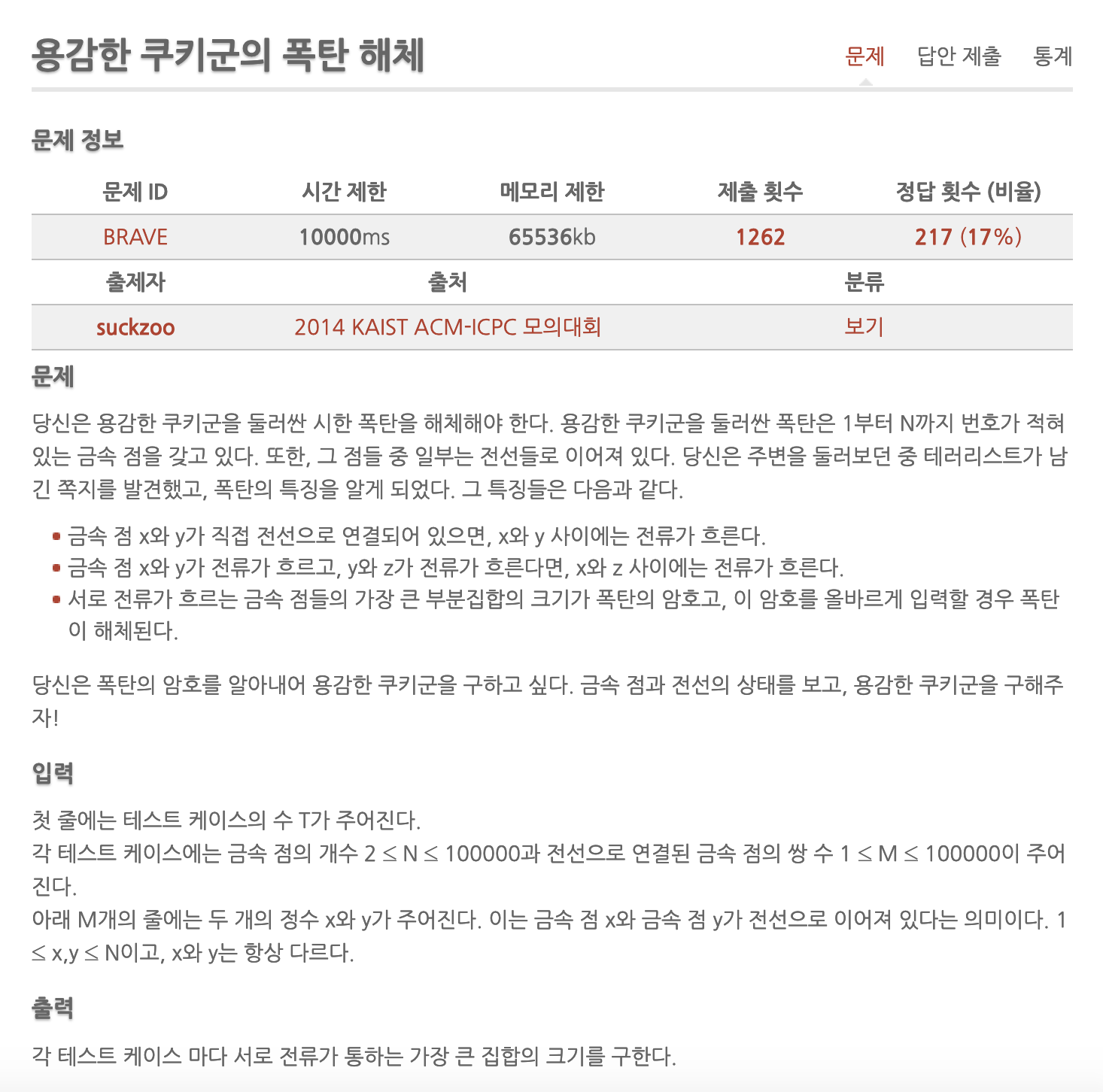
문제
- 두 금속 x, y가 연결되어 있고, 두 금속 y, z가 연결되어 있으면, 두 금속 x, z 또한 연결되어 있다.
- 서로 연결되어 있는 금속 들의 가장 큰 부분집합의 크기를 구하시오.
- 2 <= n <= 10만 (n은 정점의 개수), 1<= m <= 10만 (m은 간선의 개수)
- 시간 제한 10초
- 문제 링크
접근 과정
1. 그래프
- 1) 하나의 금속을 정점, 2) 두 금속 간의 연결 관계를 간선으로 생각하고, 금속간의 관계를 그래프로 설계할 수 있습니다.
2. 집합
- 두 정점이 연결되어 있는지 즉, 같은 집합에 속하는 지를 알아보는 알고리즘에는 disjoint-set(union-find) 가 있습니다.
