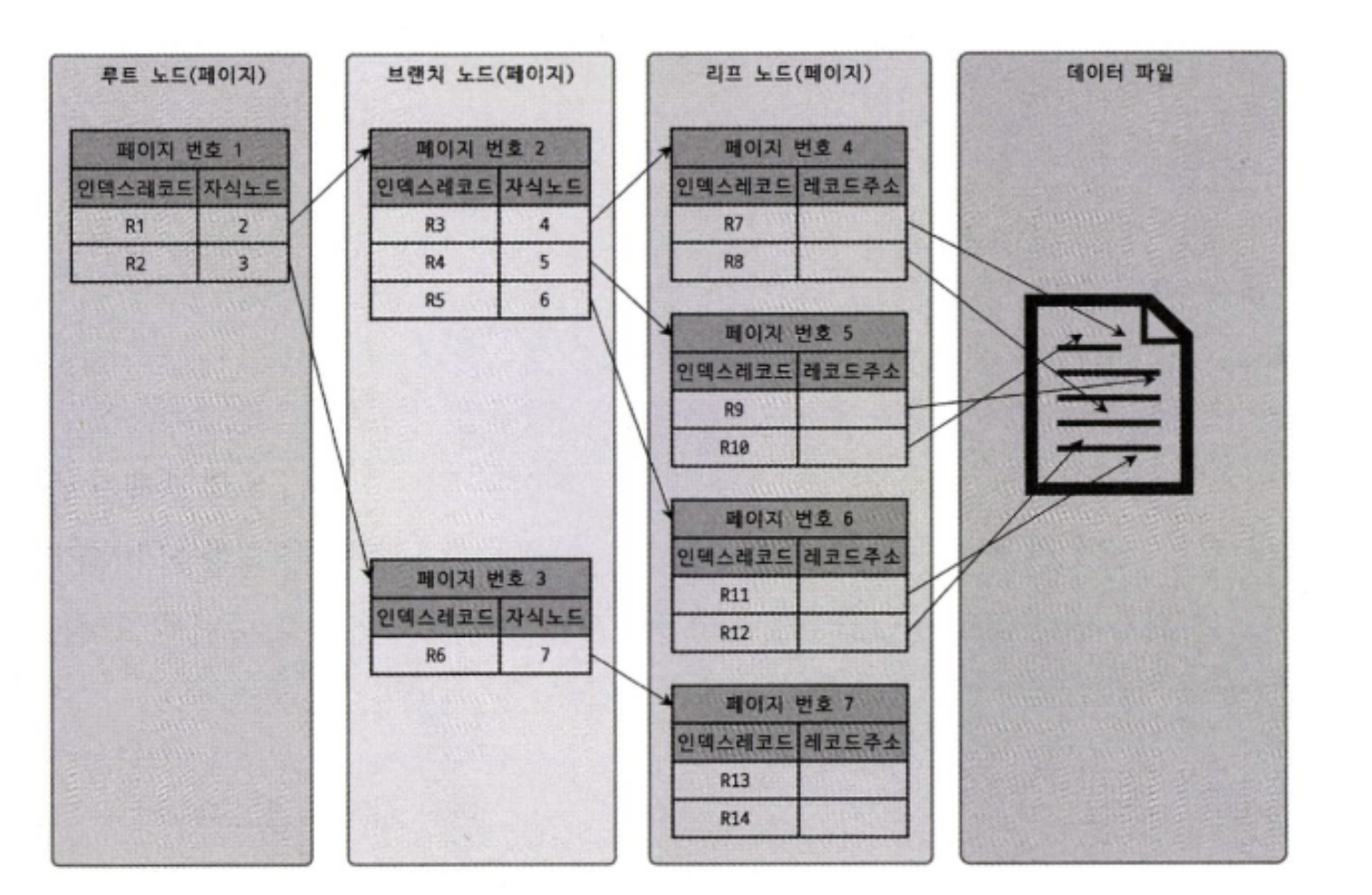
The R-Tree is an index created using the inclusion relationships of MBRs (Minimum Bounding Rectangles). Therefore, the index can only be utilized when searching with functions provided by MySQL, such as ST_CONTAINS, ST_WITHIN, and ST_INTERSECTS, which compare inclusion relationships.
