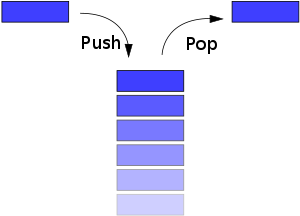
자료 저장 형태 중 스택에 대해 설명
- 스택은 데이터를 후입선출(LIFO, Last-In-First-Out)의 원리로 관리한다.
즉, 가장 최근에 삽입된 데이터가 가장 먼저 삭제되는 구조이다. - 데이터를 삽입하는 함수를 push(), 데이터를 삭제하는 함수를 pop()이라고 하며, 스택의 최상단에 위치한 요소를 top이라고 한다.
- 작업 대기열, 메시지 큐, 버퍼 등이 스택의 예로 사용된다.
배열을 이용한 스택
//배열을 이용한 스택 자료구조
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> //malloc, realloc(기존의 메모리 복사 -> 새 메모리에 저장)
#pragma warning (disable : 4996)
typedef struct stack
{
int* arr; //동적 메모리의 주소를 저장(동적할당)
int top; //배열을 저장하려는 위치(배열의 인덱스)
int capacity; //배열의 최대 용량
}stack;
void stackInitialize(stack* p, int size) //top = 0 & capacity = 3(size)
{
p->arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
p->top = 0;
p->capacity = size;
}
void push(stack* p, int data)
{
if (p->top >= p->capacity)
{
//printf("\n\n\t\tstack overflow\n");
//return;
p->capacity = p->capacity * 2;
//새 메모리의 주소 = realloc (원래 메모리의 주소, 재할당된 크기)
p->arr = realloc(p->arr, sizeof(int) * p->capacity);
printf("\n\n\t\t스택 메모리의 크기가 2배로 확장됐습니다.\n");
}
p->arr[p->top] = data;
printf("\n\n\t\t%d push\n", p->arr[p->top]);
(p->top)++;
}
void print(stack stk) //LIFO
{
int i;
printf("\n\nInteger stack : ");
for (i = stk.top - 1; i >= 0; i--)
printf("%d", stk.arr[i]);
puts("");
}
void pop(stack *p)
{
if (p->top == 0)
{
printf("\n\n\t\t stack underflow\n");
return;
}
(p->top)--;
printf("\n\n\t\t %d pop!!", p->arr[p->top]);
}
int main()
{
int size, choice, data;
stack stk; //구조체 변수 선언
printf("\n스택 크기 입력 :");
scanf("%d ", &size);
while (getchar() != '\n');
stackInitialize(&stk, size); //stack = call by address // size = call by value
while (1)
{
system("cls");
printf("\n\n\t\t ***Integer stack***\n\n");
printf("1. push 2. pop 3. print 4.clear 0.terminate\n");
printf("choice : [ ]\b\b");
scanf("%d", &choice);
while (getchar() != '\n');
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
printf("\n\nenter integer : ");
scanf("%d", &data);
while (getchar() != '\n');
push(&stk, data); //push함수 호출
break;
case 2:
pop(&stk);
break;
case 3:
print(stk);
break;
case 4:
stk.top = 0;
break;
case 0:
free(stk.arr); //동적 메모리 해제
exit(0);
break;
}
printf("\n\n\t\t");
system("pause");
}
return 0;
}연결리스트를 이용한 스택
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#pragma warning (disable : 4996)
typedef struct node
{
int value;
struct node* next;
}node;
node* head = NULL;
void push(int data)
{
node *newNode = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
newNode->value = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (head == NULL) //첫 노드인 경우
{
head = newNode; //새 노드를 head로 설정
}
else
{
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
}
printf("\n\n\t\t%d push!!", head->value);
}
void pop()
{
node* delNode = head; //delNode를 첫 노드(head)로 설정
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("\n\n\t\tstack underflow\n");
return;
}
//LIFO : 첫 노드 삭제
head = head->next; //다음 노드로 head 변경
printf("\n\n\t\t%d pop!!", delNode->value);
free(delNode);
}
void print()
{
node* curNode = head;
if (head == NULL)
return;
printf("\n\nstack display : ");
while (curNode->next != NULL) //다음 노드가 있다면
{
printf("%d => ", curNode->value);
curNode = curNode->next; //방문 노드를 다음 노드로 이동
}
printf("%d\n", curNode->value); //마지막 노드 출력
}
void clear()
{
node* delNode = head;
if (head == NULL)
return;
while (head) //방문 노드가 있다면
{
head = head->next; //head를 다음 노드로 변경
free(delNode); // 노드 제거
delNode = head; // head가 있는 곳으로 delNode 이동
}
}
int main()
{
int choice, data;
while (1)
{
system("cls");
printf("\n\n\t\t ***Integer stack(linked list)***\n\n");
printf("1. push 2. pop 3. print 4.clear 0.terminate\n");
printf("choice : [ ]\b\b");
scanf("%d", &choice);
while (getchar() != '\n');
switch (choice)
{
case 1:
printf("\n\nenter integer : ");
scanf("%d", &data);
while (getchar() != '\n');
push(data); //노드 맨 앞 삽입
break;
case 2:
pop();
break;
case 3:
print();
break;
case 4:
clear(); //모든 노드 삭제
break;
case 0:
clear();
exit(0);
break;
}
printf("\n\n\t\t");
system("pause");
}
return 0;
}