자바 설정
환경변수 설정
운영체제가 컴퓨터의 어떤 경로에서든지 파일을 인식하도록 하는 것이다.
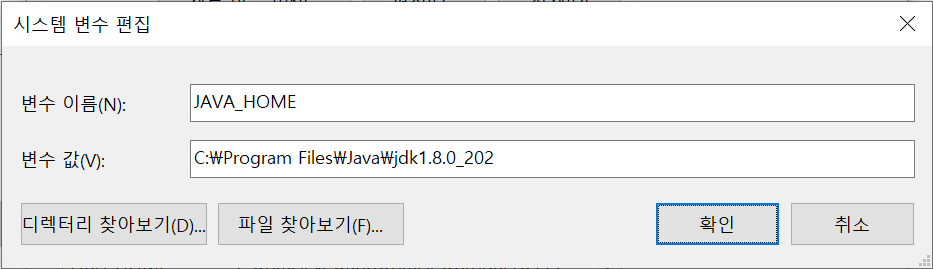
환경 변수를 설정할때 jdk의 bin 주소까지 등록하는 이유는 bin 폴더 안에 실행파일이 있기 때문이다.
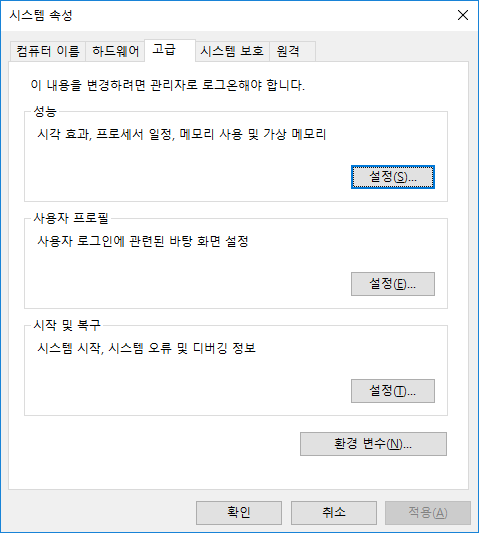
고급 시스템 설정 클릭
환경변수 클릭
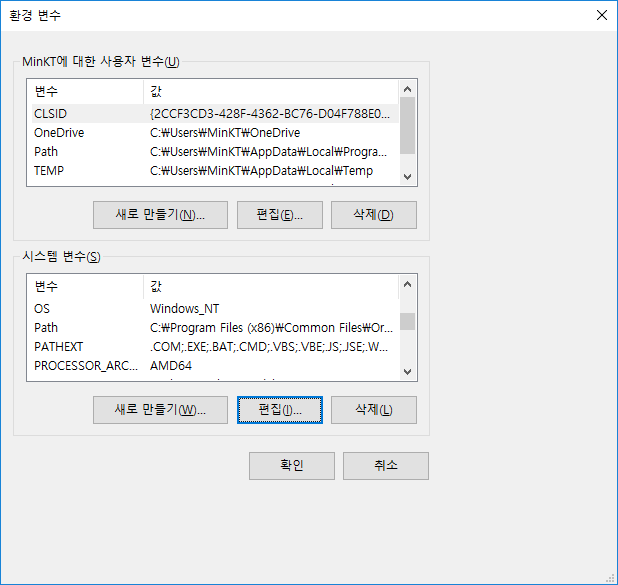
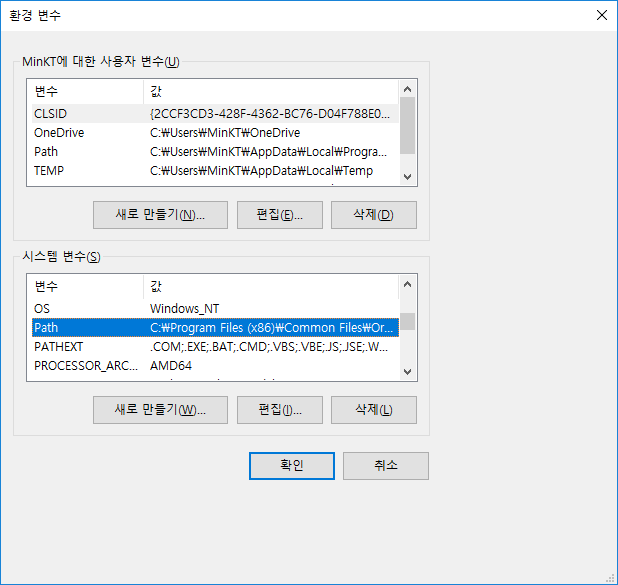
시스템 변수의 새로만들기를 눌러서 아래와 같이 생성해 준다.
