1. 아래를 프로그래밍 하시오.
이름:kom
국어:80
영어:90
수학:100
kom님의 평균은90.0성적은수입니다.
계속?y
이름:yun
국어:90
영어:70
수학:55
yun님의 평균은71.66666666666667성적은미입니다.
계속?yes
이름:한글
국어:90
영어:75
수학:80
한글님의 평균은81.66666666666667성적은우입니다.
계속?klsjdaf
종료되었습니다.
종료되었습니다.
class Grade{
private int kor, eng, math;
private String name;
Grade(String name, int kor, int eng, int math) {
this.kor = kor;
this.eng = eng;
this.math = math;
this.name = name;
}
double getAvg(){
return (kor + eng + math) / 3.0; // double 이라서 .0을 붙여야 함
}
public void showInfo() {
System.out.println(name + "님의 평균은" + getAvg() + "성적은" + getGrade() + "입니다.");
}
char getGrade() {
char ch = '가';
double avg = getAvg();
if(avg >= 90) {
ch = '수';
}
else if(avg >= 80) {
ch = '우';
}
else if(avg >= 70) {
ch = '미';
}
else if(avg >= 60) {
ch = '양';
}
else {
ch = '가';
}
return ch;
}
}
Scanner sc = null;
Grade grade = null;
int kor, eng, math;
String name;
///////////////////////////////////비지니스 로직
while (true) {
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("이름:");
name = sc.next();
System.out.print("국어:");
kor = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("영어:");
eng = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("수학:");
math = sc.nextInt();
grade = new Grade(name, kor, eng, math);
grade.showInfo();
System.out.print("계속?");
String choice = sc.next();
if (choice.compareToIgnoreCase("yes") == 0 || choice.compareToIgnoreCase("y") == 0)
continue;
else
break;
}
System.out.println("종료되었습니다.");2. 아래의 String 함수에 대하여 예를들어 설명하시오.
-equals()
-indexOf()
-length()
-substring()
-toUpperCase()와 toLowerCase()
-concat()
-startWith()
-replace
-trim()
-contains
equals
: 문자열이 같은지 여부를 확인.
"hello".equals("hello")는 true를 반환.
indexOf
: 문자열에서 특정 문자열의 인덱스를 반환.
"hello".indexOf("l")는 1을 반환.
length
: length() : 문자열의 길이를 반환.
"hello".length()는 5를 반환.
substring
: 문자열의 일부를 반환.
"hello".substring(2)는 "llo"를 반환.
toUpperCase,toLowerCase
: 문자열을 대문자 또는 소문자로 변환.
"hello".toUpperCase()는 "HELLO"를 반환
"hello".toLowerCase()는 "hello"를 반환.
concat
: 두 개의 문자열을 연결.
"hello".concat("world")는 "helloworld"를 반환.
startWith
: 문자열이 특정 문자열로 시작하는지 여부를 확인.
"hello".startWith("hel")는 true를 반환.
replace
: 문자열에서 특정 문자열을 다른 문자열로 바꿈.
"hello".replace("l", "w")는 "hewo"를 반환.
trim
: 문자열의 앞뒤 공백을 제거.
"hello".trim()는 "hello"를 반환.
contains
: 문자열이 특정 문자열을 포함하는지 여부를 확인.
"hello".contains("ll")는 true를 반환.
3. 아래를 프로그래밍 하시오.
======================
힌트) length 함수와 charAt 함수사용
영어 단어를 입력하세요.
dakjfivnlwe
총 글자 수는: 11개 입니다.
모음은 : 3개 입니다.
자음은 : 8개 입니다.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("영어 단어를 입력하세요.");
String word = sc.next();
int length = word.length();
int vowelCount = 0;
int consonantCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char ch = word.charAt(i);
if (isVowel(ch)) {
vowelCount++;
} else {
consonantCount++;
}
}
System.out.println("총 글자 수는: " + length + "개 입니다.");
System.out.println("모음은 : " + vowelCount + "개 입니다.");
System.out.println("자음은 : " + consonantCount + "개 입니다.");}
public static boolean isVowel(char ch) {
char[] vowels = {'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u', 'y'};
for (char vowel : vowels) {
if (ch == vowel) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}1. 가위바위보 프로그램을 짜시오.
힌트 - random 함수 사용
가위, 바위, 보 중 하나를 입력하세요.
가위 // 유저가 입력
바위 //
졌습니다.
계속하시겠습니까?(Y/N)
Y
가위, 바위, 보 중 하나를 입력하세요.
바위
가위
이겼습니다.
