[자바] Java 8 버전 특징
1. 개요
1) 2021년 가장 많이 사용하고 있는 버전
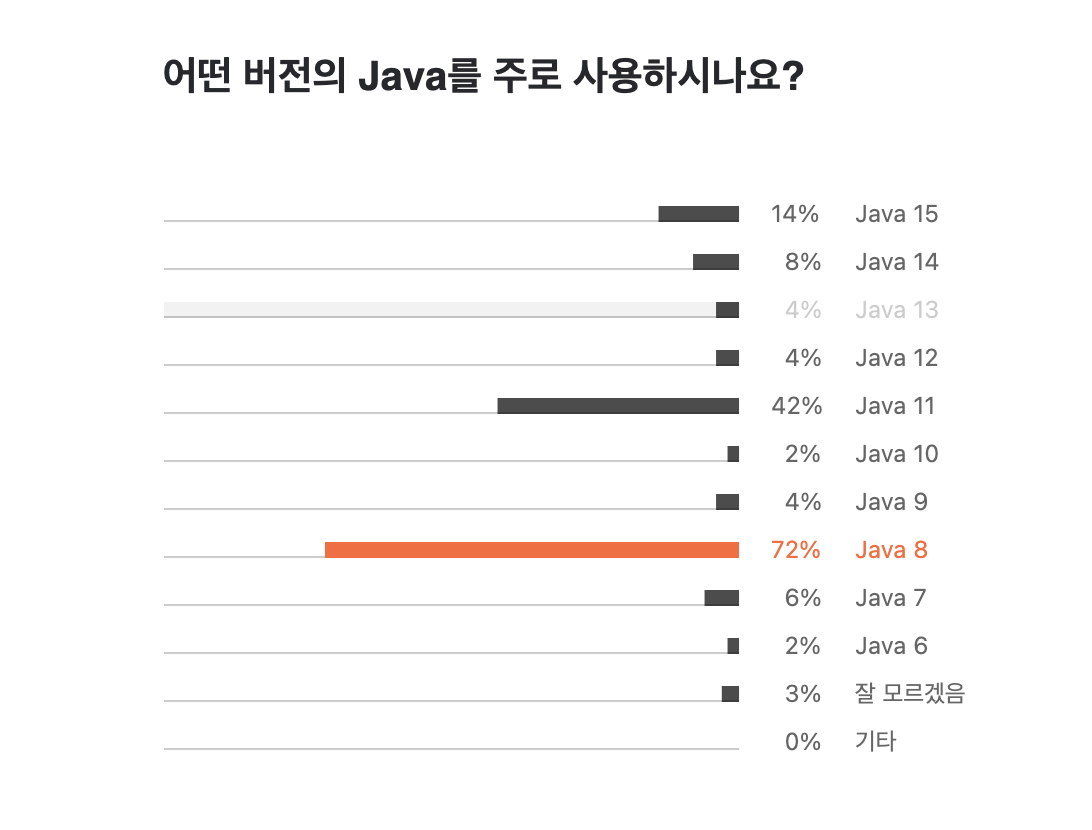
2021 jetbran report 에 따르면 가장 많이 사용하고 있는 버전은 자바 8으로 사용 비율은 약 72%입니다.
2) 몇 버전까지 나왔나요?
2021년 9월 자바 17버전까지 나왔습니다.
9버전 이후 부터는 6개월 마다 새로운 버전이 출시되고, 매년 3월, 9월에 배포됩니다.
3) LTS 버전 (Long Term Support)
LTS 는 오랜기간 동안 버그 픽스 등 패치를 해주는 버전을 의미합니다.
- LTS - java 8, 11, 17
- non-LTS - LTS 버전 이외
non-LTS 버전은 6개월 동안만 지원하기 때문에 실제 서비스를 개발할때는 LTS 버전을 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
2. Java 8에 추가된 내용
lambda, optional, Interface static And default method
1. lambda
1) 정의
람다는 함수를 하나의 표현식으로 나타낸것을 의미합니다.
람다는 함수형 프로그래밍 언어에서 사용되는 개념으로 메서드에 이름이 없어 익명 함수라고도 부릅니다.
2) 예시
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> numList = Arrays.asList(0, 1, 2);
// 1. 반복문 - Iterator
for(Integer num: numList) {
System.out.println(num);
}
// 2. 람다 표현식
numList.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
}
}3) 장단점
- 장점
- 코드를 간결하게 작성할 수 있습니다. - 단점
- 재활용이 불가능합니다. 만약 익명함수가 여러곳에서 반복적으로 사용된다면, 익명함수를 재활용을 위해 익명함수를 사용하지 않는 방법을 고려해야합니다.
2. optional
1) 정의
Optional은 null이 될 수 있는 객체를 담는 클래스입니다.
원소를 최대 1개 가질 수 있는 불변 컬렉션으로 생각할 수 있습니다. stream 사용 가능합니다.(자바 9에 추가, 다만, Collection<T>는 구현하지 않았습니다.)
2) 예시
import java.util.Optional;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Car car = new Car();
// 1. NullPointerException 발생
// System.out.println(car.getPerson().getName());
// 2. 옵셔널을 검사해서 없는 경우 사용자 이름 없음 출력
System.out.println(Optional.of(car)
.map(Car::getPerson)
.map(Person::getName)
.orElse("사용자 이름 없음"));
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
//getter, setter
}
class Car {
private String name;
private Person person;
//getter, setter
}3) 장점
명시적으로 반환값이 Null일 수 있음을 알려줍니다.
직접 null을 다루지 않아도 됩니다.
3. 메소드 레퍼런스
1) 정의
메소드 레퍼런스는 람다의 축약 표현입니다.
다음과 같이 사용할 수 있습니다.
클래스 이름::메소드 이름
생성자::new
2) 예시
- 클래스 이름:: 메소드이름
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
List<String> numList = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C");
// 1. 람다 표현식
numList.forEach(x -> System.out.println(x));
// 2. 메서드 레퍼런스 (클래스::메소드)
numList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}- 클래스::생성자
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
List<String> numList = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C");
// 1. 람다 표현식
List<Person> personList1 = numList.stream().map(x -> new Person(x)).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 2. 클래스::new
List<Person> personList2 = numList.stream().map(Person::new).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}4. stream
1) 정의
strem의 데이터의 흐름으로 람다를 사용할 수 있도록 제공합니다.
2) 예시
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int[] numArr = { 0, 1, 2};
Arrays.stream(numArr).forEach(System.out::println);
IntStream.range(0, 3).boxed().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}5. 인터페이스 default, static method
1) 정의
인터에페이스는 구현부가 없는 추상메소드만 가질 수 있었는데 default, static 지시어로 생성된 메서드는 구현부를 가질 수 있습니다.
2) 차이점
-
default 메서드
재정의 o
참조 변수로 호출 -
static 메서드
재정의 x
클래스 메서드이기 때문에 객체 생성하지 않고 직접 사용
3) 예시
public interface Calculator {
default int sumDefault(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
static int sumStatic(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
}class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator() {
@Override
public int sumDefault(int x, int y) {
return x * y;
}
};
int sumResultDefault = calculator.sumDefault(3, 4);
System.out.println(sumResultDefault);
int sumResultStatic = Calculator.sumStatic(1, 2);
System.out.println(sumResultStatic);
}
}6. LocalDateTime
1) 정의
불변 시간 정보를 가지고 있습니다.
2) 예시
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
LocalDateTime startTime = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime endTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(startTime);
System.out.println(endTime);
System.out.println(startTime.isBefore(endTime));
}
}