
1. Soft Delete
Soft Delete란
soft delete는 database의 테이블에서 물리적으로 데이터를 삭제하는 대신 마킹을 통해서 delete를 구현하는 방식이다.
soft delete를 구현하는 가장 보편화된 방식은 삭제여부를 나타내는 field를 추가하는 방식이다.
다음은 deleted란 field를 통해 삭제 여부를 관리하는 방식의 예시이다.
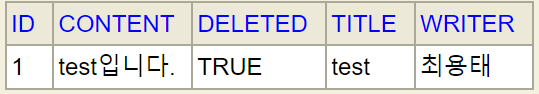
Soft Delete 수행법
해당 테이블에서 다음과 같은 SQL command를 통해 delete 작업을 수행할 수 있다.
update from post set deleted=1 where id=1soft delete 방식을 도입하면 테이블 조회 방식도 바뀌게 된다.
select * from post where deleted=02. Soft Delete 구현
post entity
@Entity
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@Builder
public class Post {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@NotNull
private String title;
@NotNull
private String content;
@NotNull
private String writer;
private boolean deleted = Boolean.FALSE;
}위 코드를 보면 post 엔티티에 default 값을 false로 둔 deleted 변수를 추가하여 soft delete를 구현한 것을 확인할 수 있다.
이런 방식으로 구현하면 삭제할 때마다 update 쿼리를 날려야 하고 조회 할때마다 where절을 통해 deleted=false인 데이터만 조회하도록 쿼리를 작성해야 한다.
다음과 같은 JPA repsitory의 delete command를 오버라이드하여 해당 작업을 간편화 할 수 있다.
@Entity
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
@Builder
@SQLDelete(sql = "UPDATE post SET deleted = true WHERE id=?") - (1)
@Where(clause = "deleted=false") - (2)
public class Post {
@Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@NotNull
private String title;
@NotNull
private String content;
@NotNull
private String writer;
private boolean deleted = Boolean.FALSE;
public void update(String title, String content) {
this.title = title;
this. content = content;
}
}(1) @SQLDelete annotation을 통해 delete command를 deleted=true로 update하는 SQL command로 바꾼다.
(2) @Where annotation을 통해 deleted=false인 데이터만 조회하도록 한다.
Repository
public interface PostRepository extends JpaRepository<Post, Long> {
}PostRepository에는 특별한 변경점이 없다.
Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class PostService {
private final PostRepository postRepository;
public Long create(PostRequest postRequest) {
Post post = postRequest.toEntity();
return postRepository.save(post).getId();
}
public PostResponse getPost(long postId) {
Post findPost = findPostById(postId);
return PostResponse.builder()
.post(findPost)
.build();
}
public PostsResponse getPosts() {
List<Post> posts = postRepository.findAll();
return PostsResponse.builder()
.postResponses(posts.stream()
.map(post -> PostResponse.builder()
.post(post)
.build())
.collect(Collectors.toList()))
.build();
}
public Long update(Long postId,PostUpdateRequest postUpdateRequest) {
Post findPost = findPostById(postId);
findPost.update(postUpdateRequest.getTitle(), postUpdateRequest.getContent());
return postRepository.save(findPost).getId();
}
public void delete(long postId) {
postRepository.deleteById(postId);
}
private Post findPostById(long postId) {
return postRepository.findById(postId).orElseThrow(() -> new NotFoundException(ErrorCode.ENTITY_NOT_FOUND.getMessage()));
}
}PostService에도 특별한 변경사항 없이 원래 쓰던 deleteById를 사용하면 update 쿼리로 변환되어 soft delete가 수행된다.
조회 메소드 또한 조회시 where절에 deleted=false가 추가되어 쿼리를 날리게 된다.


이런 기능이 있었군요~