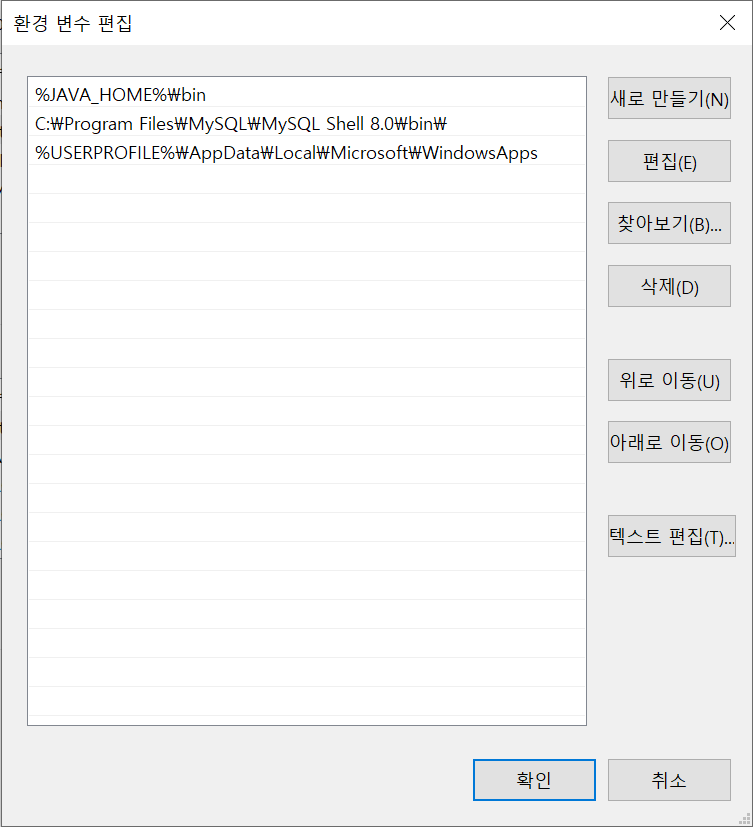
시스템 변수 안에 있는 path에 %JAVA_HOME%\bin을 넣어 준다.
JAVA_HOME을 맨 위로 올려서 먼저 인식 할 수 있게 한다.
인코딩 설정
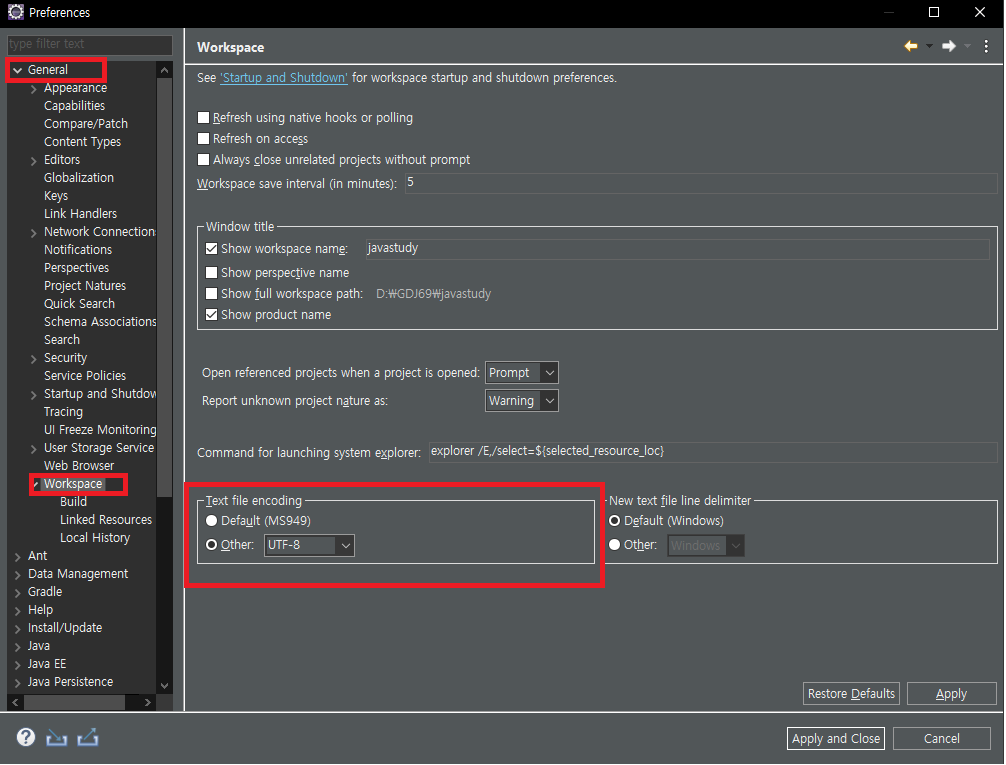
Window - Preferences - General - Workspace
Text file encoding 을 UTF-8 으로 바꿔준다.
