1. 문제 상황
우리 팀은 부동산 시각화 플랫폼을 개발하면서 심각한 성능 문제에 직면했습니다.
3D 건물 모델 1000개 이상을 동시에 렌더링해야 하는 상황에서 다음과 같은 문제가 발생했습니다.
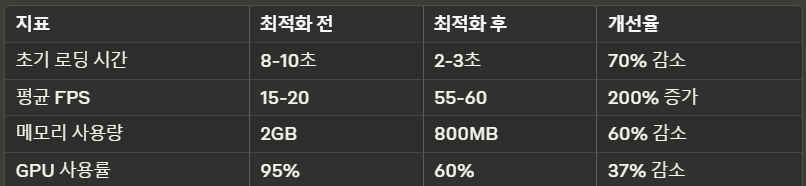
- 초기 로딩 시간: 평균 8-10초
- 프레임 속도: 15-20 FPS (목표: 60 FPS)
- 메모리 사용량: 평균 2GB 이상
- 모바일 기기에서 심각한 성능 저하
2. 원인 분석
2.1 성능 프로파일링 결과
Chrome DevTools Performance 패널을 사용한 분석 결과
// 초기 코드의 문제점
const buildings = [];
const textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
buildingData.forEach(data => {
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(
data.width,
data.height,
data.depth
);
// 🚫 문제 1: 각 건물마다 새로운 텍스처 로딩
const texture = textureLoader.load(data.textureUrl);
// 🚫 문제 2: 불필요한 머티리얼 복제
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
map: texture,
roughness: 0.7,
metalness: 0.3
});
const building = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
buildings.push(building);
scene.add(building);
});
2.2 주요 병목 지점
1. 텍스처 중복 로딩
2. 지오메트리 중복 생성
3. 불필요한 높은 폴리곤 수
4. 부적절한 LOD (Level of Detail) 관리
3. 해결 방안
3.1 텍스처 및 지오메트리 최적화
class BuildingManager {
constructor() {
this.textureCache = new Map();
this.geometryCache = new Map();
this.textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
}
getTexture(url) {
if (!this.textureCache.has(url)) {
const texture = this.textureLoader.load(url);
texture.encoding = THREE.sRGBEncoding;
texture.anisotropy = 16;
this.textureCache.set(url, texture);
}
return this.textureCache.get(url);
}
getGeometry(width, height, depth) {
const key = `${width}-${height}-${depth}`;
if (!this.geometryCache.has(key)) {
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(width, height, depth);
geometry.computeBoundingSphere();
this.geometryCache.set(key, geometry);
}
return this.geometryCache.get(key);
}
createBuilding(data) {
const geometry = this.getGeometry(
data.width,
data.height,
data.depth
);
const texture = this.getTexture(data.textureUrl);
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
map: texture,
roughness: 0.7,
metalness: 0.3
});
return new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material);
}
}3.2 LOD (Level of Detail) 구현
class LODBuilder {
constructor(buildingManager) {
this.buildingManager = buildingManager;
}
createLODBuilding(data) {
const lod = new THREE.LOD();
// 고품질 버전 (가까운 거리)
const highDetail = this.buildingManager.createBuilding(data);
lod.addLevel(highDetail, 0);
// 중간 품질 버전
const mediumDetail = this.createMediumDetail(data);
lod.addLevel(mediumDetail, 100);
// 저품질 버전 (먼 거리)
const lowDetail = this.createLowDetail(data);
lod.addLevel(lowDetail, 500);
return lod;
}
createMediumDetail(data) {
// 폴리곤 수를 50% 감소시킨 버전
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(
data.width,
data.height,
data.depth,
Math.max(1, Math.floor(data.segments / 2)),
Math.max(1, Math.floor(data.segments / 2)),
Math.max(1, Math.floor(data.segments / 2))
);
return new THREE.Mesh(
geometry,
new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
map: this.buildingManager.getTexture(data.textureUrl),
roughness: 0.7,
metalness: 0.3
})
);
}
createLowDetail(data) {
