Django ORM: Structure and Principles of QuerySet
This summary is adopted from SoungRyoul Kim's session during Pycon Korea 2020
Characteristics of ORM
Lazy Loading
- database is accessed only when needed, for only the needed amount.

Caching
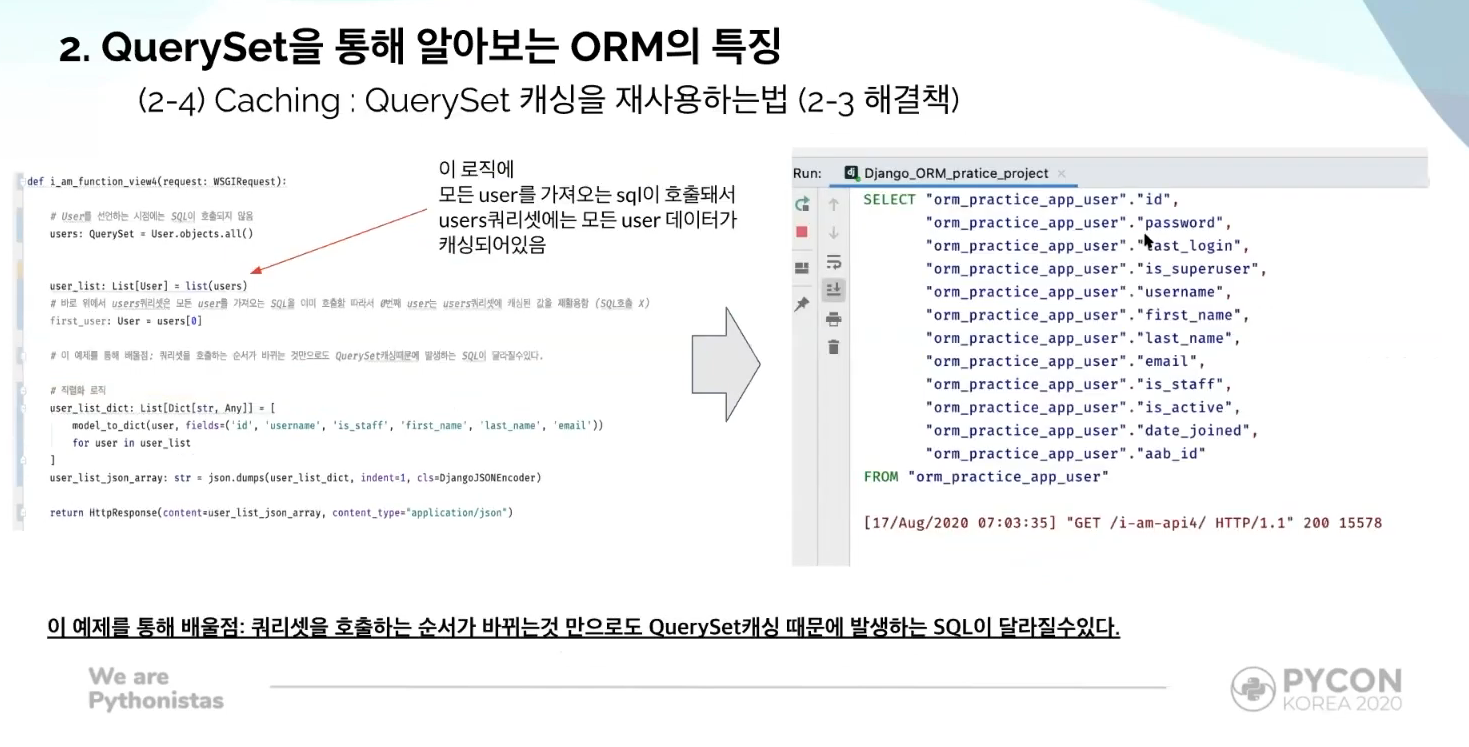
- if all users have been retrieved from the database and stored in
usersqueryset, django will return any single user information from the cached data, rather than accessing the database once more.
Eager Loading: N+1 problem
- There can be times when lazy loading may actually result in database inefficiency. The so-called N+1 problem.
