◾모델 평가
[데이터 수집/가공/변환 -> 모델 학습/예측 -> 모델 평가] 과정 반복- 대부분 다양한 모델, 다양한 파라미터를 두고, 상대적으로 비교한다.
회귀 모델의 경우 : 실제 값과 에러치를 가지고 계산분류 모델의 경우 : 정확도(Accuracy), 오차행렬(Confusion Matrix), 정밀도(Precision), 재현율(Recall), F1 score, ROC AUC 등
- 예측 결과 : 몇 개의 종류(분류) 중 결과를 선택
- IRIS, 타이타닉 등
이진 분류 모델의 경우
- TP True Positive : 실제 Positive를 Positive라고 맞춘 경우
- FN False Negative : 실제 Positive를 Negative라고 틀리게 예측한 경우
- TN True Negative : 실제 Negative를 Negative라고 맞춘 경우
- FP False Positive : 실제 Negative를 Positive라고 틀리게 예측한 경우
- Accuracy(전체 데이터 중 맞게 예측한 비율) : TP+TN+FP+FNTP+TN
- Precision(양성이라고 예측한 것 중 실제 양성의 비율) : TP+FPTP
- RECALL(참인 데이터들 중에서 참이라고 예측한 것, TPR : True Positive Ratio) : TP+FNTP
- FALL-OUT(실제 양성이 아닌데, 양성이라고 잘못 예측한 경우, FPR : False Position Ratio) : TN+FPFP
- 예측 결과 : 2개의 종류 중 결과 선택
◾이진 모델 분류
- 분류 모델은 결과를 속할 비율(확률)로 반환
- 지금까지는 비율의 threshold를 0.5로 하여 0, 1 반환(if 이진 분류)
- iris의 경우 가장 높은 확률값이 있는 클래스를 결과로 반환
- threshold를 변경해가며 지표 관찰
- Recall, Fall-out, Precision, Accuracy
- threshold = 0.3, TP = 3, FN = 0, FP = 4, TN = 0
| y | y_pred | output for threshold 0.3 | Recall | Fall-out | Precision | Accuracy |
|---|
| 0 | 0.4 | 1 | 3/3 | 4/4 | 3/7 | 3/7 |
| 1 | 0.9 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.3 | 1 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.8 | 1 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.4 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.5 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.6 | 1 | | | | |
- threshold = 0.4, TP = 3, FN = 0, FP = 3, TN = 1
| y | y_pred | output for threshold 0.4 | Recall | Fall-out | Precision | Accuracy |
|---|
| 0 | 0.4 | 1 | 3/3 | 3/4 | 3/6 | 4/7 |
| 1 | 0.9 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.3 | 0 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.8 | 1 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.4 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.5 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.6 | 1 | | | | |
- threshold = 0.5, TP = 2, FN = 1, FP = 2, TN = 2
| y | y_pred | output for threshold 0.5 | Recall | Fall-out | Precision | Accuracy |
|---|
| 0 | 0.4 | 0 | 2/3 | 2/4 | 2/4 | 4/7 |
| 1 | 0.9 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.3 | 0 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.8 | 1 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.4 | 0 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.5 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.6 | 1 | | | | |
- threshold = 0.6, TP = 2, FN = 1, FP = 1, TN = 3
| y | y_pred | output for threshold 0.6 | Recall | Fall-out | Precision | Accuracy |
|---|
| 0 | 0.4 | 0 | 2/3 | 1/4 | 2/3 | 5/7 |
| 1 | 0.9 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.3 | 0 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.8 | 1 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.4 | 0 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.5 | 0 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.6 | 1 | | | | |
- threshold = 0.8, TP = 2, FN = 1, FP = 0, TN = 4
| y | y_pred | output for threshold 0.8 | Recall | Fall-out | Precision | Accuracy |
|---|
| 0 | 0.4 | 0 | 2/3 | 0/4 | 2/2 | 6/7 |
| 1 | 0.9 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.3 | 0 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.8 | 1 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.4 | 0 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.5 | 0 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.6 | 0 | | | | |
- threshold = 0.9, TP = 1, FN = 2, FP = 0, TN = 4
| y | y_pred | output for threshold 0.9 | Recall | Fall-out | Precision | Accuracy |
|---|
| 0 | 0.4 | 0 | 1/3 | 0/4 | 1/1 | 5/7 |
| 1 | 0.9 | 1 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.3 | 0 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.8 | 0 | | | | |
| 1 | 0.4 | 0 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.5 | 0 | | | | |
| 0 | 0.6 | 0 | | | | |
| 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
|---|
| Recall | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.33 |
| Precision | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.67 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Fall-out | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Accuracy | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.86 | 0.71 |
Recall : 참인 데이터 중에서 참이라고 예측한 데이터의 비율Precision : 참이라고 예측한 것 중에서 실제 참인 데이터의 비율- 실제 양성인 데이터를 음성이라고 판단하면 안되는 경우라면, Recall이 중요하고 이 경우 Threshold를 0.3 혹은 0.4로 선정(예 - 질병 확인)
- 실제 음성인 데이터를 양성이라고 판단하면 안되는 경우라면, Precision이 중요하고, 이 경우는 Threshold를 0.8 혹은 0.9로 선정(예 - 스팸 메일)
- Recall, Precision은 서로 영향을 주기 떄문에 한 쪽을 극단적으로 높게 설정하면 안된다.
◾F1-Score
F1-Score(조화 평균) : Recall과 Precision을 결합한 지표
- Recall과 Precision이 어느 한쪽으로 치우치지 않고 둘다 높은 값을 가질 수록 높은 값을 가진다.
- Fβ = (1+β2)(precision×recall)/(β2precision+recall)
- F-Score에서 beta를 1로 두면 F1-Score
- F1 = 2(precision×recall)/(precision+recall)
- Threshold 정리
| 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
|---|
| Recall | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.33 |
| Precision | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.67 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Fall-out | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Accuracy | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.86 | 0.71 |
| F1-Score | 0.60 | 0.67 | 0.57 | 0.67 | 0.80 | 0.50 |
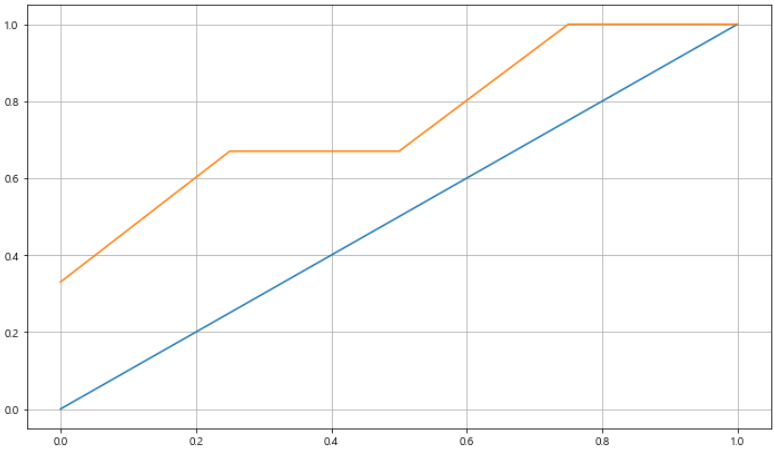
◾ROC와 AUC
ROC : 분류 검정의 민감도 대 (1 - 특이도)를 도표화하여 모형 예측의 정확도를 평가하기 위한 유용한 방법AUC : ROC 곡선의 면적을 의미한다.