// 매우 단순화된 버전
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(
data.width,
data.height,
data.depth,
1, 1, 1
);
return new THREE.Mesh(
geometry,
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0xcccccc
})
);
}
}3.3 Frustum Culling 최적화
class SceneManager {
constructor(camera, scene) {
this.camera = camera;
this.scene = scene;
this.frustum = new THREE.Frustum();
this.cameraViewProjectionMatrix = new THREE.Matrix4();
}
updateFrustum() {
this.camera.updateMatrixWorld();
this.camera.matrixWorldInverse.copy(this.camera.matrixWorld).invert();
this.cameraViewProjectionMatrix.multiplyMatrices(
this.camera.projectionMatrix,
this.camera.matrixWorldInverse
);
this.frustum.setFromProjectionMatrix(this.cameraViewProjectionMatrix);
}
isVisible(building) {
const boundingSphere = building.geometry.boundingSphere.clone();
boundingSphere.applyMatrix4(building.matrixWorld);
return this.frustum.intersectsSphere(boundingSphere);
}
update() {
this.updateFrustum();
this.scene.traverse(object => {
if (object instanceof THREE.Mesh) {
const visible = this.isVisible(object);
if (object.visible !== visible) {
object.visible = visible;
}
}
});
}
}4. 성능 개선 결과
4.1 측정 데이터
4.2 구현 결과
// 최종 사용 예시
const buildingManager = new BuildingManager();
const lodBuilder = new LODBuilder(buildingManager);
const sceneManager = new SceneManager(camera, scene);
// 건물 데이터 로딩 및 생성
buildingData.forEach(data => {
const building = lodBuilder.createLODBuilding(data);
scene.add(building);
});
// 렌더링 루프
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
sceneManager.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
animate();5. 추가 최적화 팁
5.1 Worker Thread 활용
// 지오메트리 계산을 워커 스레드로 분리
const worker = new Worker('geometry-worker.js');
worker.postMessage({
type: 'computeGeometry',
buildingData: data
});
worker.onmessage = (e) => {
const { vertices, indices } = e.data;
const geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry();
geometry.setAttribute('position', new THREE.Float32BufferAttribute(vertices, 3));
geometry.setIndex(indices);
};5.2 인스턴스 메시 활용
const instancedMesh = new THREE.InstancedMesh(
baseGeometry,
material,
1000 // 인스턴스 수
);
// 매트릭스 업데이트
const matrix = new THREE.Matrix4();
buildingData.forEach((data, i) => {
matrix.setPosition(data.x, data.y, data.z);
instancedMesh.setMatrixAt(i, matrix);
});5.3 셰이더 최적화
// 커스텀 셰이더 예시
const customMaterial = new THREE.ShaderMaterial({
uniforms: {
time: { value: 0 },
colorMap: { value: null }
},
vertexShader: `
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
vUv = uv;
gl_Position = projectionMatrix * modelViewMatrix * vec4(position, 1.0);
}
`,
fragmentShader: `
uniform sampler2D colorMap;
varying vec2 vUv;
void main() {
vec4 color = texture2D(colorMap, vUv);
gl_FragColor = color;
}
`
});6. 결론
이번 최적화 프로젝트를 통해 Three.js를 사용한 대규모 3D 시각화 애플리케이션의 성능을 크게 개선할 수 있었습니다.
특히 다음과 같은 핵심 전략이 효과적이었습니다
1. 리소스 캐싱 및 재사용
2. LOD 시스템 구현
3. Frustum Culling 최적화
4. 워커 스레드 활용
5. 인스턴스 메시 도입
이러한 최적화를 통해 사용자 경험이 크게 개선되었으며, 모바일 기기에서도 안정적인 성능을 제공할 수 있게 되었습니다.
출처: Animation Loop