- Quick solutions:
select_related&prefetch_related
QuerySet
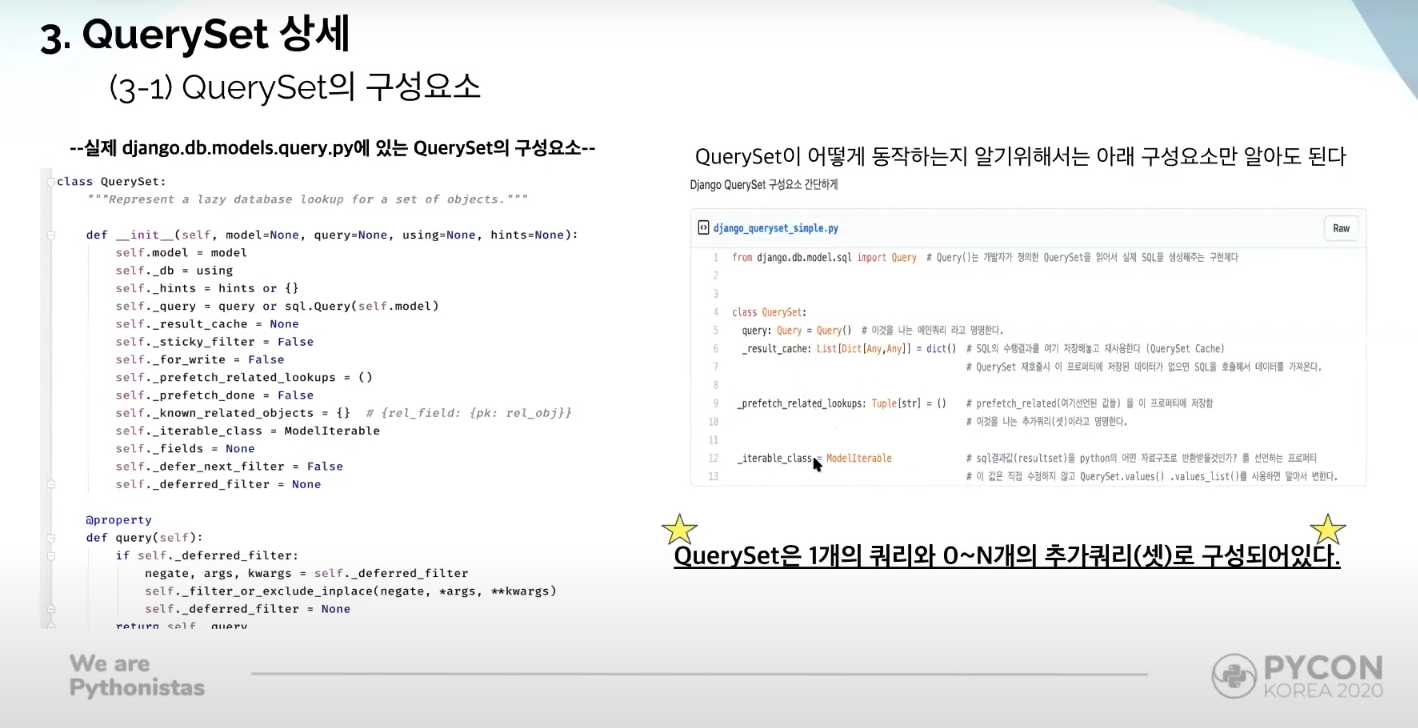
QuerySet Components
A queryset is composed of 1 main query and 0~N extra queries.
