출처: https://youtu.be/Z_ikDlimN6A
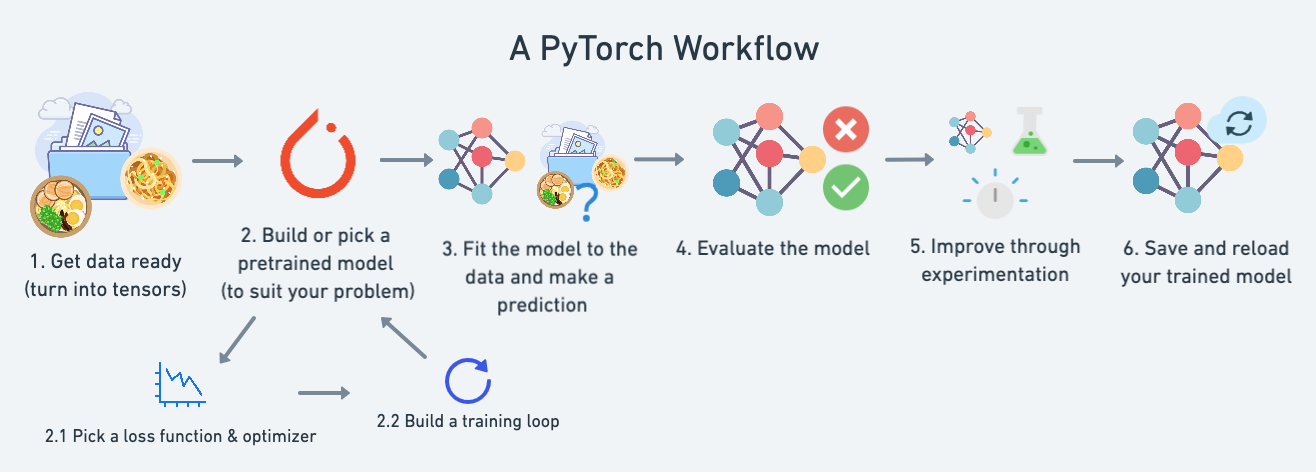
- Getting data ready
# Create weight and bias
weight = 0.7
bias = 0.3
# Create range values
start = 0
end = 1
step = 0.02
# Create X and y (features and labels)
# without unsqueeze, errors will happen later on
# (shapes within linear layers)
X = torch.arange(start, end, step).unsqueeze(dim=1)
y = weight * X + bias
X[:10], y[:10]# Import dependencies
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Set the hyperparameters for data creation
NUM_CLASSES = 4
NUM_FEATURES = 2
RANDOM_SEED = 42
# 1. Create multi-class data
X_blob, y_blob = make_blobs(n_samples=1000,
n_features=NUM_FEATURES, # X features
centers=NUM_CLASSES, # y labels
cluster_std=1.5, # give the clusters a little shake up
random_state=RANDOM_SEED
)
# 2. Turn data into tensors
X_blob = torch.from_numpy(X_blob).type(torch.float)
y_blob = torch.from_numpy(y_blob).type(torch.LongTensor)
print(X_blob[:5], y_blob[:5])
# 3. Split into train and test sets
X_blob_train, X_blob_test, y_blob_train, y_blob_test = train_test_split(
X_blob,
y_blob,
test_size=0.2,
random_state=RANDOM_SEED
)
# 4. Plot data
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
plt.scatter(X_blob[:, 0], X_blob[:, 1], c=y_blob, cmap=plt.cm.RdYlBu);# Setup training data
train_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data", # where to download data to?
train=True, # get training data
download=True, # download data if it doesn't exist on disk
transform=ToTensor(), # images come as PIL format, we want to turn into Torch tensors
target_transform=None # you can transform labels as well
)
# Setup testing data
test_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=False, # get test data
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)# Write transform for image
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
# Resize the images to 64x64
transforms.Resize(size=(64, 64)),
# Flip the images randomly on the horizontal
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(p=0.5), # p = probability of flip, 0.5 = 50% chance
# Turn the image into a torch.Tensor
transforms.ToTensor() # this also converts all pixel values from 0 to 255 to be between 0.0 and 1.0
])from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
# Setup the batch size hyperparameter
BATCH_SIZE = 32
# Turn datasets into iterables (batches)
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_data, # dataset to turn into iterable
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, # how many samples per batch?
shuffle=True # shuffle data every epoch?