- disjoint-set은 먼저 find() 함수를 통해 한 정점의 최상위 부모 정점을 찾습니다. 그리고, 다른 정점과 비교할 때 1) 두 정점의 최상위 부모가 같으면 서로 연결되어 있고, 2) 최상위 부모가 다르다면, 연결되어 있지 않은 것입니다.
- 이번 문제에서 각 금속의 최상위 부모를 find() 함수를 통해 찾고, 최상위 부모의 정보를 d 배열에 저장합니다. 그리고, 다른 금속과의 최상위 부모 비교를 통해 연결되어 있는지 여부를 찾고, 마지막으로 find() 함수를 통해 최상위 부모를 가지고 있는 정점의 개수를 구해서 집합의 크기를 찾습니다.
3. 시간 복잡도 계산
-
1) find() 함수의 시간 복잡도는 O(n), 그리고 간선의 개수 m 만큼 수행되기 때문에 시간 복잡도는 O(nm) 입니다.
-
2 <= n <= 100000 (n은 정점의 개수), 1<= m <= 100000 (m은 간선의 개수) 이기 때문에 O(nm)은 O(10억) 문제의 시간 제한이 10초 이기 때문에 아슬아슬하게 들어옵니다.
코드
1. C++
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define max_int 100001
using namespace std;
//시간 복잡도: O(n^2)
//공간 복잡도: O(n)
//사용한 알고리즘: disjoint-set
//사용한 자료구조: 1차원 배열
int t, n, m, a, b, result;
// 정점 a의 부모를 담을 배열 d
// d[a] = b라면, 정점 a의 부모는 b다.
int d[max_int];
// 정점 a를 최상위 부모로 가지고 있는 정점들의 개수
// cnt[a] = 4라면, 정점 a를 최상위 부모로 가지는 정점들의 개수는 4개이다.(자기 자신 포함)
int cnt[max_int];
// 최상위 부모를 찾는 함수
int find(int node){
// 1) 만약, 현재 노드의 부모와 현재 노드가 같다면 최상위 노드이다.
if(d[node] == node) return node;
// 2) 다르다면, 재귀 호출을 통해 최상위 부모를 찾아서 넣어준다.
else return d[node] = find(d[node]);
}
// 초기화 함수
void init() {
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
// 정점 i의 부모는 i다.
d[i] = i;
cnt[i] = 0;
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d", &t);
for(int test_case = 1; test_case <= t; test_case++){
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
// 1. 초기화, 1) 부모의 정보를 담는 배열 d, 2) 개수 정보를 담을 배열 i초기화
init();
// 2. 두 금속을 입력받는다.
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
// 1) 각 금속의 부모를 찾는다.
a = find(a);
b = find(b);
// 2) 각 금속의 최상위 부모가 다르다면
if(a != b){
// a 금속의 최상위 부모의 부모는 b가 된다.
d[a] = b;
}
}
// 모든 정점의 최상위 부모를 찾고, 개수를 증가시켜준다.
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
cnt[find(i)]++;
}
result = 0;
// 최상위 부모로 가장 많이 선택된 정점에 대해 선택된 개수를 갱신해준다.
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
result = max(result, cnt[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", result);
}
}2. python3
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
print = sys.stdout.write
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)
# 시간 복잡도: O(nm)
# 공간 복잡도: O(n)
# 사용한 알고리즘: disjoint-set
# 사용한 자료구조: 리스트
def find(node):
if d[node] == node:
return node
else:
d[node] = find(d[node])
return d[node]
t = int(input())
for _ in range(t):
n, m = map(int, input().split())
d = [0] * (n+1)
for i in range(1, n+1):
d[i] = i
cnt = [0] * (n+1)
for _ in range(m):
a, b = map(int, input().split())
a = find(a)
b = find(b)
if a != b:
d[a] = b
for i in range(1, n+1):
cnt[find(i)] += 1
result = 0
for i in range(1, n+1):
result = max(result, cnt[i])
print("%d\n" % result)3. java
import java.util.*;
// 시간 복잡도: O(nm)
// 공간 복잡도: O(n)
// 사용한 알고리즘: disjoint-set
// 사용한 자료구조: 배열
public class Main {
static int t, n, m, a, b, result;
static int[] d;
static int[] cnt;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
t = sc.nextInt();
for(int test_case = 1; test_case <= t; test_case++){
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
d = new int[n+1];
cnt = new int[n+1];
init();
for(int i=0; i<m; i++){
a = sc.nextInt();
b = sc.nextInt();
a = find(a);
b = find(b);
if(a != b){
d[a] = b;
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
cnt[find(i)]++;
}
result = 0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
result = max(result, cnt[i]);
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
static int find(int node){
if(d[node] == node) return node;
else return d[node] = find(d[node]);
}
static void init() {
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
d[i] = i;
cnt[i] = 0;
}
}
static int max(int a, int b){
return a > b ? a : b;
}
}