query : the main query requested by the user
_result_cache : the queryset cache; if any requested information is not contained in this cache, django will attempt to retrieve the information from the database
_prefetch_related_lookups : prefetch_related values
_iterable_class : defining in which python data structure should the resulting queryset be returned
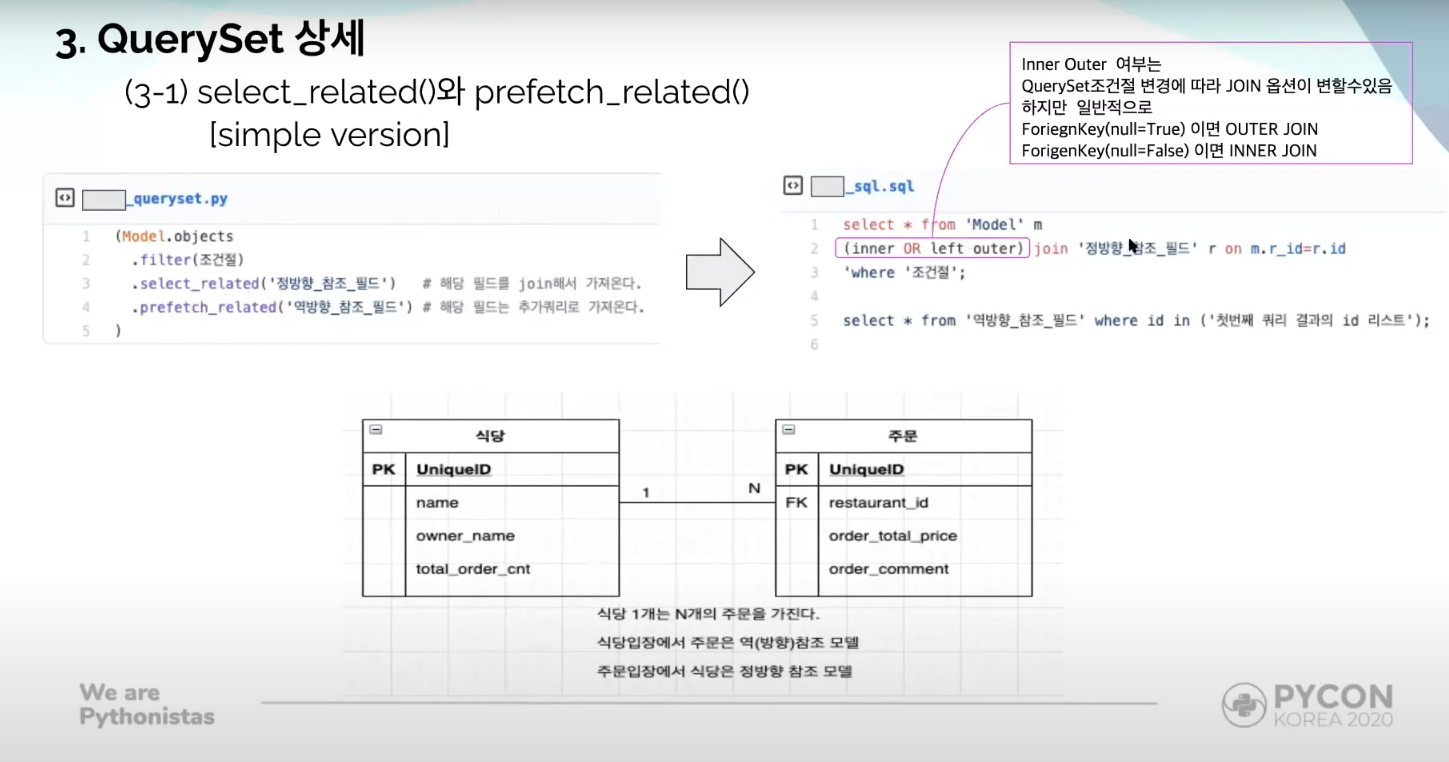
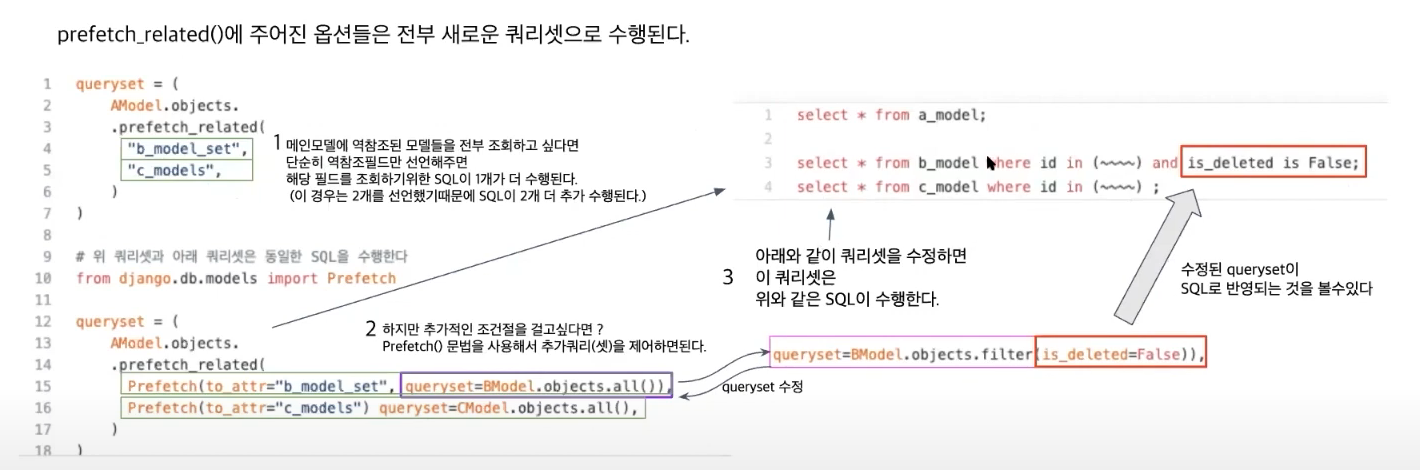
select_related() and prefetch_related()
select_related() retrieves information by joining the requested fields
prefetch_related() retrieves information by creating an extra SQL query.