폰트 설정
General - Appearance- Colors and Fonts -
Basic Text Font Edit...
Syntax Coloring
Java
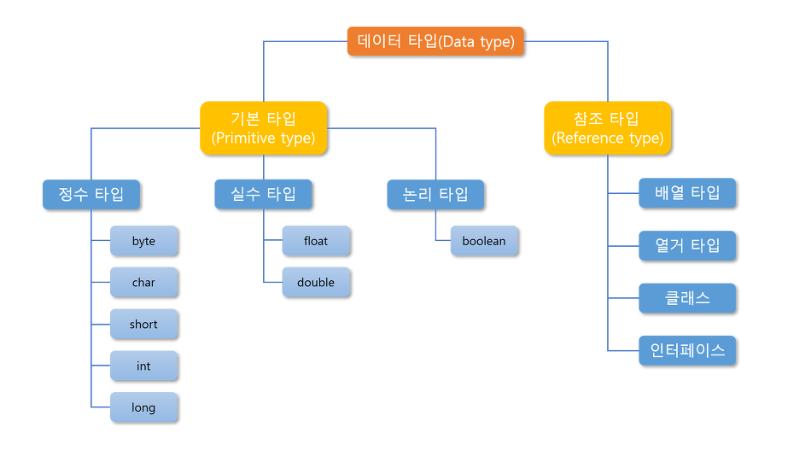
변수
Primitive Type
종류
- Boolrean : 논리타입 true, false의 값을 가진다.
- char : 문자타입 한개의 문자를 가진다. ex) 'A', '가'
- int, long: 정수타입 int(-2의 31승 ~ 2의 31승 -1의 범위), long(-2의 63승 ~ 2의 63승 -1의 범위)
- float,double : 실수타입 double이 더 넓은 범위를 가진다.
- String : 참조타입, 문자열이다.
- 기본 값이 있기에 Null이 존재하지 않는다.
- 기본형 타입에 Null을 넣고 싶다면 레퍼 클래스를 활용해야 한다.
- 실제 값을 저장하는 공간으로 Stack메모리에 저장된다.
Reference Type
- 기본형 타입을 제외한 타입들(문자열, 배열, 열거, 클래스, 인터페이스)이 모두 참조형 타입이다.
- 빈객체를 의미하는 Null이 존재한다.
- 값이 저장되어 있는 곳의 주소값을 저장하는 공간으로 Heap 메모리에 저장된다.
자동변환
/*
* 자동 변환(promotion)
* 1. 작은크기 -> 큰 크기
* 2. 정수 -> 실수 (5->5.0)
*/
byte num1 = 127; //byte는 128 ~127 범위가 가능
int num2 = num1; //1 byte 크기를 가진 num1을 4바이트 크기로 자동 변환
System.out.println(num2);
double addResult = 1.5 + 5; // 5를 5.0으로 자동 변환
System.out.println(addResult);
/*
* 강제 변환 (casting)
* 1. 큰 크기 -> 작은크기
* 2. 실수 -> 정수
*
*/
int bigNum = 256;
byte smallNum = (byte)bigNum; // 4바이트 bigNum을 강제로 1바이트로 변화
System.out.println(smallNum); //원본이 훼손될 수 있다.
double pct = 0.5;
int iPct = (int)pct;
System.out.println(iPct);
/*
* 구문 분석(parsing)
* 1. 문자열 -> 정수(int, long)
* 2. 문자열 -> 실수 (double)
*/
String strScore = "100";
int score = Integer.parseInt(strScore); //자바에서 모든 함수는 메소드이다.
String strMoney = "10000000000";
long money = Long.parseLong(strMoney);
String strComm = "0.5";
double comm = Double.parseDouble(strComm);
System.out.println(score);
System.out.println(money);
System.out.println(comm);
/* web 개발에 필요한 이유 : 검색란에 100을 누르고 검색을 하면 String query = "100"; 라고 저장된다.