- FPR(False Positive Rate)이 변할 때, TPR(True Positive Rate)의 변화를 그린 그림
- FPR을 x축, TPR을 y축으로 놓고 그림
- TPR은 Recall(Sensitivity : 민감도), FPR은 Fall-out
- 직선에 가까울 수록 머신 러닝 모델의 성능이 떨어지는 것으로 판단(AUC = 0.5)

- 수직에 가까울 수록 높은 성능을 의미한다.
- 위의 예제에서의 ROC 곡선
- Fall-out이 같을 경우 Recall이 작은 것을 선택한다.
- AUC는 1에 가까울 수록 좋은 수치로 0.5보다 커야한다.
- recall = [1., 1., 0.67, 0.67, 0.67, 0.33]
- fall-out = [1., 0.75, 0.5, 0.25, 0., 0.]
- 4번째 요소와 5번째 요소의 fall-out이 같으므로 작은 값이 5번째 요소만 사용한다.
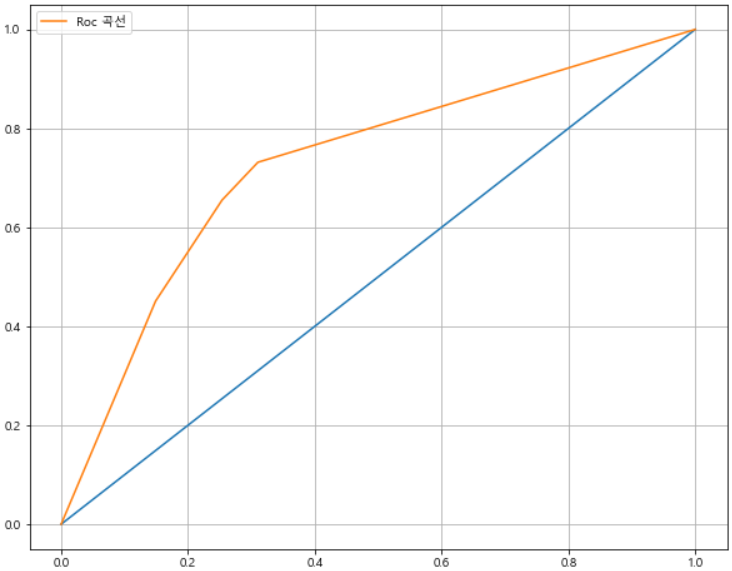
◾ROC 커브 그리기
import pandas as pd
red_wine = pd.read_csv('winequality-red.csv', sep=';')
white_wine = pd.read_csv('winequality-white.csv', sep=';')
red_wine['color'] = 1
white_wine['color'] = 0
wine = pd.concat([red_wine, white_wine])
wine.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
wine['taste'] = [1. if grade > 5 else 0. for grade in wine['quality']]
X = wine.drop(['taste', 'quality'], axis=1)
y = wine['taste']
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=13)
wine_tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2, random_state = 13)
wine_tree.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred_tr = wine_tree.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test = wine_tree.predict(X_test)
print("Train Acc : {}".format(accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred_tr)))
print("Test Acc : {}".format(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_test)))

from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score, roc_auc_score, roc_curve
print('Accuracy : {}'.format(accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred_test)))
print('Recall : {}'.format(recall_score(y_test, y_pred_test)))
print('Precision : {}'.format(precision_score(y_test, y_pred_test)))
print('AUC Score : {}'.format(roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_test)))
print('F1_score : {}'.format(f1_score(y_test, y_pred_test)))

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import set_matplotlib_korean
pred_proba = wine_tree.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
fpr, tpr, threshols = roc_curve(y_test, pred_proba)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1])
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, label='Roc 곡선')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()