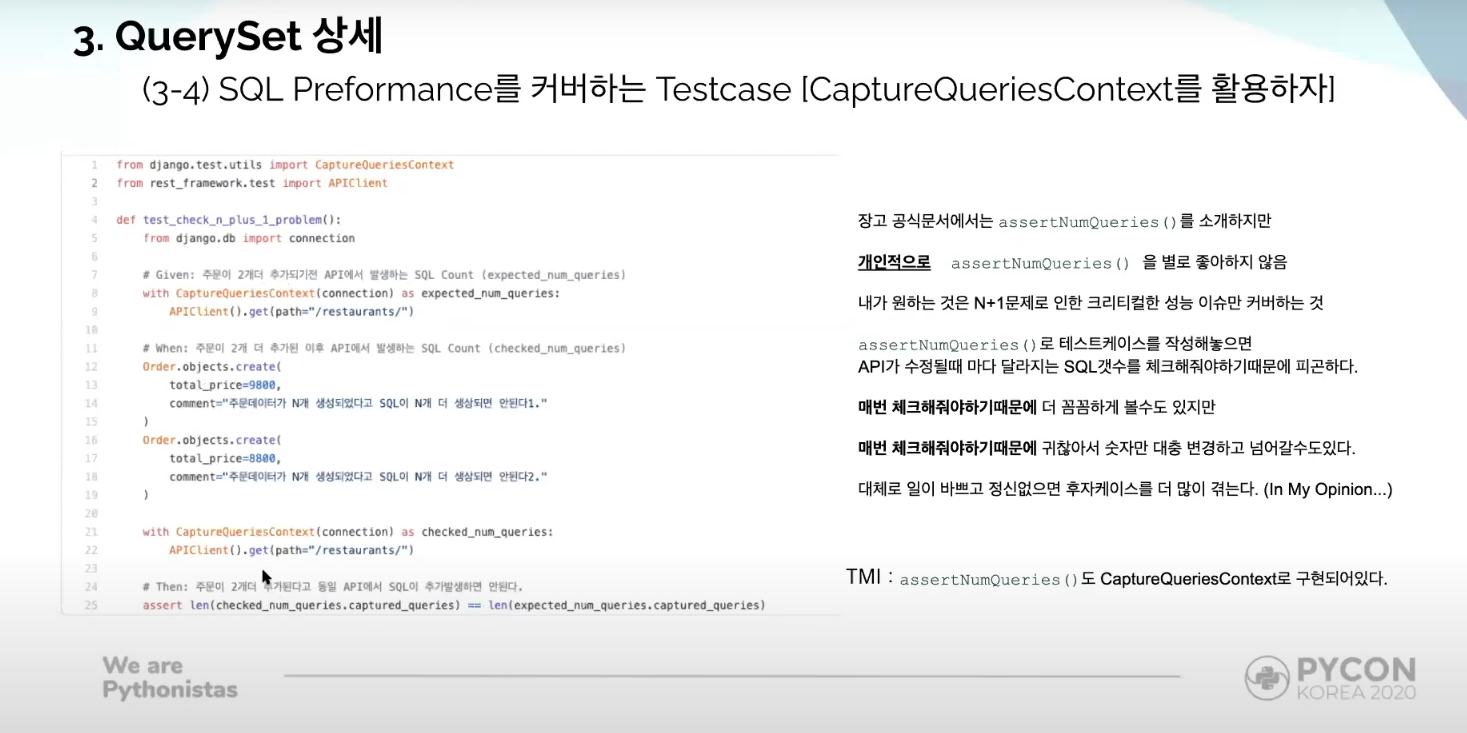
Testcases that can cover SQL performance
- use
CaptureQueriesContextfromdjango.test.utils.