계속하시겠습니까?(Y/N)
N
프로그램을 종료합니다.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] a = {"가위","주먹","보"};
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
int num= (int)(Math.random()*3);
System.out.println("가위,바위,보 중 하나를 입력하세요");
String b=sc.next();
System.out.println();
if(b.equals("가위")) {
if(num==0) {
System.out.println("가위 : 유저");
System.out.println("바위");
System.out.println("졌습니다.");
}
if(num==1) {
System.out.println("가위 : 유저");
System.out.println("보");
System.out.println("이겼습니다.");
}
if(num==2) {
System.out.println("가위 : 유저");
System.out.println("가위");
System.out.println("비겼습니다.");
}
System.out.println("계속 하시겠습니까? Y/N");
System.out.println();
String choice = sc.next();
if (choice.compareToIgnoreCase("yes") == 0 || choice.compareToIgnoreCase("y") == 0)
continue;
else
break;
}
if(b.equals("바위")) {
if(num==0) {
System.out.println("바위 : 유저");
System.out.println("바위");
System.out.println("비겼습니다.");
}
if(num==1) {
System.out.println("바위 : 유저");
System.out.println("보");
System.out.println("졌습니다.");
}
if(num==2) {
System.out.println("바위 : 유저");
System.out.println("가위");
System.out.println("이겼습니다.");
}
System.out.println("계속 하시겠습니까? Y/N");
System.out.println();
String choice = sc.next();
if (choice.compareToIgnoreCase("yes") == 0 || choice.compareToIgnoreCase("y") == 0)
continue;
else
break;
}
if(b.equals("보")) {
if(num==0) {
System.out.println("보 : 유저");
System.out.println("바위");
System.out.println("이겼습니다.");
}
if(num==1) {
System.out.println("보 : 유저");
System.out.println("보");
System.out.println("비겼습니다.");
}
if(num==2) {
System.out.println("보 : 유저");
System.out.println("가위");
System.out.println("졌습니다.");
}
System.out.println("계속 하시겠습니까? Y/N");
System.out.println();
String choice = sc.next();
if (choice.compareToIgnoreCase("yes") == 0 || choice.compareToIgnoreCase("y") == 0)
continue;
else
break;
}
}Point
-
concat : 두개를 붙이는것 (str1 + str2)에서 + 역할

- 이어서 가능 ("AB".concat('cd').concat("EF")) 식으로
-
substring : 프로그래밍 언어에서 첫자리는 1이 아니라 0이다
- 2면 2 이후 내용, 2,4면 2와 (<0,1,2,3>4-1)
-
compareTo : 두 문자열 비교
(a가 10쪽, b가 20쪽이면 a가 사전앞, b가 사전뒤) -
compareToIgnoreCase : 대소문자 관계없이 비교
-
valueOf : 외워야함
- 앞에 데이터 타입으로 자료형을 바꿈
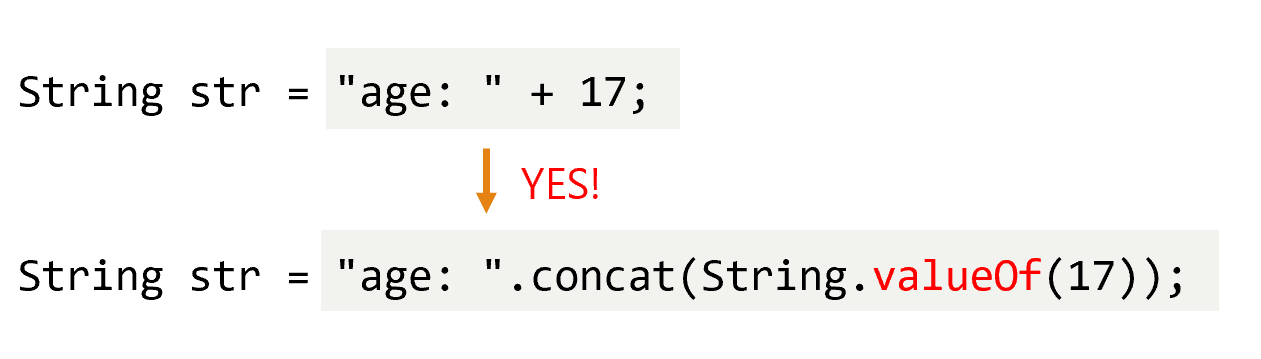
- 앞에 데이터 타입으로 자료형을 바꿈
-
equal 사용례
if(str1.equals(str3)) // 문자열 내용물만 비교
System.out.println("str1과 str3는 동일 인스턴스 참조");
else
System.out.println("str1과 str3는 다른 인스턴스 참조");- StringBuilder
- 메모리 최적화를 위해 가변(따라와서 메모리 차지하는 것들을 줄임)
- stbuf.로 문자열 변환
요즘엔 입력을 콘솔로 받는곳은 없다
-
Scnner 클래스 (입력)
- System.in : 키보드 (in : static 클래스)
-
import java.util.Scanner;
-
배열 : 선언 방법 = 메모리 할당
- [ ]
- 메모리가 연속적으로 잡혀야 한다
- 랜덤생성 math.random
- -1은 j<i 하나로