)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data,
batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle=False # don't necessarily have to shuffle the testing data
)
# Let's check out what we've created
print(f"Dataloaders: {train_dataloader, test_dataloader}")
print(f"Length of train dataloader: {len(train_dataloader)} batches of {BATCH_SIZE}")
print(f"Length of test dataloader: {len(test_dataloader)} batches of {BATCH_SIZE}")- Building a model
# Subclass nn.Module to make our model
class LinearRegressionModelV2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# Use nn.Linear() for creating the model parameters
self.linear_layer = nn.Linear(in_features=1,
out_features=1)
# Define the forward computation
# (input data x flows through nn.Linear())
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
return self.linear_layer(x)
# Set the manual seed when creating the model
torch.manual_seed(42)
model_1 = LinearRegressionModelV2()
model_1, model_1.state_dict()from torch import nn
# Build model
class BlobModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_features, output_features, hidden_units=8):
"""Initializes all required hyperparameters for a multi-class classification model.
Args:
input_features (int): Number of input features to the model.
out_features (int): Number of output features of the model
(how many classes there are).
hidden_units (int): Number of hidden units between layers, default 8.
"""
super().__init__()
self.linear_layer_stack = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=input_features, out_features=hidden_units),
# nn.ReLU(), # <- does our dataset require non-linear layers? (try uncommenting and see if the results change)
nn.Linear(in_features=hidden_units, out_features=hidden_units),
# nn.ReLU(), # <- does our dataset require non-linear layers? (try uncommenting and see if the results change)
nn.Linear(in_features=hidden_units, out_features=output_features), # how many classes are there?
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear_layer_stack(x)
# Create an instance of BlobModel and send it to the target device
model_2 = BlobModel(input_features=NUM_FEATURES,
output_features=NUM_CLASSES,
hidden_units=8).to(device)
model_2# Make prediction logits with model
y_logits = model_2(X_blob_test.to(device))
# Perform softmax calculation on logits across dimension 1 to get prediction probabilities
y_pred_probs = torch.softmax(y_logits, dim=1)
print(y_logits[:5])
print(y_pred_probs[:5])# Create a convolutional neural network
class FashionMNISTModelV2(nn.Module):
"""
Model architecture copying TinyVGG from:
https://poloclub.github.io/cnn-explainer/
"""
def __init__(self, input_shape: int, hidden_units: int, output_shape: int):
super().__init__()
self.block_1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=input_shape,
out_channels=hidden_units,
kernel_size=3, # how big is the square that's going over the image?
stride=1, # default
padding=1),# options = "valid" (no padding) or "same" (output has same shape as input) or int for specific number
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=hidden_units,
out_channels=hidden_units,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,
stride=2) # default stride value is same as kernel_size
)
self.block_2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(hidden_units, hidden_units, 3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(hidden_units, hidden_units, 3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2)
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Flatten(),
# Where did this in_features shape come from?
# It's because each layer of our network compresses and changes the shape of our inputs data.
nn.Linear(in_features=hidden_units*7*7,
out_features=output_shape)
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor):
x = self.block_1(x)
# print(x.shape)
x = self.block_2(x)
# print(x.shape)
x = self.classifier(x)
# print(x.shape)
return x
torch.manual_seed(42)
model_3 = FashionMNISTModelV2(input_shape=1,
hidden_units=10,
output_shape=len(class_names)).to(device)
model_3- Fitting the model to data (training)
# Create loss function
loss_fn = nn.L1Loss()
# Create optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params=model_1.parameters(), # optimize newly created model's parameters
lr=0.01)def train_step(model: torch.nn.Module,
data_loader: torch.utils.data.DataLoader,
loss_fn: torch.nn.Module,
optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer,
accuracy_fn,
device: torch.device = device):
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(data_loader):
# Send data to GPU
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 1. Forward pass
y_pred = model(X)
# 2. Calculate loss
loss = loss_fn(y_pred, y)
train_loss += loss
train_acc += accuracy_fn(y_true=y,
y_pred=y_pred.argmax(dim=1)) # Go from logits -> pred labels