Common mistakes when using QuerySet
Prefetch_related() != filter()
Company.objects
.prefetch_related('product_set')
.filter(name='company_name1', product__name__isnull=False)prefetching 'product_set' wouldn't help the performance of filtering 'product__name__isnull.' Instead, it will create an extra query for prefetching step.
Two solutions in this case
// First solution
Company.objects
//.prefetch_related('product_set')
.filter(name='company_name1', product__name__isnull=False)
//Second solution
Company.objects
.filter(name='company_name1')
.prefetch_related(
'product_set', Prefetch(queryset=Product.objects.filter(product__name__isnull=False))
)Suggested way of writing Django querysets
.annotate -> select_related -> filter & exclude -> only & defer -> prefetch_related (if there is a need for eager loading)

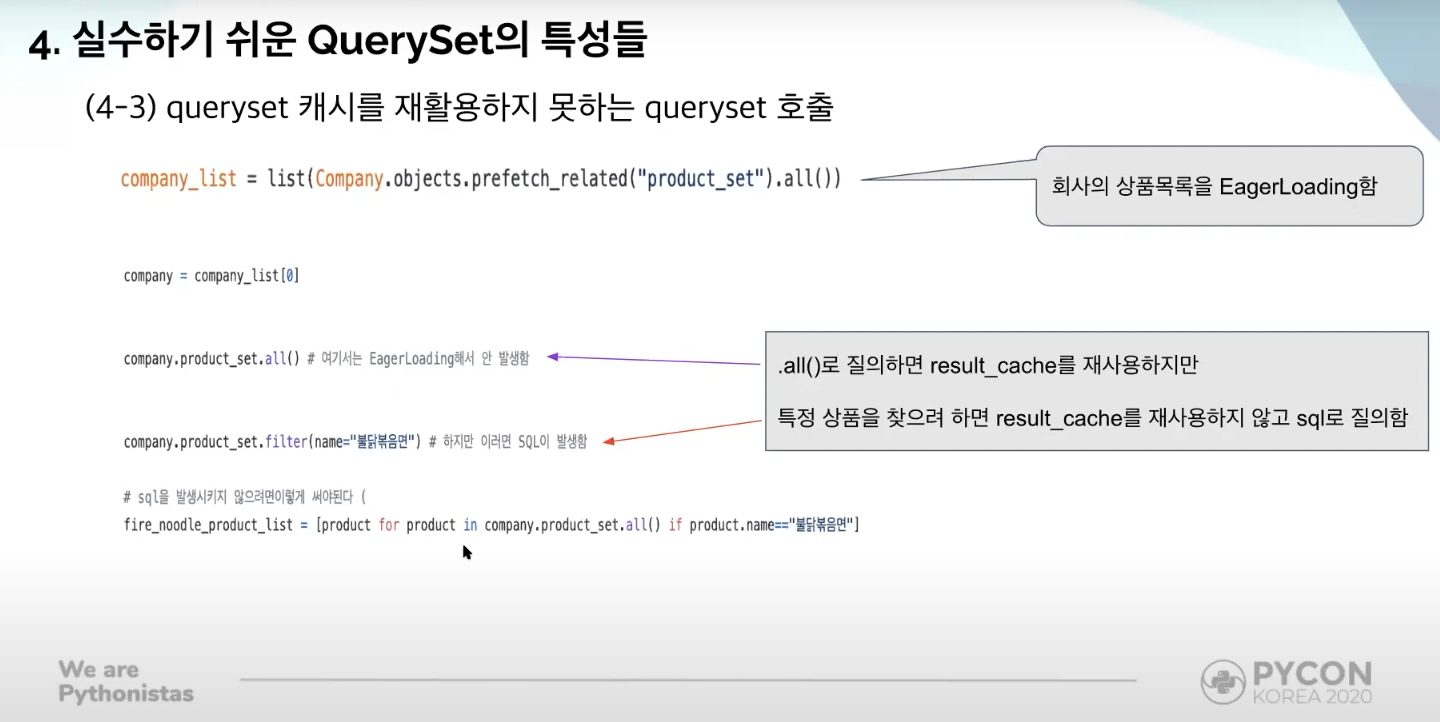
filter() cannot reuse eager-loaded cache
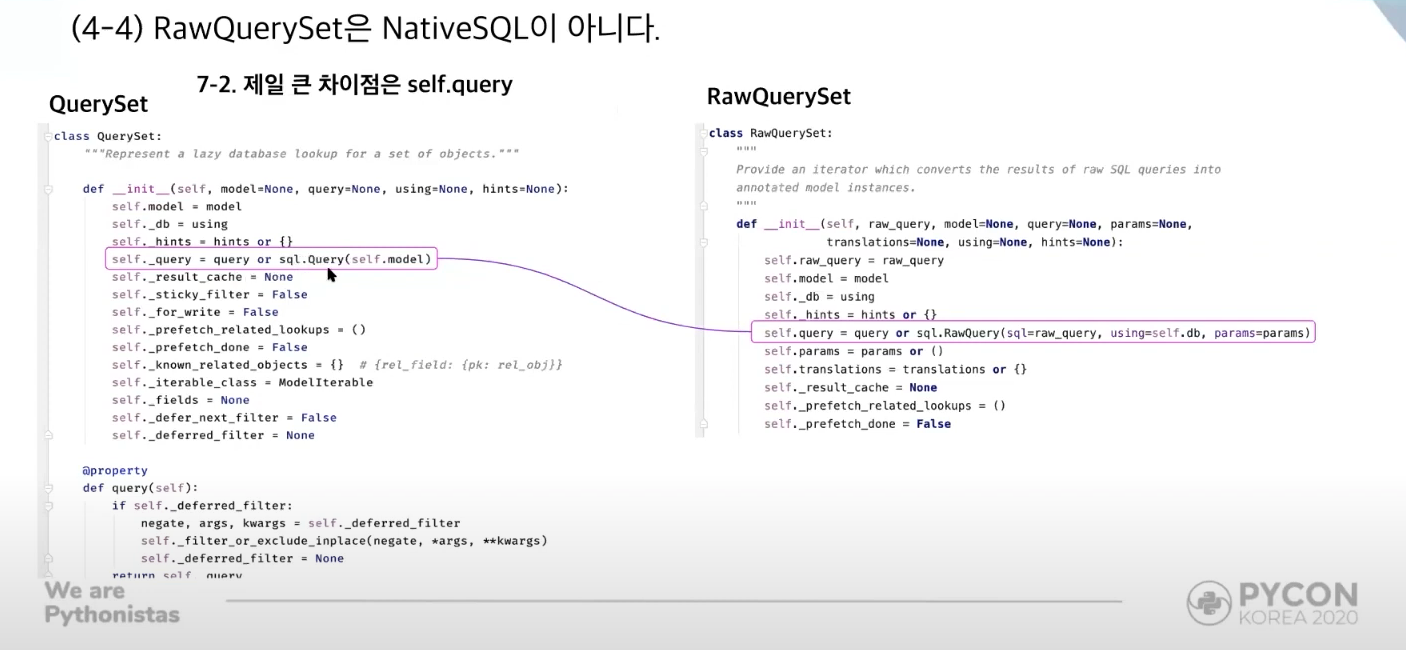
RawQuerySet is not NativeSQL
RawQuerySetis still within the boundaries of ORM (can still be used withprefetch_related()), yet its main query can be written in nativeSQL- However, methods that are used to modify the queryset's main query cannot be used with
RawQuerySet, and they will have to be included in the NativeSQL portion of the queryset.
Sub Queryset Occurrence Conditions
1. When a queryset is within another queryset.
To avoid this problem, execute a queryset before it gets evaluated as a sub queryset.

