[Wecode] HTML / CSS Study Takeaways
Position property
4 different kinds of positions: static, fixed, absolute, relative
Static
By default, all blocks are in position:static
Any new element will be positioned “according to the normal flow of the page”
Fixed
- position:fixed fixes the box on the screen, stays where it is even when scrolling
- When an element’s position is fixed, 4 properties are unlocked: top / bottom / left / right
- Position shifts relative to the viewport (or the browser window) and not the flow
Absolute
- position:absolute is just like fixed,but it doesn’t stay on the screen when the user scrolls; position absolute goes into the html and looks for a closest relative parent whose position is not static
- the element’s attribute values will be relative to a parent element whose position is not static. If there is no such parent, it will default all the way back up to the element, meaning it will be placed relative to the page itself
- absolute position elements are removed from the flow of elements and float on the page
- The default position of an absolute element is according to the normal flow of the document, or a parent element
- Another characteristic of absolute elements is that block elements that normally took up the entire width of the page (of its parent container) are reduced to the size of their contents
Relative
- position:relative means “relative to itself”
- If you set the position as relative, but include no other positioning attributes (top, left, bottom, right), it will have no effect on its positioning at all, just the same as static
but if you do give it some other positioning attribute, say, top: 10px, it will shift its position 10px down from where it would normally be - It limits the scope of absolutely positioned child elements: any element that is a child of the relatively positioned element can be absolutely positioned within that block
- If the father does not have a position of relative, the abs-child will be executed as it is initially coded (position itself relative to the body)
- If there is a relative father, the child will align itself to the relative father
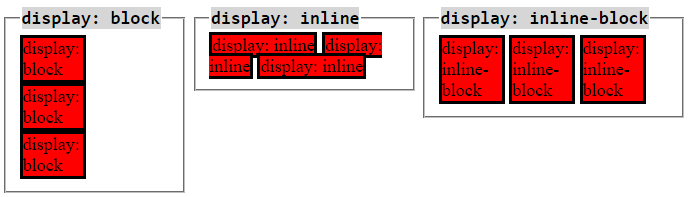
Inline vs Inline-block vs Block
display: inline-block
- behaves like an inline element while retaining the properties of a box
- respects top & bottom margins and padding
- respects height & width
display: inline
- removes every box property of designated elements, including width and height
- only respects left & right margins and padding, but not top & bottom
- equivalent to saying, “this element is not a block anymore. It becomes like text”
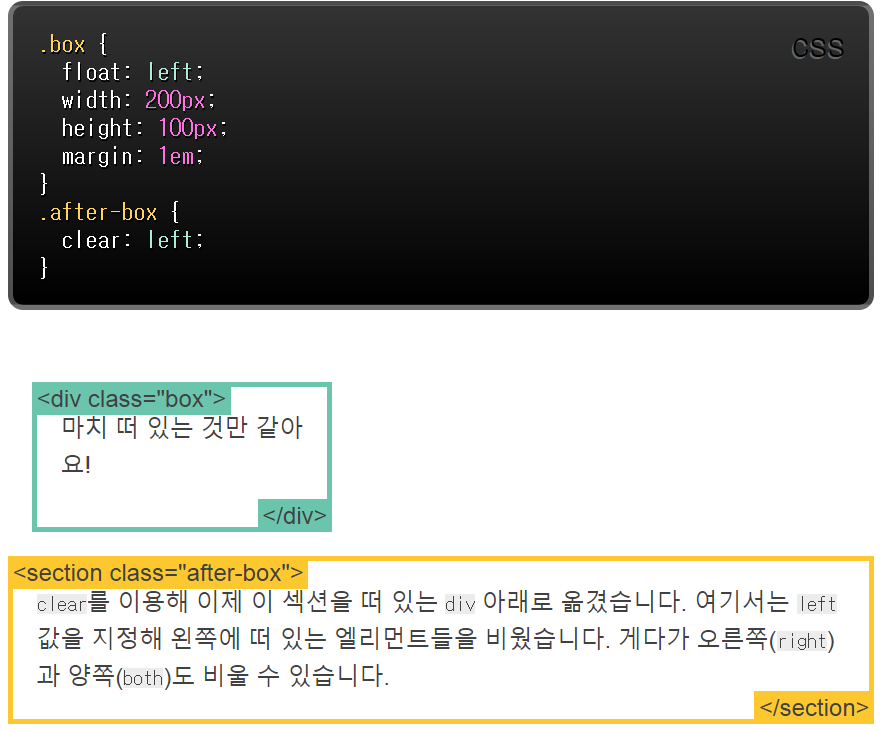
Float
-
The Float property places an element on the left or right side of its container, allowing text and inline elements to wrap around it.
-
An element with float property is removed from the normal flow of the page, but still remains as a part of the flow (unlike absolute positioning)
-
Syntax: (https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/float)


-
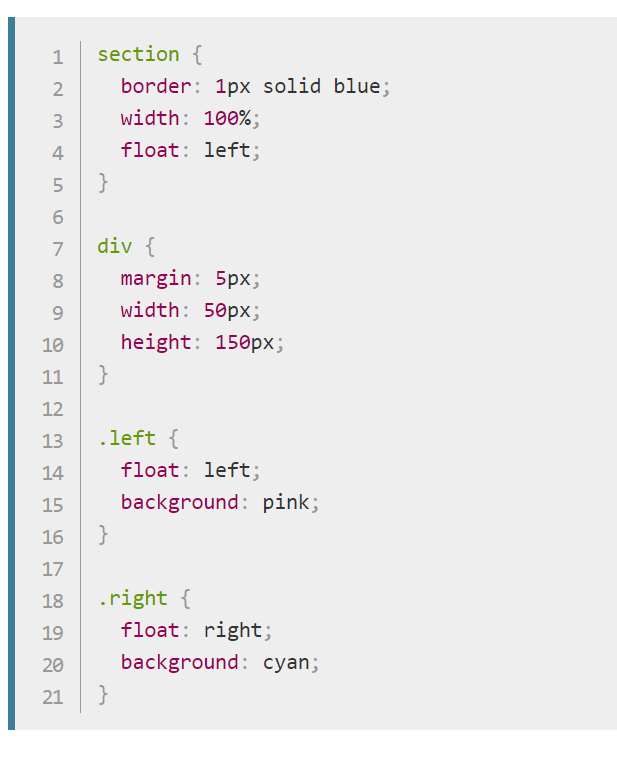
Sometimes float does not yield appropriate heights for containers Three solutions to such problem are:
- give any tag to a parent div container and apply clear property
- give overflow: hidden; property to a parent div container
- have the parent div container float → the downside of this method is that the parent class loses block property, so the user needs to manually give width of 100% to retain the block property