# 3. Optimizer zero grad
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 4. Loss backward
loss.backward()
# 5. Optimizer step
optimizer.step()
# Calculate loss and accuracy per epoch and print out what's happening
train_loss /= len(data_loader)
train_acc /= len(data_loader)
print(f"Train loss: {train_loss:.5f} | Train accuracy: {train_acc:.2f}%")
def test_step(data_loader: torch.utils.data.DataLoader,
model: torch.nn.Module,
loss_fn: torch.nn.Module,
accuracy_fn,
device: torch.device = device):
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
model.eval() # put model in eval mode
# Turn on inference context manager
with torch.inference_mode():
for X, y in data_loader:
# Send data to GPU
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 1. Forward pass
test_pred = model(X)
# 2. Calculate loss and accuracy
test_loss += loss_fn(test_pred, y)
test_acc += accuracy_fn(y_true=y,
y_pred=test_pred.argmax(dim=1) # Go from logits -> pred labels
)
# Adjust metrics and print out
test_loss /= len(data_loader)
test_acc /= len(data_loader)
print(f"Test loss: {test_loss:.5f} | Test accuracy: {test_acc:.2f}%\n")from tqdm.auto import tqdm
# 1. Take in various parameters required for training and test steps
def train(model: torch.nn.Module,
train_dataloader: torch.utils.data.DataLoader,
test_dataloader: torch.utils.data.DataLoader,
optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer,
loss_fn: torch.nn.Module = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),
epochs: int = 5):
# 2. Create empty results dictionary
results = {"train_loss": [],
"train_acc": [],
"test_loss": [],
"test_acc": []
}
# 3. Loop through training and testing steps for a number of epochs
for epoch in tqdm(range(epochs)):
train_loss, train_acc = train_step(model=model,
dataloader=train_dataloader,
loss_fn=loss_fn,
optimizer=optimizer)
test_loss, test_acc = test_step(model=model,
dataloader=test_dataloader,
loss_fn=loss_fn)
# 4. Print out what's happening
print(
f"Epoch: {epoch+1} | "
f"train_loss: {train_loss:.4f} | "
f"train_acc: {train_acc:.4f} | "
f"test_loss: {test_loss:.4f} | "
f"test_acc: {test_acc:.4f}"
)
# 5. Update results dictionary
results["train_loss"].append(train_loss)
results["train_acc"].append(train_acc)
results["test_loss"].append(test_loss)
results["test_acc"].append(test_acc)
# 6. Return the filled results at the end of the epochs
return results- Making predictions and evaluating a model (inference)
# Move values to device
torch.manual_seed(42)
def eval_model(model: torch.nn.Module,
data_loader: torch.utils.data.DataLoader,
loss_fn: torch.nn.Module,
accuracy_fn,
device: torch.device = device):
"""Evaluates a given model on a given dataset.
Args:
model (torch.nn.Module): A PyTorch model capable of making predictions on data_loader.
data_loader (torch.utils.data.DataLoader): The target dataset to predict on.
loss_fn (torch.nn.Module): The loss function of model.
accuracy_fn: An accuracy function to compare the models predictions to the truth labels.
device (str, optional): Target device to compute on. Defaults to device.
Returns:
(dict): Results of model making predictions on data_loader.
"""
loss, acc = 0, 0
model.eval()
with torch.inference_mode():
for X, y in data_loader:
# Send data to the target device
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
y_pred = model(X)
loss += loss_fn(y_pred, y)
acc += accuracy_fn(y_true=y, y_pred=y_pred.argmax(dim=1))
# Scale loss and acc
loss /= len(data_loader)
acc /= len(data_loader)
return {"model_name": model.__class__.__name__, # only works when model was created with a class
"model_loss": loss.item(),
"model_acc": acc}# Get model_2 results
model_2_results = eval_model(
model=model_2,
data_loader=test_dataloader,
loss_fn=loss_fn,
accuracy_fn=accuracy_fn
)
model_2_results- Saving and loading a model
from pathlib import Path
# 1. Create models directory
MODEL_PATH = Path("models")
MODEL_PATH.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
# 2. Create model save path
MODEL_NAME = "01_pytorch_workflow_model_1.pth"
MODEL_SAVE_PATH = MODEL_PATH / MODEL_NAME
# 3. Save the model state dict
print(f"Saving model to: {MODEL_SAVE_PATH}")
torch.save(obj=model_1.state_dict(), # only saving the state_dict() only saves the models learned parameters
f=MODEL_SAVE_PATH)# Instantiate a fresh instance of LinearRegressionModelV2
loaded_model_1 = LinearRegressionModelV2()
# Load model state dict
loaded_model_1.load_state_dict(torch.load(MODEL_SAVE_PATH))
# Put model to target device (if your data is on GPU, model will have to be on GPU to make predictions)
loaded_model_1.to(device)
print(f"Loaded model:\n{loaded_model_1}")
print(f"Model on device:\n{next(loaded_model_1.parameters()).device}")# Evaluate loaded model
loaded_model_1.eval()
with torch.inference_mode():
loaded_model_1_preds = loaded_model_1(X_test)
y_preds == loaded_model_1_preds