2. When imposing an exclude() condition in reverse relation sets
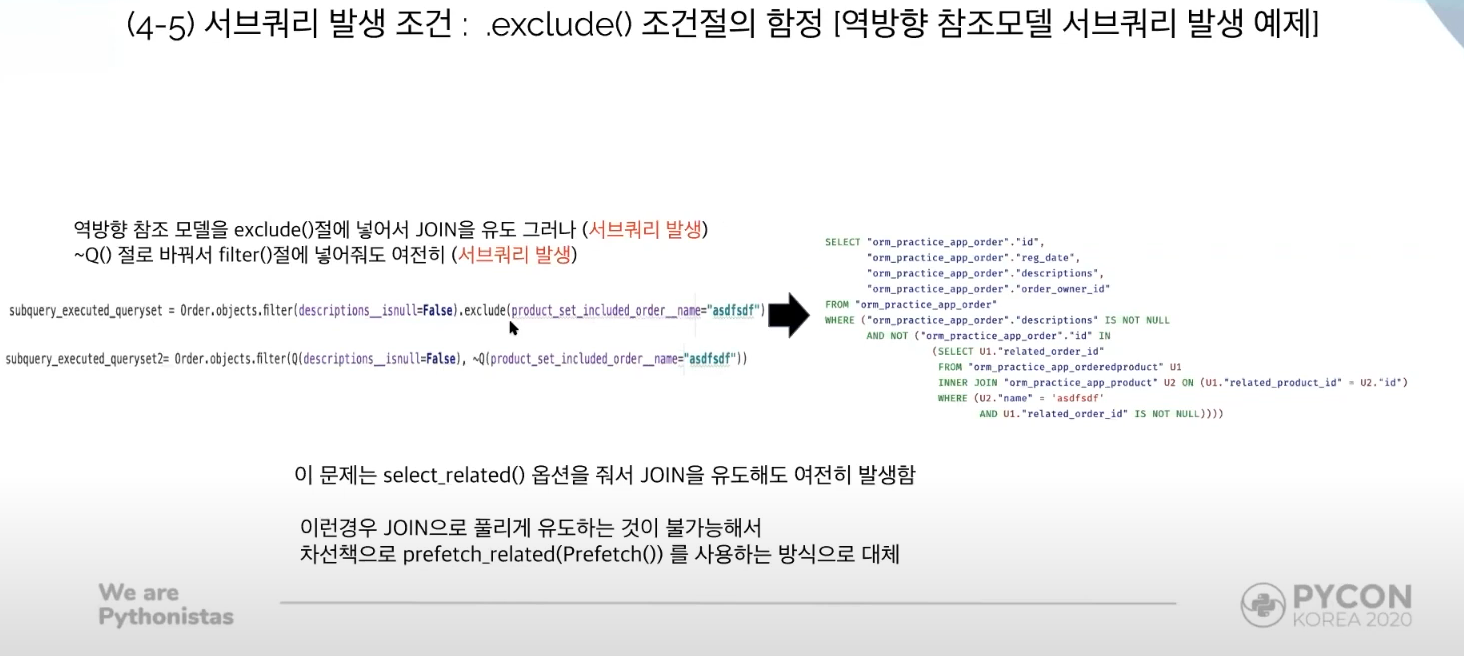
Forward relation models can be joined without trigger a subquery sql with exclude().
