1. 알고리즘을활용하기위해..
웹 애플리케이션에서 사용자들이 게시글, 댓글, 리뷰 등의 콘텐츠를 자유롭게 작성할 수 있는 경우, 동일하거나 유사한 내용이 반복적으로 등록되는 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다.
이로 인해 서비스 품질이 저하되거나 불필요한 데이터가 DB에 축적되어 성능 저하를 초래할 수 있습니다.
이를 해결하기 위해 라빈-카프(Rabin-Karp) 알고리즘을 활용하여 텍스트 기반 콘텐츠의 중복 여부를 빠르게 검사하는 서비스를 Spring Boot 기반으로 구현해 보겠습니다.
2. 라빈-카프 알고리즘 개요
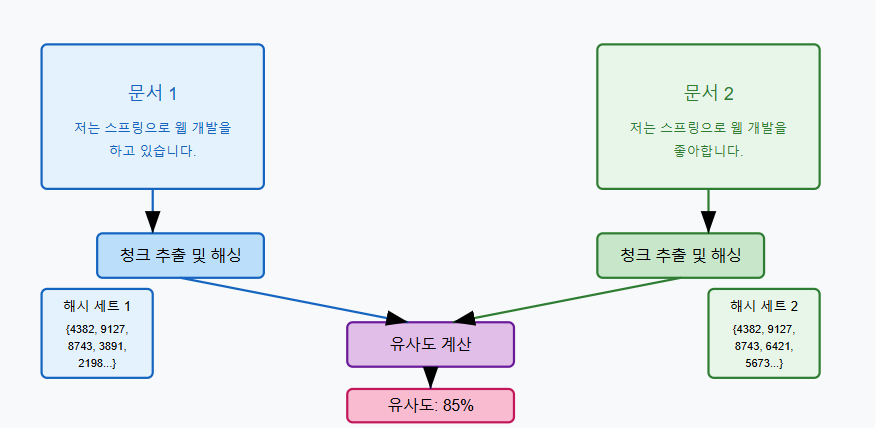
라빈-카프 알고리즘은 해시 함수(Hash Function)를 활용한 문자열 검색 알고리즘으로, 특정 패턴이 주어진 텍스트 내에 존재하는지 빠르게 검사할 수 있습니다.
이 알고리즘은 롤링 해시(Rolling Hash) 기법을 사용하여 문자열 비교 연산을 최적화하며, 중복 콘텐츠 탐지에 적합합니다.
라빈-카프 알고리즘의 주요 특징:
- 해시 기반 검색: 문자열을 해시 값으로 변환하여 빠르게 비교
- 롤링 해시(Rolling Hash): 일정 길이의 해시 값을 슬라이딩 윈도우 방식으로 이동하면서 비교
- 시간 복잡도: 평균적으로 O(n+m) (텍스트 길이 n, 패턴 길이𝑚)
라빈-카프 알고리즘은 일반적으로 문장 내 특정 패턴 검색에 사용되지만, 이를 응용하여 유사한 콘텐츠 탐지 및 중복 검사 서비스를 구축할 수 있습니다.
3. 시스템 설계
3.1. 주요 기능
1. 콘텐츠 등록 시 중복 검사
- 사용자가 새 게시글(혹은 댓글, 리뷰)을 작성할 때 기존 데이터와 비교하여 유사한 내용이 있는지 확인
2. 해시 기반 콘텐츠 저장
- 저장된 콘텐츠에 대해 라빈-카프 해시 값을 유지하여 빠른 비교 수행
3. 유사 콘텐츠 추천
중복은 아니지만 유사한 콘텐츠를 찾아서 추천 가능
3.2. 프로젝트 구조
rabin-karp-duplicate-checker
├── src/main/java/com/example/rabinkarp
│ ├── config # 설정 관련 클래스
│ ├── controller # API 컨트롤러
│ ├── service # 비즈니스 로직
│ ├── repository # DB 접근 계층
│ ├── entity # JPA 엔티티
│ ├── util # 라빈-카프 알고리즘 유틸
├── src/main/resources
│ ├── application.yml # 환경설정
3.3 라빈-카프 알고리즘 구현
RabinKarpUtil.java
package com.example.rabinkarp.util;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class RabinKarpUtil {
private static final int BASE = 31; // 해시 기법에 사용할 소수 기반 값
private static final int MOD = 1000000007; // 충돌 방지를 위한 모듈러 값
/**
* 문자열에서 특정 길이의 해시 값을 계산하는 함수
*/
public static int computeHash(String s, int length) {
int hashValue = 0;
int power = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
hashValue = (hashValue + (s.charAt(i) - 'a' + 1) * power) % MOD;
power = (power * BASE) % MOD;
}
return hashValue;
}
/**
* 롤링 해시를 활용한 중복 검사 (Sliding Window 적용)
*/
public static boolean isDuplicate(String newContent, Set<Integer> existingHashes, int patternLength) {
if (newContent.length() < patternLength) {
return false;
}
int hash = computeHash(newContent, patternLength);
if (existingHashes.contains(hash)) {
return true; // 기존 데이터와 동일한 내용이 존재
}
int power = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < patternLength; i++) {
power = (power * BASE) % MOD;
}
for (int i = 0; i + patternLength < newContent.length(); i++) {
hash = (hash - (newContent.charAt(i) - 'a' + 1) + MOD) % MOD;
hash = (hash * BASE) % MOD;
hash = (hash + (newContent.charAt(i + patternLength) - 'a' + 1)) % MOD;
if (existingHashes.contains(hash)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
3.4 중복 검사 서비스 구현
ContentService.java
package com.example.rabinkarp.service;
import com.example.rabinkarp.repository.ContentRepository;
import com.example.rabinkarp.util.RabinKarpUtil;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Service
public class ContentService {
private final ContentRepository contentRepository;
private final Set<Integer> contentHashes;
public ContentService(ContentRepository contentRepository) {
this.contentRepository = contentRepository;
this.contentHashes = contentRepository.findAll()
.stream()
.map(content -> RabinKarpUtil.computeHash(content.getText(), 10)) // 10글자 단위 비교
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
public boolean isDuplicateContent(String text) {
return RabinKarpUtil.isDuplicate(text, contentHashes, 10);
}
public void saveContent(String text) {
if (!isDuplicateContent(text)) {
contentHashes.add(RabinKarpUtil.computeHash(text, 10));
contentRepository.save(new Content(text));
}
}
}
3.5 REST API 컨트롤러
ContentController.java
package com.example.rabinkarp.controller;
import com.example.rabinkarp.service.ContentService;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/content")
public class ContentController {
private final ContentService contentService;
public ContentController(ContentService contentService) {
this.contentService = contentService;
}
@PostMapping("/check")
public ResponseEntity<?> checkDuplicate(@RequestBody String text) {
boolean isDuplicate = contentService.isDuplicateContent(text);
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(isDuplicate ? "중복된 콘텐츠입니다." : "등록 가능합니다.");
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public ResponseEntity<?> saveContent(@RequestBody String text) {
contentService.saveContent(text);
return ResponseEntity.ok().body("콘텐츠가 저장되었습니다.");
}
}
결론
이제 사용자가 새로운 게시글을 작성할 때, 라빈-카프 알고리즘을 활용한 해시 기반 중복 검사를 수행하여 중복된 콘텐츠를 차단할 수 있습니다.
이를 통해 서비스 품질을 유지하고 불필요한 데이터 저장을 방지하여 DB 성능을 최적화할 수 있습니다.