* 숫자로 바꿔주기 위해서 구문 분석이 필요할 수 있다. 전달은 다 'string'
*/연산
// ex01 메소드 만들기(메소드 정의)
public static void ex01() {
System.out.println("Hello World");
//정수 연산
int a = 5;
int b = 2;
int add = a + b; //등호 오른쪽을 항상 먼저 한다.
int sub = a - b;
int mul = a * b;
int mok = a / b; //몫
int mod = a % b; //나머지
System.out.println(add);
System.out.println(sub);
System.out.println(mul);
System.out.println(mok);
System.out.println(mod);
//실수 연산
double x = 5;
double y = 2;
double addResult = x + y;
double subResult = x - y;
double mulResult = x * y;
double divResult = x / y; //나누기 소수점으로 나온다.
System.out.println(addResult);
System.out.println(subResult);
System.out.println(mulResult);
System.out.println(divResult);
//미션 정수끼리 계산해서 실수 경과 도출하기
int i = 5;
int j = 2;
double result = (double)i / j; //5.0 / (자동형변화)2.0
System.out.println(result); //2.5
}
// ex02 메소드 정의
public static void ex02() {
//증감 연산(++ ,--)
//전위연산(먼저 증감)
int a = 10;
System.out.println(++a); //a를 증가시킨 뒤 출력 한다.
System.out.println(a);
//후위 연산(나중에 증감)
int b = 10;
System.out.println(b++); //b를 출력한 뒤 증가시킨다.
System.out.println(b);
}
// ex03 메소드 정의
public static void ex03() {
// 대입 연산 (=)
int a = 10;
int b = a; //a를 b로 보내라
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
// 복합 연산 (복합 대입 연산)
int x = 10;
int y = 1;
y += x; // y = y + x; 로 해석. y 값을 x 만큼 늘리기
System.out.println(x); //10
System.out.println(y); //11
}
// ex04 메소드 정의
public static void ex04() {
// 관계 연산(크기 비교)
int a = 3;
int b = 5;
boolean result1 = a > b; //a가 b 보다 크면 true, 아니면 false
boolean result2 = a >= b; //a가 b 보다 크거나 같음면 true, 아니면 false
boolean result3 = a < b; //a가 b 보다 작으면 true, 아니면 false
boolean result4 = a <= b; //a가 b 보다 작거나 같음면 true, 아니면 false
boolean result5 = a == b; //a 와 b 가 같으면 true, 아니면 false
boolean result6 = a != b; //a 와 b 가 다르면 true, 아니면 false
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println(result2);
System.out.println(result3);
System.out.println(result4);
System.out.println(result5);
System.out.println(result6);
// 논리 연산
//1. 논리 AND : &&, 모든 조건이 만족하면 TRUE, 아니면 FALSE
//2. 논리 OR : ||, 하나의 조건이라도 만족하면 TRUE 아니면 FALSE
//3. 논리 NOT : !, 조건 결과가 TRUE 이면 FALSE, 조건 결과가 FALSE이면 TRUE
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
boolean andResult = (x == 10) && (y == 10); //모든 조건을 만족하지 않기 때문에 false
boolean orResult = (x == 10) || (y == 10); // 하나의 조건을 만족하므로 true
boolean notResult = !(x == 10); //x != 10와 동일한 조건
System.out.println(andResult);
System.out.println(orResult);
System.out.println(notResult);
// Short Circuit Evaluation
//1. 논리 AND : 결과가 false인 조건이 나타나면 더 이상 조건을 체크하지 않는다. 최종결과는 false이기 때문이다.
//2. 논리 OR : 결과가 true인 조건이 나타나면 더 이상 조건을 체크하지 않는다. 최종 결과가 true로 정해졌기 때문이다.
int i = 10;
int j = 10;
boolean andSceResult = (++i == 10) && (++j == 10);
System.out.println(andSceResult);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(j);
boolean orSceResult = (j++ == 10) || (i++ == 10);
System.out.println(orSceResult);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(j);
}
// ex05 메소드 정의
public static void ex05() {
// 조건 연산자(3개의 항을 사용하므로 삼항 연산이라고 한다.)
// 조건식 ? true인 경우 결과 : false인 경우 결과
int score = 50;
String result = (score >= 60) ? "합격" : "불합격";
System.out.println(result);
}
// ex06 메소드 정의
public static void ex06() {
//문자열 연결
String str1 = "구디" + "아카데미";
String str2 = 4 + "달라";
String str3 = 1 + 2 + "번지";
// 정수 -> 문자열
// 실수 -> 문자열
String str4 = 100 + ""; //빈 문자열("")을 더해주면 된다.
String str5 = 1.5 + "";
// 참고. 문자열로 변환하는 메소드가 있다.
String str6 = String.valueOf(100); //잘 안 쓸 뿐이다.
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str2);
System.out.println(str3);
System.out.println(str4);
System.out.println(str5);
System.out.println(str6);
}