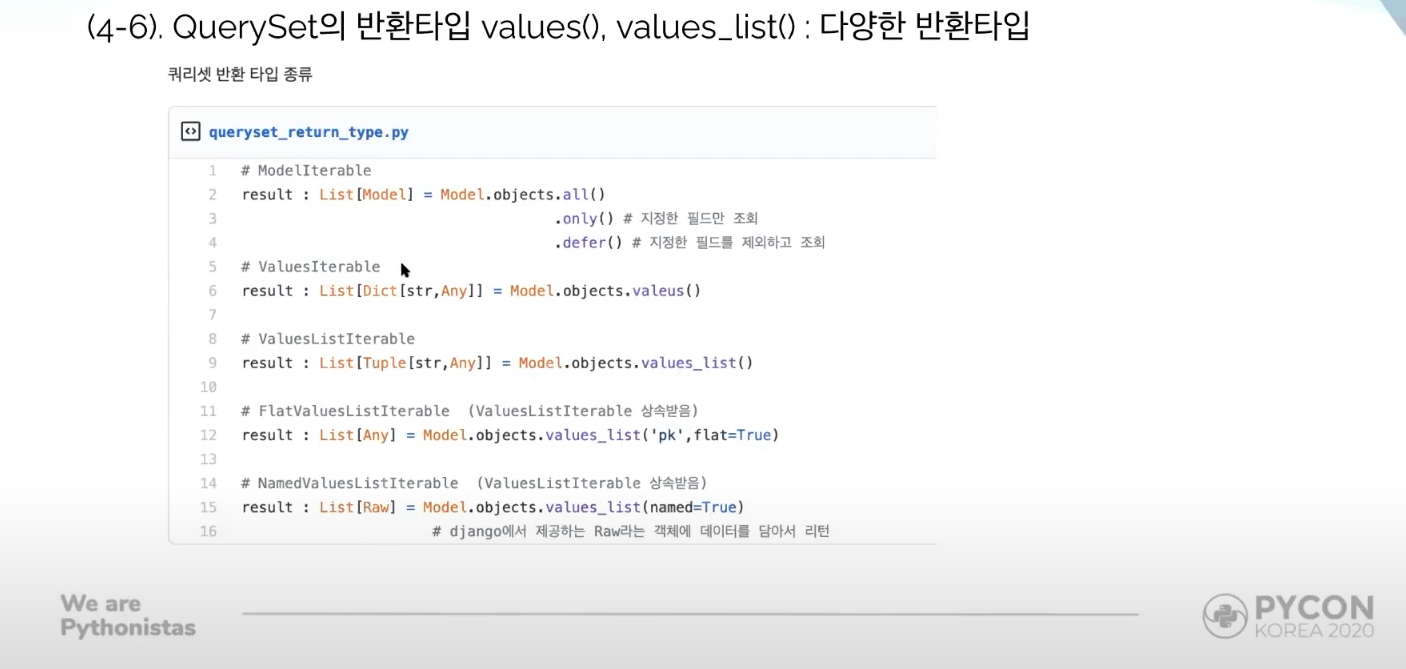
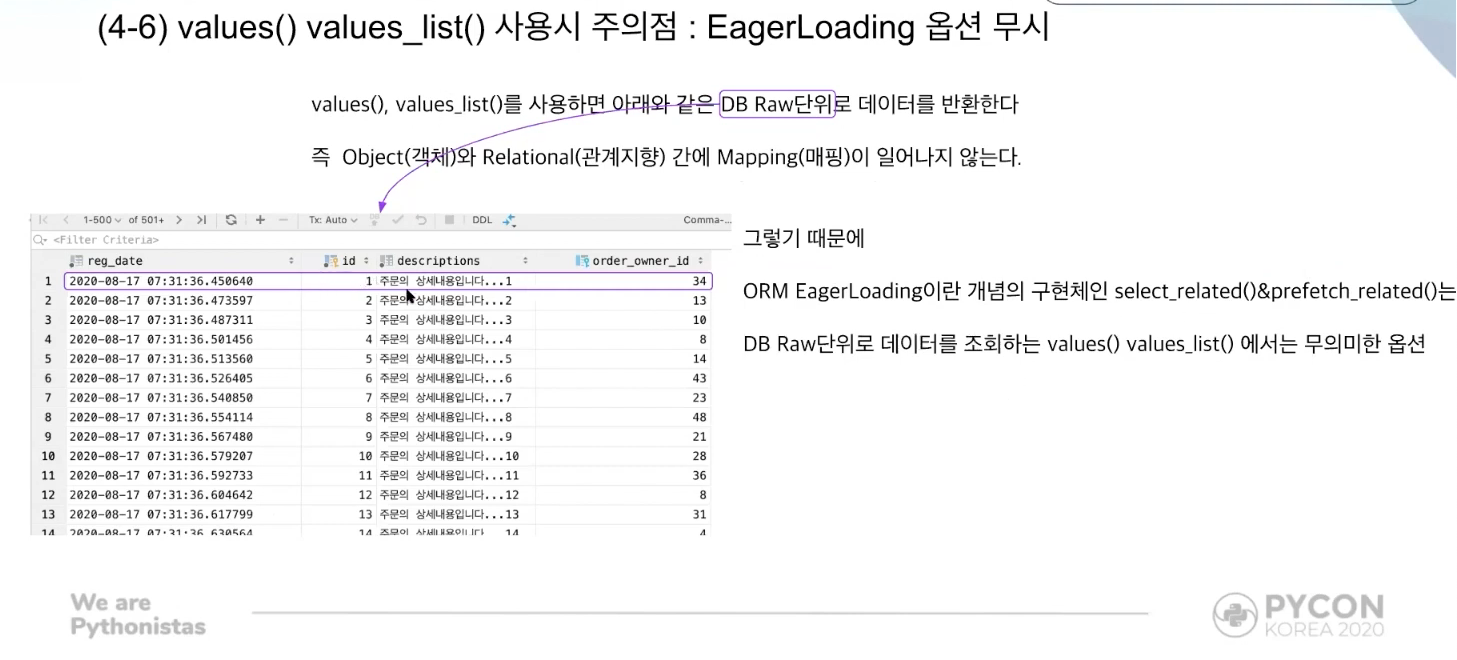
values(), values_list() ignoring EagerLoading
QuerySet return types
Conclusion

