문제
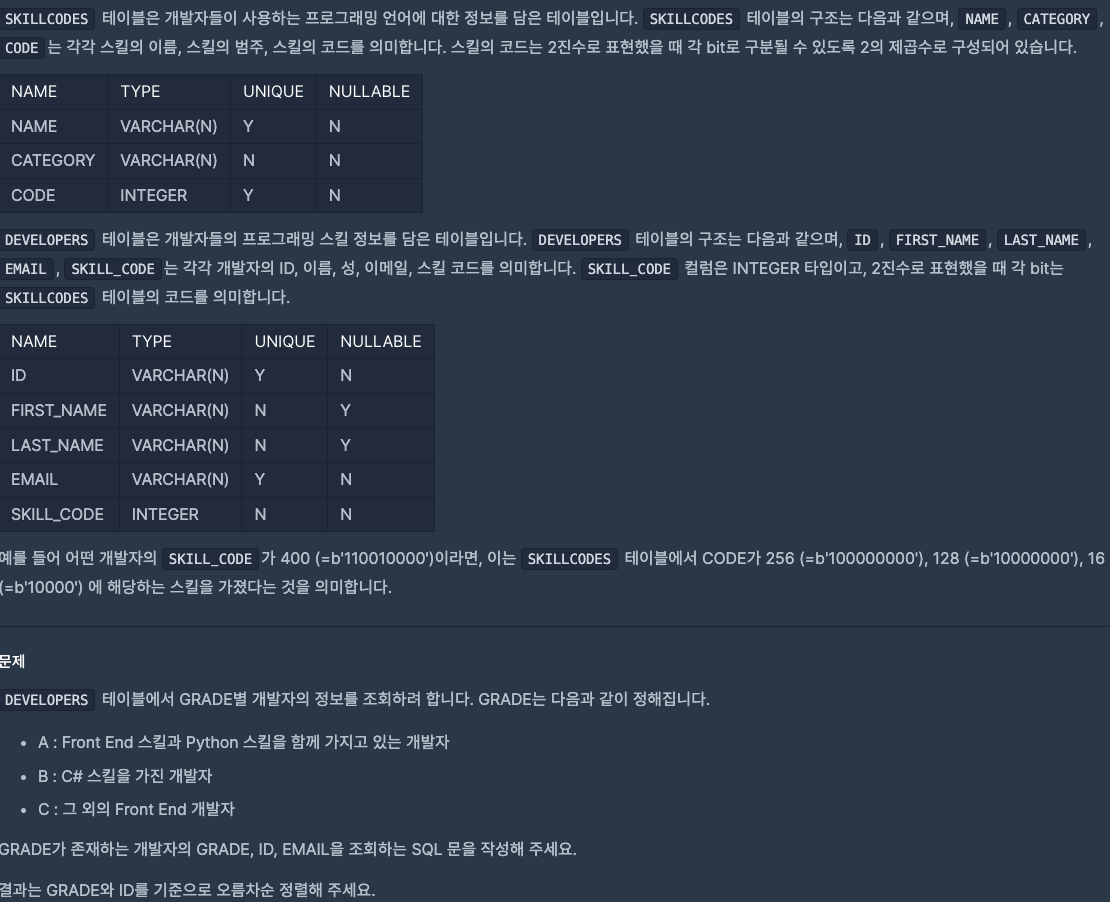
제출
with grade_rank as (
select *,
(case when skill_code & (select sum(code) from skillcodes where NAME = 'Python')
and skill_code & (select sum(code) from skillcodes where category = 'Front End') then 'A'
when skill_code & (select code from skillcodes where name = 'c#') then 'B'
when skill_code & (select sum(code) from skillcodes where category = 'front end') then 'C' end) as GRADE
from developers
)
SELECT grade, id, email
from grade_rank
where grade is not null
order by 1 asc, 2 asc📌 알게된 것
case when 에서도 and 를 사용해 조건을 여러개 달 수 있다.
또 다른 답
SELECT (case when skill_code & (select sum(code) from skillcodes where NAME = 'Python')
and skill_code & (select sum(code) from skillcodes where category = 'Front End') then 'A'
when skill_code & (select code from skillcodes where name = 'c#') then 'B'
when skill_code & (select sum(code) from skillcodes where category = 'front end') then 'C' end) as GRADE, id, email
from developers
having grade is not null
order by 1 asc, 2 ascselect 보다 where 이 먼저 실행되기 때문에 where grade is not null 은 에러가 뜨고, having 은 select 보다 나중에 실행되므로 having grade is not null 이렇게 써도 작동은 한다.
하지만 비효율적이다.
❌ 비효율적인 이유: HAVING은 집계 함수(Aggregate Function)에 주로 사용되기 때문이다.
